Education
Sub Category
Although ethers are the most unreactive functional groups, they still undergo a few chemical reactions. Let's explore a few such reactions in this video.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
This lecture is about VSEPR theory and molecular shapes or valence shell electron repulsion theory in chemistry.
To learn more about vsepr theory, watch this animated lecture till the end.
#vseprtheory
#molecularshapes
#chemistry
#najamacademy
subscribe my channel at:https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC_ltCdLVMRZ7r3IPz
Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC_ltCdLVMRZ7r3IPz
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/Najamacademy/
Lucas test is a common laboratory test that is used to differentiate between the different types of alcohols. Let's see what mechanism is followed by different alcohols in their reaction with the Lucas reagent.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Let's figure out the effect of substituents on the acidic strength of phenols. How will an electron-donating group or an electron-withdrawing group affect the acidic strength of phenol?
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
In this video, we will discuss about disproportionation reactions and their applications.
Timestamps
00:05 - What is a disproportionation reaction?
00:45 - Examples of disproportionation reactions.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Master the concept of “Displacement reactions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Redox reactions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11, chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
In this video, we will talk about decomposition reactions and see what type of decomposition reactions can also be redox reactions
Timestamps
00:03 - How do we represent decomposition reactions?
00:20 - Example of a decomposition reaction.
00:56 - Is decomposition of calcium carbonate a redox reaction?
02:59 - Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Master the concept of “Displacement reactions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Redox reactions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11, chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
In this video, we will look at different displacement reactions and look at their applications.
Timestamps
00:05 - How do we represent a displacement reaction?
00:48 - Examples of a displacement reaction.
03:00 - Double displacement reaction.
03:34 - Example of an application of double displacement reaction.
04:05 - Different types of double displacement reaction.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Master the concept of “Displacement reactions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Redox reactions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11, chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
In this video, we will learn about the combination reactions along with their examples and applications.
Timestamps
00:00 - What is a combination reaction?
00:20 - Examples of combination reactions.
01:50 - Combination reaction with more than two reactants.
04:02 - Are all combination reactions redox reactions?
04:17 - Example of a combination reaction that is NOT a redox reaction.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Redox reactions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11 chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
Identifying the anode and cathode in a galvanic cell, and calculating the voltage using standard electrode potentials.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/shorthand-notation-for-galvanicvoltaic-cells?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/galvanic-cell-voltaic-cell?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
"Identifying the anode and cathode in a galvanic cell, and calculating the voltage using standard electrode potentials.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/shorthand-notation-for-galvanicvoltaic-cells?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/galvanic-cell-voltaic-cell?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
What happens when you add zinc to a solution of copper sulfate? Identifying the half reactions to see what got oxidized and reduced.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/galvanic-cell-voltaic-cell?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/redox-titration?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
"How to use a redox reaction to construct a galvanic/voltaic cell to produce a flow of current.. Shows the flow of electrons and ions, and explains the role of the salt bridge.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/electrodes-and-voltage-of-galvanic-cell?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/redox-reaction-from-dissolving-zinc-in-copper-sulfate?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
A redox titration is a titration in which the analyte and titrant react through an oxidation–reduction reaction. As in acid–base titrations, the endpoint of a redox titration is often detected using an indicator. Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) is a popular titrant because it serves as its own indicator in acidic solution. View more lessons or practice this subject at https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/ap-chemistry-b
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate or volunteer today! Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Volunteer here: https://www.khanacademy.org/contribute?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
When balancing equations for redox reactions occurring in basic solution, it is often necessary to add OH⁻ ions or the OH⁻/H₂O pair to fully balance the equation. In this video, we'll walk through this process for the reaction between ClO⁻ and Cr(OH)₄⁻ in basic solution. View more lessons or practice this subject at https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/ap-chemistry-b
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate or volunteer today! Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Volunteer here: https://www.khanacademy.org/contribute?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
When balancing equations for redox reactions occurring in acidic solution, it is often necessary to add H⁺ ions or the H⁺/H₂O pair to fully balance the equation. In this video, we'll walk through this process for the reaction between dichromate (Cr₂O₇²⁻) and chloride (Cl⁻) ions in acidic solution. View more lessons or practice this subject at https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/ap-chemistry-b
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate or volunteer today! Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Volunteer here: https://www.khanacademy.org/contribute?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
How to identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/disproportionation?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/redox-reaction-with-iron?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
How to identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/disproportionation?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/redox-reaction-with-iron?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
For the reaction between Fe and HCl, identifying the half reactions and what is getting oxidized and reduced.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/oxidizing-and-reducing-agents-1?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/oxidation-reduction-or-redox-reactions?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
Finding the half reactions in a combustion reaction, and identifying what is getting oxidized and reduced.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/redox-reaction-with-iron?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/unusual-oxygen-oxidation-states?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
Determining oxidation numbers in hydrogen peroxide and oxygen difluoride.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/oxidation-reduction-or-redox-reactions?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/practice-determining-oxidation-states?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
"Determining oxidation numbers in magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/unusual-oxygen-oxidation-states?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/oxidation-state-trends-in-periodic-table?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
Trends in common oxidation states for main group elements.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/practice-determining-oxidation-states?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/introduction-to-oxidation-and-reduction?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
Introducing oxidation states, oxidation, and reduction. Some tips for remembering oxidation and reduction.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/redox-oxidation-reduction/v/oxidation-state-trends-in-periodic-table?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/thermodynamics-chemistry/gibbs-free-energy/v/standard-change-in-free-energy-and-the-equilibrium-constant?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #youcanlearnanything
subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
In redox reactions, both reduction and oxidation take place. Let's learn more about them.
Let's understand the old definition of oxidation and reduction.
Prerequisite: https://youtu.be/vDLMSiBENCY
Watch the video above to know the basics.
In this video I have discussed how to multiply two numbers using vedic math method, by finding base of a number and the poorak, which is what I have called a supplement.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Devashish Phadnis
In this video you will learn about basic method of division using vedic math which is done by specific method called Nikhilam! This video of divison is among three parts of nikhilam method we have. This is the first part.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Devashish Phadnis
Now that we know how alcohols can be synthesized using Grignard reagents, let's look at an example and see how to deconstruct an alcohol and figure out the starting reactants.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Let's briefly discuss the mechanism behind the addition of Grignard reagents to carbonyl compounds to obtain different types of alcohols with the help of a few examples.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Reduction of carbonyl compounds_worked ex. | Alcohols, phenols and ethers | Chemistry | Khan Academy
Reduction of carbonyl compounds using reducing agents, lithium aluminium hydride and sodium borohydride, gives alcohols. Let's explore the mechanism of this reduction reaction and also solve a few problems based on the same.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Lithium aluminium hydride and sodium borohydride are versatile reducing agents, yet they cannot be used interchangeably. One is more selective while the other is highly reactive. Let's explore what makes these reducing agents unique and when can we use them.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
How can we obtain alcohols from alkenes of anti-Markovnikov orientation? Using a selective method called hydroboration followed by oxidation. Let's solve a few questions based on the same.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Let's discuss the type of products that is formed in the acid-catalysed hydration of alkenes.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Phenol is prepared commercially from cumene and this synthesis involves some interesting chemistry concepts like a phenyl shift. Let's take a brief look at this preparation method.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Alcohols, phenols and ethers” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
The video helps us recall the various factors that help stabilise a carbocation. This helps us to compare the various substrates during an SN1 reaction
00:00- Need to talk about the stability of carbocations.
01:03- Comparing the rates of SN1 reaction for the given substrates.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
and
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “SN1/SN2/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and Haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry” , find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - https://www.google.com/url?client=internal-element-cse&cx=004984196166817161901:gt3nscsxv5o&q=https://www.khanacademy.org/science/class-12-chemistry-india&sa=U&ved=2ahUKEwiukczwjvT9AhWCxDgGHfXPAtoQFnoECAAQAQ&usg=AOvVaw0f5A9FAvkuC8TX7FNf1t3c
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about the effect of substrate on the rate of an SN1 reaction. It helps compare various substrates having the same type of leaving group and also briefly helps recall the mechanism of the SN1 rate.
00:00- Recall the mechanism of SN1 reaction.
00:50- Factors affecting the rate of an SN1 reaction.
01:16- Why does the strength of a nucleophile not affect the rate of an SN1 reaction?
01:50- Comparing various substrates for their reactivity towards an SN1 reaction.
6:15- What happens in the next video?
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
and
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “SN1 reactions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 12 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions might involve the formation of more than one product. How is that possible? And, which would be the major product? This video talks about why and how carbocation rearrangement occurs, leading to the formation of unexpected major products!
00:00- Introduction
00:39- 1,2-Hydride shift.
4:23- 1,2-Methyl shift
6:45- How to know when rearrangement happens?
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
and
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “SN1/SN2/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about the mechanism involved in an SN1 reaction. It also elaborates on what is a rate determining step and how it affects the rate of a reaction. We learn how to calculate the rate of an SN1 reaction and also, what is the order of an SN1 reaction. In the end, it tells why the nucleophile does not affect the rate of an SN1 reaction while the concentration and type of substrate does.
00:00- Introduction
00:30- What is nucleophilic substitution?
1:15- How does nucleophilic substitution occur?
1:40- Mechanism of SN1 reaction
3:00- What is RDS?
4:11- Equation for reaction rate
5:47- Factors affecting the rate
Master the concept of “SN1/SN2/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and Haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about the effect of a leaving group and solvent on the rate of an SN1 reaction.
00:11- Mechanism of SN1 reaction.
00:35- Why care about the leaving group stability?
1:12- Examples!
4:54- Effect of solvent
Master the concept of “SN1/SN2/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about the effect of leaving group on the rate of an SN2 reaction.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “sn2/sn1/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - Link to topichttps://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and Haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about how the strength of a nucleophile affects the rate of an SN2 reaction.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “sn2/sn1/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - Link to topichttps://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and Haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about what happens when HBr is added to an alkene in the presence of a peroxide and how is that different from the usual addition of HBr to an alkene.
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Master the concept of “Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrophilic Addition of alkenes and alkynes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video gets a little more interesting than the other two parts as it talks about whether or not the attacking nucleophile will be able to replace the leaving group.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of “sn2/sn1/E1/E2” through practice exercises and videos - Link to topichttps://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Haloalkanes and Haloarenes” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about the mechanism involved when a symmetrical alkyne is treated with a hydrogen halide.
00:00- Introduction
1:03-Reaction between ethyne and HBr
1:44- Why is there no resonance in case of a vinylic carbocation?
3:40- What happens if we have excess HBr?
4:42- How do we decide the major product?
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Master the concept of “Alkynes: Properties” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Hydrocarbons” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry , find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about what happens when an unsymmetrical terminal alkyne is treated with excess of HCl.
00:00- Introduction
1:10- Mechanism
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Master the concept of “Alkynes: Properties” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Hydrocarbons” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry , find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class 11 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video depicts how the inductive effect helps stabilise or destabilise a given reaction intermediate.
00:00- Introduction
00:32- Common reaction intermediates
02:50- Reaction intermediates and inductive effect
3:27- Examples
Master the concept of “Electron-displacement effects” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on the unit - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for Class 11 Chemistry here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video depicts how the inductive effect helps stabilise or destabilise a given reaction intermediate.
Master the concept of “Electron-displacement effects” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on the unit - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for Class 11 Chemistry here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects.
Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
In this video, we will look at the mechanism behind Reimer-Tiemann reaction where phenol is converted to ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde (also called salicylaldehyde).
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Master the concept of “Reimer-Tiemann Reaction” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrophilic aromatic substitution” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic Chemistry Essentials” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
Description
In this video, we will look at the product that is formed when aniline undergoes bromination. We will also see how to modify the substrate, aniline, in order to selectively obtain the para-product.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Master the concept of “Bromination of Aniline” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic Chemistry Essentials” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
Comparing basic strength of nitrogenous aromatic molecules | Basic strength | Orgchem | Khan Academy
In this video how to compare basic strength of some basic nitrogenous aromatic organic molecules.
Timestamps
What are we doing? - 0:00
Comparing Ammonia with its aromatic derivatives - 0:14
Playing with aniline - 2:42
Steric inhibition of protonation - 3:00
Basic strength of pyrrole - 5:15
What did we learn? - 6:27
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/de....vadmin/content/exerc
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Ishani Rathore
In this video how to compare basic strength of some basic aliphatic organic molecules.
Timestamps
What are we doing? - 0:00
What are Bronsted-Lowry bases? - 0:20
Set #1 (Formate ion vs. aliphatic carboxylate ions) - 0:35
Set #2 (Hydroxide ion vs. azanide ion) - 2:35
Which atom is most apt to be protonated? - 3:50
Which atom is most apt in this molecules? - 5:58
What did we learn? - 7:30
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Ishani Rathore
Comparing organic molecules using all EE Part - 2 | Acidic strength |Organic chemistry| Khan Academy
In this video, we take up random basic organic molecules and compare their acidic strength using electronic effects.
Timestamps
Introduction - 0:00
Set #3 (Salicylic acid vs. Nitrobenzoic acid vs. Catechol vs. Nitrophenol) - 0:11
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Master the concept of “Acidic strength” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Acidic and basic strength of organic molecules” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Created by Ishani Rathore
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Comparing organic molecules using all EE Part - 1 | Acidic strength |Organic chemistry| Khan Academy
In this video we take up random basic organic molecules and compare their acidic strength using electronic effects.
Timestamps
Introduction - 0:00
Set #1 (Alcohol vs. sulphonic acid vs. phenol vs. carboxylic acid) - 0:09
Set #2 (Wate vs. hydrogen sulphide vs. benzene vs. ethyne) - 5:34
What do we learn in part 2 - 10:00
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Master the concept of “Acidic strength” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Acidic and basic strength of organic molecules” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Created by Ishani Rathore
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrophilic aromatic substitution” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic Chemistry Essentials” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
In this video, we will learn how to prepare p-nitrophenol, a very important intermediate in the synthesis of the drug, paracetamol.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Master the concept of “Nitration of Phenols” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrophilic aromatic substitution” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Organic Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic Chemistry Essentials” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
In this video, we will explore the mechanism of bromination of phenol. We will also see how the product varies when we change the solvent and why does that happen so?
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Master the concept of “Bromination of phenol” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on “Curious Case of Phenol and Aniline” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis#x1918b84b5bb1f2e6:the-curious-case-of-phenol-and-aniline
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Organic Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
This video talks about the methods to form amides in a laboratory using carboxylic acid and its derivatives. It also talks about why do we add a base in a mixture of acid halide and ammonia to get an amide, or why do we heat a mixture of an acid and ammonia to form an amide.
00:00- Introduction
01:40- Acid and ammonia
2:22- Why heat?
2:45- Acid chloride and ammonia
6:00- Acid chloride and amines
7:16- Use of a base while reacting an acid chloride with ammonia
8:18- Acid anhydride and ammonia
9:11- Ester and ammonia
9:51- Summary
Practice this concept -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of "Formation of amides from CADs" through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Check out more videos and exercises on "Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of CADs" - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/organic-chemis
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
This video talks about how a nucleophile attacks a given carbonyl compound, the mechanism involved, and the change in hybridisation of the central atom during the process. The video also talks about the difference in mechanism observed when a neutral nucleophile attacks an aldehyde or a ketone instead of an anionic one.
00:00- Introduction
00:10- What are nucleophiles?
1:30- Mechanism of nucleophilic attack
3:22- Hybridisation of the central atom in the reactant, intermediate and product.
4:45- Attack of a neutral nucleophile
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Master the concept of Introduction to Aldehydes and Ketones through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for Class 12 Chemistry (India) here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Aanchal Arora
How can we separate dissolved salt from water? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
This video shows oxidation reduction reactions and explains the formation of the products.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a weak base strong acid titration.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the measurement of the pH of aqueous solutions of ionic compounds.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a weak acid strong base titration.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the standardization of an unknown solution of NaOH with KHP with experimental data.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows for the standardization of an unknown solution of NaOH with KHP without experimental data.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the titration of a sample of standardized HCl with an unknown solution of NaOH to determine its molarity.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows titration of a solution of HCl using a pH probe and CBL.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video is an exploration of what buffers are and buffer capacity. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAf1/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a strong acid strong base titration. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfa/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the relative hydrogen ion concentrations is a solution of HCl , CH3COOH, and a CH3COOH-CH3COONa buffer by comparing the rate of reaction with CaCO3. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfb/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the addition of a strong acid and a strong base to water as part of the buffer activity lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfc/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the addition of HCl and NaOH to a 0.10 M CH3COOH/ CH3COONa buffer as part of the buffer activity lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAff/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for phosphoric acid. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfg/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for sodium carbonate. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfh/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the mass percent of sodium hypochlorite in household bleach. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfJ/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the shifting of the FeSCN2+ equilibrium in the LeChatelier's Principle lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfx/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of spectrophotometric data to determine the Ksp for silver chromate. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfw/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data to determine the Ksp of Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2.
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfv/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of data to determine the K sp of Ca(OH)2 in water and a solution of CaCl2. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfu/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of titration data to determine the equilibrium constant for the hydrolysis of an ester. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAft/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video is the introduction to Chapter 14 of the web course. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfs/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the technique of an acid-base titration. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiJ/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the yield of NaCl from the reaction of NaHCO3 and HCl . http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiF/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the conductivity titration of Ba(OH)2 with H2SO4 using a conductivity probe. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiD/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the mole ratio in an acid-base reaction by measuring the temperature change in the reaction with a temperature probe. The method of continuous variations and a Job's plot is used. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiC/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: Part 2 of 2 videos shows gravimetric determination of a two component mixture of carbonates. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiB/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the measurement of the conductivity of different concentrations of calcium chloride with a conductivity probe and the determination of the concentration of an unknown solution. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiS/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the freezing of a sample of t-Butanol. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAix/
Lesson - 5 : The Gaseous and Liquid State part -1 (Types of Intermolecular Interactions/Forces)
Lesson - 25 Compounds of Carbon containing Halogens (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)
Chemical Bonding
#NEET #JEE, #JEEADV, #CentumAcademy #JEE2020
This Video Series cater to the needs of aspirants of KVPY, JEE Mains and Advanced. A step by step guide to ace these examinations is what an aspirant needs. CENTUM ACADEMY’s e-learning modules have been designed to help students get a structured approach towards preparation for examinations like KVPY, JEE Mains and JEE Advanced.
You can let us know if you want to get video sessions on specific topics by mentioning the same in Comments Section.
Enjoy Learning!!!
Do also visit
www.centum.learnyst.com for mock tests and topic wise Daily Practice Sheets.
#NEET #JEE, #JEEADV, #CentumAcademy #JEE2020
This Video Series cater to the needs of aspirants of KVPY, JEE Mains and Advanced. A step by step guide to ace these examinations is what an aspirant needs. CENTUM ACADEMY’s e-learning modules have been designed to help students get a structured approach towards preparation for examinations like KVPY, JEE Mains and JEE Advanced.
You can let us know if you want to get video sessions on specific topics by mentioning the same in Comments Section.
Enjoy Learning!!!
Do also visit
www.centum.learnyst.com for mock tests and topic wise Daily Practice Sheets.
Basic Introduction. System Definitions and their types, Surroundings and types of Boundary
This Video Series for those who want to delve a little deep into the world of Geometry. The gems of Geometry .i.e. the theorems and their proofs have been compiled in this series. This series is for students - those who want to explore geometry as well as those who are appearing for Mathematics Olympiads (PRMO, RMO, INMO, IMO) and for Maths enthusiasts.
For more such sessions, please visit:
www.wiki.centumacademy.com
#Olympiads #Geometry #Theorems
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. AS Chem: States of Matter (Gas Laws)
Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Quiz section for MSE 170: Fundamentals of Materials Science.
Recorded Summer 2020
Leave a comment if I got something wrong. Happy to receive feedback.
Checkout our undergraduate journal:
https://sites.google.com/uw.edu/urmse/volumes
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. A2 Chem: Electrochemistry Revision 1
Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Crude Oil Fractions & Their Uses | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Learn the basics about the uses of crude oil fractions.
Before watching this video you should watch our video explaining how crude oil is separated into its different length hydrocarbon fractions by utilising the different boiling points of each hydrocarbon fraction.
JOIN US ON PATREON
https://www.patreon.com/fuseschool
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
VISIT us at [a]www.fuseschool.org%2C[/a] where all of our videos are carefully organised into topics and specific orders, and to see what else we have on offer. Comment, like and share with other learners. You can both ask and answer questions, and teachers will get back to you.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Biology videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Physics videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Maths videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/fuseschool/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the FuseSchool platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Befriend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This is an Open Educational Resource. If you would like to use the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about halogenation within the alkanes and alkenes part of organic chemistry.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about condensation polymerisation within the overall organic chemistry topic.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about synthetic polymers when learning about polymers as a part of the organic chemistry topic.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about natural polymers. What are natural polymers? where are they found and how are they structured?
Find out more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn about carbohydrates within the overall topic of organic chemistry.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about how alcohol is made? What are the steps necessary? And, what happens during the process of fermentation? and is Ethene? Find out in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn the basics about alcohols and what they are. SUBSCRIBE to our channel to access many more educational videos. At The Fuse School, teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT. Our OER are available free of charge to anyone. Make sure to subscribe - we are going to create 3000 more!
This video is part of the Chemistry Journey project - a Chemistry Education project by The Fuse School sponsored by Fuse. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseschool
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Google+: http://www.gplus.to/FuseSchool
Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/virtualschooluk
Email: info@fuseschool.org
Website: www.fuseschool.org
This video is distributed under a Creative Commons License:
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs CC BY-NC-ND
Learn the basics about testing alkenes with bromine water. Why is bromine water used to test alkenes? What is bromine water made of? Find out more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Bond enthalpy is the energy required to break one mole of a specific type of bond in a gaseous molecule. It is usually represented as ΔH or ΔHrxn.
Enthalpy of reaction, also known as heat of reaction, is the change in enthalpy that occurs during a chemical reaction when the reactants are converted into products. It is also represented as ΔH or ΔHrxn.
The relationship between bond enthalpy and enthalpy of reaction can be explained using the concept of bond breaking and bond forming.
In a chemical reaction, bonds in the reactant molecules are broken, and new bonds are formed in the product molecules. The energy required to break the bonds (bond enthalpy) is an endothermic process, as energy needs to be supplied to weaken the bonds.
On the other hand, the energy released when new bonds are formed (bond formation) is an exothermic process, as energy is released during the formation of stronger bonds.
The enthalpy of reaction is the net energy change in the reaction, taking into account the energy required to break the bonds and the energy released when new bonds are formed.
Mathematically, the enthalpy of reaction (ΔHrxn) can be calculated using the bond enthalpies of the bonds broken (ΣΔHbroken) and the bond enthalpies of the bonds formed (ΣΔHformed):
ΔHrxn = ΣΔHformed - ΣΔHbroken
If the sum of the bond energies for the bonds broken is greater than the sum of the bond energies for the bonds formed, then the ΔHrxn will be positive, indicating an endothermic reaction. Conversely, if the sum of the energies for the bonds formed is greater than the sum of the energies for the bonds broken, then the ΔHrxn will be negative, indicating an exothermic reaction.
Using the Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential when concentrations are not standard conditions. Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.About Khan Academy: Tebtalks offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions that are reknown
How to use a table of standard reduction potentials to calculate standard cell potential. Identifying trends in oxidizing and reducing agent strength.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/cell-potential/v/using-reduction-potentials?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/nickel-cadmium-battery?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
This video talks about how we can use the reduction potential values to construct a galvanic cell.Practice this concept - “:electrochemistryTo get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry", find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - Sure! Let's practice constructing a galvanic cell using reduction potential values.
First, let's choose a redox reaction that has known reduction potential values. A common reaction that is often used in galvanic cells is the reduction of copper ions (Cu2+) by zinc metal (Zn) in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4):
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (reduction half-reaction, E° = +0.34 V)
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- (oxidation half-reaction, E° = -0.76 V)
The reduction potential values (E°) for these half-reactions are given in volts (V). The reduction half-reaction has a positive E° value, indicating it is spontaneous in nature.
To construct a galvanic cell, we need two half-cells, each consisting of an electrode and an electrolyte solution. The reduction half-reaction will be our cathode (positive electrode), and the oxidation half-reaction will be our anode (negative electrode).
Now, let's assemble the galvanic cell step by step:
1. Start by creating the anode compartment: Place a strip of zinc metal (Zn) into a beaker containing a solution of zinc sulfate (ZnSO4). This is the anode half-cell.
2. Next, create the cathode compartment: Place a strip of copper metal (Cu) into a beaker containing a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4). This is the cathode half-cell.
3. Connect the two half-cells: Connect a wire between the zinc metal in the anode half-cell and the copper metal in the cathode half-cell. This allows the flow of electrons through the wire from the anode to the cathode.
4. Complete the circuit: Connect the two half-cells using a salt bridge. A salt bridge can be made by soaking a piece of filter paper in a salt solution (e.g., KCl) and placing it between the two half-cells. The salt bridge completes the circuit and allows ions to flow between the two half-cells, maintaining electrical neutrality.
5. Observe the flow of electrons: Electrons flow from the zinc anode, where zinc atoms are oxidized, to the copper cathode, where copper ions are reduced. This flow of electrons generates an electric current that can be used to do work.
So, by using the reduction potential values, we have successfully constructed a galvanic cell using a zinc-copper redox reaction
This video talks about the use of Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential for a given cell at a particular temperature (other than the standard conditions).
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Master the concept of “Cell potentials under non-standard conditions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrochemistry” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry", find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - https://www.google.com/url?client=internal-element-cse&cx=004984196166817161901:gt3nscsxv5o&q=https://www.khanacademy.org/science/class-12-chemistry-india&sa=U&ved=2ahUKEwiToa_q0ID-AhVp8jgGHQ-eCtIQFnoECAEQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2TEFUhHpIMyKNfZE-8Jrv_
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
This video explains how molar conductivity varies with dilution in case of both strong and weak electrolytes. It also graphically explains why the increase in the molar conductivity is higher for a weak electrolyte as compared to a strong one.
Master the concept of “Electrolytic cells and electrolysis” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrochemistry” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for Class 12 Chemistry here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Colligative properties are properties of a solution that depend solely on the concentration of solute particles in the solvent and not on the nature of the solute. One of the colligative properties is the elevation of boiling point.
The elevation of boiling point is the phenomenon where the boiling point of a solvent is raised when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it. This occurs because the presence of solute particles in the solvent disrupts the intermolecular forces between solvent molecules, making it more difficult for the solvent to vaporize and reach its boiling point.
Some key points about the elevation of boiling point are:
1. Explanation: Dissolving a non-volatile solute in a solvent increases the number of solute particles in the solution. These solute particles create additional obstacles for solvent molecules to overcome in order to escape into the vapor phase during boiling. As a result, more energy is required to reach the boiling point, causing an elevation in the boiling point of the solution compared to the pure solvent.
2. Relationship with Concentration: The extent of the elevation of boiling point is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute particles in the solution. This relationship is described by the equation:
ΔTb = Kb * m
Where ΔTb is the elevation in boiling point, Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant specific to the solvent, and m is the molality of the solute particles in the solution.
3. Colligative Property: The elevation of boiling point is a colligative property because it depends only on the number of solute particles and not on their size or chemical nature. This means that any solute that does not vaporize at the boiling point of the solvent will affect the boiling point similarly, regardless of its identity.
4. Applications: The elevation of boiling point has practical applications. For example, it is utilized in antifreeze solutions, where the addition of solutes (such as ethylene glycol) raises the boiling point of water in vehicle cooling systems. It also plays a role in adjusting cooking times and temperatures at higher altitudes, where the lower atmospheric pressure results in a lower boiling point of water.
It is important to note that the elevation of boiling point is just one of the colligative properties exhibited by solutions, along with other properties like vapor pressure lowering, depression of freezing point, and osmotic pressure. These properties are especially important in fields such as chemistry, biology, and pharmaceuticals and contribute to various applications and processes.
We are familiar with the various concentration terms like molarity, molality, mole fraction and so on. In this video, we will solve few questions on these concepts.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Classification of elements and periodicity in properties” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Let's solve a few questions on electronic configurations of elements.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Classification of elements and periodicity in properties” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into VSEPR theory and molecular structure. It contains examples and practice problems of drawing lewis structures along with the correct molecular geometry. Structures include the tetrahedral shape, bent, linear, trigonal planar, and trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry as well as their bond angles.
How To Draw Lewis Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NFZtjSeT3XE
VSEPR Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DBrq31w8vC4
Molecular Geometry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Cw0_cJzkSI
Lewis Dot Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ymf3kZePDnU
Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhItoqhHoEE
_________________________________
Octet Rule Exceptions:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=96L6_IwyHRM
Resonance Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9B5FGPDwX_E
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ykSzYl_4vI
Formal Charge Calculations:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_SIjijCouE
Lewis Structures - Mega Review:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PeY_sihSh8E
________________________________
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdJeQUd2g_4
Molecular Orbital Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6tB6E6R_XpQ
Dipole Dipole Forces of Attraction:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zOvnu0KYyxo
Hydrogen Bonding:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZDjJOqOKeCI
Unit Cell Chemistry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HCWwRh5CXYU
_________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
https://www.video-tutor.net/
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
https://www.patreon.com/MathSc....ienceTutor/collectio
This video tutorial provides a basic introduction into organic chemistry. Here is a list of topics:
1. How to draw lewis structures of organic compounds
2. Identifying functional groups - alkanes, alkenes, & alkynes
3. Formal charge calculations
4. Resonance structures
5. Basic IUPAC nomenclature of alkanes
___________________________________
Organic Chemistry - Basic Introduction:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B_ketdzJtY8
Which Bond Is More Polar?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o0-a5HzSzdE
How To Draw Lewis Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6unef5Hz6SU
Condensed Structures to Skeletal Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HRkvjKHFNDA
Functional Groups Review:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9jM8lWxrAE
Primary, Secondary, & Tertiary Functional Groups:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r_Zhb0nQEvE
_________________________________
How To Calculate Formal Charge:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C2l-76VP8s0
Finding Lone Pairs Using Formal Charge:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jlCPY6iXQ1c
Dipole Moment & Electronegativity:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFAU1GMJmnI
Predicting Bond Angles:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPS7zdg8HzY
Valence Bond Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vqx9a2aU99c
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdJeQUd2g_4
_______________________________
Bond Strength and Bond Length:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSRY95IAwF8
Orbital Overlap and Bond Length:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BatJrR5sblA
Organic Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
https://www.video-tutor.net/orgo-chem.html
Organic Chemistry Exam 1 Playlist:
https://bit.ly/3kJnNXU
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
https://www.patreon.com/MathSc....ienceTutor/collectio
This video introduces one to Organic Chemistry from the basics while also highlighting some of the basic terminologies in Organic Chemistry.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on the study of carbon compounds. Carbon atoms can form stable covalent bonds with other atoms, allowing for the formation of a wide range of complex molecules, including those found in living organisms.
Here are some basic terminologies commonly used in organic chemistry:
1. Carbon (C): Carbon is an element that forms the backbone of organic molecules. It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
2. Hydrocarbon: A hydrocarbon is a molecule consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It is the simplest type of organic compound. There are two main types of hydrocarbons: alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) and alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond).
3. Functional group: A functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms that gives a compound its characteristic chemical properties and reactivity. Examples of functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines.
4. Isomers: Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. There are different types of isomers, such as structural isomers (different connectivity), geometric isomers (cis-trans isomerism), and enantiomers (mirror-image isomers).
5. Alcohols: Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group attached to a carbon atom. They are characterized by the "-ol" suffix in their names. For example, ethanol is a common alcohol.
6. Aldehydes and Ketones: Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O). Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of a carbon chain, whereas ketones have it within the carbon chain.
7. Carboxylic acids: Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are characterized by the "-oic acid" suffix in their names. Examples include acetic acid and formic acid.
8. Amines: Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom attached to carbon atoms or hydrogen atoms. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines based on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
These are just a few basic terminologies in organic chemistry. The subject encompasses many more concepts and reactions, including polymerization, aromatic compounds, stereochemistry, and reactions like substitution, elimination, and addition reactions.
h In this lesson, you will learn about the periodic table and how it is used in chemistry. We will focus on how the periodic table is organized by atomic number, and discuss how properties of elements are periodic in nature throughout the table due to the electrons in the outer shells of the atoms. We will also discuss atomic mass and valence electrons, including predicting when an atom will gain or lose an electron in a chemical reaction.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements based on their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus). It organizes all the known elements in a specific order which allows for classification and understanding of their properties and relationships.
The table is composed of rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements in the same period share the same energy levels, while elements in the same group share similar chemical properties.
The elements on the periodic table are represented by symbols, and each element has its own unique atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical symbol. The order of elements is based on increasing atomic number, which also corresponds to the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
The periodic table is an essential tool for scientists, students, and researchers as it provides valuable information about elements, such as their atomic masses, electron configurations, and various trends in their chemical behavior.
What is an Atom?
An atom is the basic unit of matter, and it is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms are the building blocks of all matter in the universe. They are composed of three main subatomic particles:
1. Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of the atom.
2. Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also located in the nucleus.
3. Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels.
The protons and neutrons are tightly packed in the central nucleus of the atom, while the electrons move in various energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus defines its atomic number, which, in turn, determines the element to which the atom belongs. The number of electrons typically matches the number of protons, creating a neutral atom.
Atoms can combine to form molecules through chemical bonding, and they can participate in chemical reactions by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. The study of atoms and their interactions is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics and has led to a deeper understanding of the properties and behavior of matter.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Let's learn IUPAC Naming of Organic Compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and functional groups such as halides, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids. We discuss the IUPAC Naming rules with lots of examples!
To identify the best oxidizing agent using Eo(red.) values, you need to compare the Eo(red.) values of the potential oxidizing agents. The species with the higher Eo(red.) value will be the stronger oxidizing agent.
Here are some general rules for comparing Eo(red.) values:
1. The species with the higher Eo(red.) value will be more likely to undergo reduction and, therefore, act as the oxidizing agent.
2. The species with the lower Eo(red.) value will be more likely to undergo oxidation and, therefore, act as the reducing agent.
3. The larger the difference in Eo(red.) values between two species, the stronger the oxidizing agent and the weaker the reducing agent.
For example, consider the following half-reactions:
Half-reaction 1: A+ + e- --> A (Eo(red.) = 0.8 V)
Half-reaction 2: B2+ + 2e- --> 2B+ (Eo(red.) = 1.5 V)
In this case, half-reaction 2 has the higher Eo(red.) value (1.5 V) compared to half-reaction 1 (0.8 V). Therefore, B2+ is the stronger oxidizing agent.
It is important to note that Eo(red.) values can only be compared within the same system, meaning you cannot directly compare Eo(red.) values from different reference electrodes or different systems. Additionally, other factors such as concentration and temperature can also influence the oxidizing strength of a species, so it is important to consider these variables as well.
Le Chatelier's Principle is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how systems at equilibrium respond to changes in conditions. According to this principle, when a system at equilibrium is subjected to an external influence, it will adjust in such a way as to counteract the change and reestablish equilibrium.
Adding a catalyst to a reaction is one such external influence. However, unlike changes in temperature, pressure, or concentrations, adding a catalyst does not directly affect the position of the equilibrium or alter the concentrations of reactants or products. Instead, a catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, lowering the activation energy barrier. This allows the reaction to proceed at a faster rate without being consumed itself.
In the context of Le Chatelier's Principle, adding a catalyst to a reaction at equilibrium does not cause any immediate response. The equilibrium composition and concentrations of reactants and products remain unaffected. However, the presence of a catalyst can increase the rate at which the reaction reaches equilibrium.
It's important to note that catalysts do not shift the equilibrium position or favor the formation of products or reactants. They only enhance the rate at which the equilibrium is reached by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. Once equilibrium is attained, the catalyst does not affect the equilibrium concentrations.
On Khan Academy, you can find more detailed explanations and examples of Le Chatelier's Principle, as well as related topics in equilibrium chemistry. Their resources, including videos, articles, and practice exercises, can help you fully understand the principles and applications of equilibrium reactions in chemistry.
Enjoy your learning and exploration of this fascinating field!
A step-by-step guide on how to do so.
1. Identify the balanced chemical equation: Begin by identifying the balanced chemical equation that represents the dissolution of the compound. This equation shows how the compound dissociates into its constituent ions in aqueous solution.
2. Write the dissolution equation: Write the dissolution equation using the appropriate state symbols (s for solid and aq for aqueous). Ensure that the equation is balanced in terms of atoms and charges. For example, let's consider the dissolution of calcium carbonate (CaCO3):
CaCO3 (s) → Ca2+ (aq) + CO3^2- (aq)
3. Write the Ksp expression: The Ksp expression represents the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of the compound. It is written by taking the product of the concentrations of the constituent ions, each raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. For the dissolution of calcium carbonate, the Ksp expression would be:
Ksp = [Ca2+]^1 * [CO3^2-]^1
4. Exclude solids from the expression: Only the concentrations of the dissolved ions are included in the Ksp expression. Any solid compounds are excluded. In this case, the solid calcium carbonate (CaCO3) would not be included.
5. Use brackets to denote concentration: The concentrations of the ions in the Ksp expression are typically denoted within square brackets, [ ]. However, if the ion is a polyatomic ion, such as CO3^2-, the brackets are still used, but the charge is outside the brackets.
6. Include units: It is important to include the units of concentration used in the Ksp expression. Typically, molarity (M) or moles per liter (mol/L) are used. Make sure to use consistent units for all concentrations in calculations or comparisons.
7. Don't include coefficients: The Ksp expression does not include any coefficients in front of the ions. Only the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation are used to determine the powers to which the concentrations are raised.
I hope this guide assists you in writing Ksp expressions. If you have any further questions or require additional explanation, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Thank you for your attention.
Best regards,
The relationship between Ksp (solubility product constant) and precipitation is fundamental in understanding how solids dissolve and come out of solution. Here's the key concept:
* **Ksp is a constant value for a specific ionic compound.** It represents the equilibrium point at which the dissolved ions (from the compound) and the undissolved solid are in balance within a solution.
* **Precipitation occurs when the concentration of dissolved ions exceeds the Ksp value.** This means there are more ions floating around in the solution than the system can stably hold at equilibrium. To re-establish equilibrium, the excess ions come together and form a solid precipitate.
Here's a breakdown of the relationship:
* **Ksp > Qsp (ionic product):** Solution is unsaturated. No precipitation occurs.
* **Ksp = Qsp:** Solution is saturated. Ions are at equilibrium and neither dissolving nor precipitating.
* **Ksp < Qsp:** Solution is supersaturated. Precipitation will occur to reduce the ion concentration and reach equilibrium.
In essence, Ksp acts as a threshold. If you push the system past this point (by adding more solute or changing conditions), precipitation will happen to restore equilibrium.
Completely soluble salts are those that dissolve entirely in water to form a homogeneous solution. The solubility of these salts in water depends on various factors such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the salt and solvent.
There are some general rules for predicting the solubility of ionic compounds in water. These rules are based on the principle that “like dissolves like,” where polar substances dissolve in polar solvents, and nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
1. Salts containing group 1 cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+) are completely soluble in water.
2. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are completely soluble in water.
3. Salts containing the nitrate ion (NO3-) are completely soluble in water.
4. Salts containing the chloride ion (Cl-) are mostly soluble in water. However, some chloride salts of less electronegative metals such as AgCl and PbCl2 are insoluble.
5. Salts containing the sulfate ion (SO42-) are mostly soluble in water. However, some sulfate salts of less electronegative metals such as BaSO4 and PbSO4 are insoluble.
6. Salts containing the carbonate ion (CO32-) and the phosphate ion (PO43-) are mostly insoluble in water. However, some of their soluble salts, such as Na2CO3 and Na3PO4, are completely soluble.
These rules are useful in predicting the solubility of completely soluble salts in water and can help in identifying insoluble salts. Keep in mind that these rules are not absolute, and some exceptions to them can occur.
A titration pH curve is a graphical representation of how the pH of a solution changes as a titration progresses. It typically exhibits several distinct features that can provide valuable information about the reaction being studied. The main features of a titration pH curve are:
1. Initial pH: At the start of the titration, before any titrant has been added, the initial pH is determined by the solution being titrated. For example, if an acidic solution is being titrated against a basic titrant, the initial pH will be low (acidic).
2. Slow pH change: Initially, as the titrant is added slowly, the change in pH is relatively slow because the reaction between the titrant and analyte is not yet significant enough to alter the pH dramatically. This region is often referred to as the buffering region, as the solution's pH remains relatively stable.
3. Equivalence point: The equivalence point is the point at which the stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have reacted. At this point, the pH undergoes a rapid change. For the reaction between a strong acid and a strong base, the equivalence point occurs at pH 7, indicating a neutral solution.
4. Midpoint of the buffering region: Before reaching the equivalence point, there is a point where the pH undergoes the steepest slope, known as the midpoint of the buffering region. This point corresponds to approximately halfway between the initial pH and the pH at the equivalence point. It is an important reference point as it helps determine the pH range over which the buffer works effectively.
5. Endpoint: The endpoint is the point at which the indicator used in the titration changes color, indicating that the reaction is approaching completion. Ideally, the endpoint should coincide with the equivalence point, but in practice, slight differences may occur.
6. Post-equivalence region: After passing the equivalence point, the pH continues to change, but at a slower rate compared to the pre-equivalence region. In the case of titrating a strong acid with a strong base or vice versa, the pH in this region approaches the pH of the excess titrant. Thus, if a strong acid is being titrated with a strong base, the pH will increase above 7. The shape and steepness of this region depend on the nature and concentration of the titrant and analyte.
These features collectively provide insight into the behavior of the titration, helping determine the equivalence point, the stoichiometry of the reaction, the strength of the acid or base, and the buffering capacity of the solution. Analyzing the pH curve allows for the proper interpretation of the experimental data obtained during titration.
Steam distillation is a technique used for the purification of substances, particularly volatile or organic compounds, which are highly sensitive to heat. It involves the process of separating a mixture based on the difference in boiling points of the components. The principle of steam distillation lies in the fact that when a substance is mixed with water and heated, the vapor produced will have a higher concentration of the more volatile component.
The procedure of purifying substances by steam distillation involves the following steps:
1. A mixture of the substance to be purified and water is placed in a distillation flask.
2. The mixture is heated, and as the temperature rises, vapor is produced. The vapor consists of the volatile component(s) of the mixture, along with steam.
3. The vapor passes through a condenser, where it is cooled and liquified.
4. The condensed liquid is collected in a separate flask, which contains the purified substance.
The conditions under which steam distillation is performed can vary depending on the specific substance or mixture being purified. However, some general conditions include maintaining a controlled temperature and ensuring a sufficient supply of water to produce steam.
Advantages of steam distillation include:
1. Preservation of the heat-sensitive components: Steam distillation allows for the separation of substances that would be damaged or decomposed by higher temperatures. By using steam as a heat transfer medium, the mixture can be heated more gently, preserving the integrity of the volatile components.
2. Removal of impurities: Steam distillation can effectively remove impurities from the substance being purified. As the volatile components vaporize along with the steam, any impurities left behind in the boiling flask are not carried over into the distilled product.
3. Relatively simple technique: Steam distillation is a straightforward and commonly used technique in the laboratory. It doesn't require sophisticated equipment or complex procedures, making it accessible and cost-effective.
Overall, steam distillation is a valuable method for purifying substances that are sensitive to high temperatures while efficiently separating the desired components from impurities.
This is a continuation of thermochemistry. The greatest component of this video is about enthalpy diagrams.
Solubility is an important concept in chemistry as it helps us understand the behavior of different substances when they interact with solvents. In particular, we will be focusing on the solubility of soluble salts and sparingly soluble salts.
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a given solvent. When a substance is soluble, it means it has the ability to dissolve in a significant amount in a particular solvent, while sparingly soluble substances can only dissolve in a small quantity.
Soluble salts are those that readily dissolve in a solvent, usually water, to form a homogeneous solution. These salts usually dissociate into their constituent ions when dissolved. For example, when table salt (sodium chloride) is dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-). This process is reversible, and the dissociated ions can recombine to form the original salt when the solvent is evaporated.
On the other hand, sparingly soluble salts have a limited ability to dissolve in a solvent. This means that only a small amount of the salt can dissolve, resulting in an unsaturated solution. Some examples of sparingly soluble salts include silver chloride (AgCl) and lead(II) iodide (PbI2). When these salts are added to water, only a small fraction will dissolve, while the rest will remain as solid particles.
There are several factors that affect the solubility of both soluble and sparingly soluble salts. They include temperature, pressure, and the presence of other substances in the solvent. For example, for most salts, their solubility increases with increasing temperature. However, this is not always the case, as some salts exhibit a decrease in solubility with increasing temperature.
Understanding the solubility of soluble and sparingly soluble salts is important for various applications in chemistry. It helps us predict the formation of precipitates when two solutions are mixed, determine the concentrations of ions in a solution, and even design drug formulations that can be readily absorbed by the body.
In conclusion, the solubility of soluble and sparingly soluble salts is a fundamental concept in chemistry. It allows us to understand the behavior of substances when they interact with solvents, and it has important applications in various fields of study. As advanced level chemistry students, it is crucial to grasp the concept of solubility and its implications in order to enhance our understanding of chemical reactions and equilibrium.
Certainly! Here are a few more calculations involving Faraday's laws of electrolysis:
1. Calculation of Theoretical Yield:
Faraday's Second Law states that the ratio of the quantities of different substances formed or reacted at the electrodes is given by their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. Therefore, to calculate the theoretical yield of a product, you can use the formula:
Theoretical Yield = (Amount of Substance Formed at the Desired Electrode / Stoichiometric Coefficient)
Here, Amount of Substance Formed at the Desired Electrode refers to the quantity of the desired substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles), and Stoichiometric Coefficient is the coefficient of the desired substance in the balanced chemical equation.
2. Calculation of Charge Passed:
The total electric charge passed through the cell during electrolysis can be determined using Faraday's First Law. The formula is:
Charge Passed = Current × Time
Here, Current is the electric current passing through the cell (in Amperes), and Time is the duration of electrolysis (in seconds).
3. Calculation of Mass of a Substance:
To calculate the mass of a substance deposited or consumed during electrolysis, you can use the formula:
Mass of Substance = Amount of Substance × Molar Mass
Here, Amount of Substance is the quantity of the substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles), and Molar Mass is the molar mass of the substance (in g/mol).
4. Calculation of Faraday's Constant:
Faraday's Constant represents the amount of electric charge (in Coulombs) required to deposit or produce one mole of a substance during electrolysis. It can be calculated using the formula:
Faraday's Constant = (Current × Time) / Amount of Substance
Here, Current is the electric current passing through the cell (in Amperes), Time is the duration of electrolysis (in seconds), and Amount of Substance is the quantity of the substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles).
These calculations illustrate some applications of Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Make sure to use the appropriate units and values for accurate results.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis describe the fundamental relationship between the mass of a substance produced or consumed during electrolysis, the amount of electrical charge passed through the electrolyte, and the chemical properties of the substances involved. These laws are named after the British physicist and chemist Michael Faraday, who first described them in the early 19th century. There are two laws:
1. Faraday's First Law: The amount of a substance produced or consumed during electrolysis is directly proportional to the amount of electrical charge passed through the electrolyte.
Mathematically, this law can be expressed as:
Mass of substance produced / consumed ∝ Electrical charge passed
or,
m = zQ
where m is the mass of the substance produced or consumed, Q is the electrical charge passed, and z is a constant known as the electrochemical equivalent of the substance.
2. Faraday's Second Law: The amounts of different substances produced or consumed during electrolysis are directly proportional to their equivalent weights.
Mathematically, this law can be expressed as:
Mass of substance A / Mass of substance B = Equivalent weight of substance A / Equivalent weight of substance B
or,
m_A / m_B = EWE_A / EWE_B
where m_A and m_B are the masses of substances A and B produced or consumed, respectively, and EWE_A and EWE_B are the equivalent weights of A and B, respectively.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis are important because they explain the behavior of many electrochemical systems, and are used in a variety of applications, including electroplating, battery technology, and corrosion prevention.
Factors affecting the electrolytic conductivity of electrolytes include:
1. Concentration: The concentration of the electrolyte affects conductivity. Higher concentrations result in more ions available for conduction, thus increasing conductivity.
2. Nature of Electrolyte: Different electrolytes have varying conductivities. Strong electrolytes, such as strong acids or bases, dissociate fully into ions and tend to have higher conductivity compared to weak electrolytes.
3. Temperature: Temperature impacts the mobility of ions in solution. Generally, higher temperatures increase ionic mobility and, therefore, conductivity.
4. Solvent: The nature of the solvent also influences conductivity. Polar solvents, like water, enhance ion dissociation and promote conductivity compared to nonpolar solvents.
5. Presence of Impurities: Impurities, such as dissolved gases or other substances, can affect conductivity either positively or negatively. They can alter the movement of ions and thus impact conductivity.
6. Pressure: Pressure can influence the solubility and mobility of ions, impacting electrolyte conductivity. Higher pressure often leads to higher conductivity.
7. Electrolyte Purity: The purity of the electrolyte is vital. Impurities introduced during production or storage can interfere with conductivity.
8. Presence of Additives: Some additives can enhance or hinder conductivity. They may increase ion dissociation or introduce additional ions that influence conductivity.
It's essential to consider these factors when studying or using electrolytes for various applications, including electrochemistry, batteries, and electrolysis processes.
1. Electroplating: Electrolysis is used in the electroplating industry to coat objects with a thin layer of metal. For example, silver plating is used to enhance the appearance and durability of jewelry, while chrome plating is used to give a shiny finish to car parts.
2. Production of chlorine and hydrogen: Electrolysis of brine (a solution of sodium chloride) is used to produce chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. Chlorine is used in the production of PVC, bleach, and various plastics, while hydrogen gas is used in various industrial processes, such as the production of ammonia and in fuel cells.
3. Electrorefining: Electrolysis is used to purify crude metals obtained from mining operations. For example, electrolysis is used to purify copper, zinc, and nickel to remove impurities, resulting in high-quality metals that can be used in various industrial applications.
4. Water splitting: Electrolysis of water can separate it into hydrogen and oxygen gases. These gases can then be used as a fuel source, for example, in fuel cells which produce electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen.
5. Electroforming: Electrolysis is used in the process of electroforming, where a metal object is produced by depositing metal ions onto a substrate through electrolysis. This process is used to create complex and detailed metal objects, such as jewelry, statues, and precision mechanical components.
6. Electrochemical machining: Electrolysis is used in electrochemical machining processes where a metal workpiece is shaped or machined by controlled removal of material through electrolysis. This can be used to achieve precise and intricate machining on difficult-to-machine materials like superalloys.
7. Electrolytic cells for industrial processes: Electrolytic cells are used in various industrial processes, such as electrowinning and electrorefining, where metals are extracted or purified from their ores. This includes processes like the extraction of aluminum from bauxite ore through the Hall–Héroult process.
Overall, electrolysis has extensive applications in industries ranging from metal refining and plating to chemical production and energy generation.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis provide a framework for quantitative calculations involving the amount of electricity and the mass of substances deposited or liberated during electrolysis.
Here are the two main laws and some examples of calculations you can perform:
**Faraday's First Law:**
This law states that the **mass (m)** of a substance deposited or liberated at an electrode is **directly proportional** to the **amount of charge (Q)** passed through the electrolyte. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
```
m ∝ Q
```
where the symbol "∝" represents proportionality.
**Example 1:**
* You electrolyze copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution for 30 minutes with a current of 2 amps.
* You need to calculate the mass of copper deposited at the cathode.
**Steps:**
1. **Convert time to seconds:** 30 minutes * 60 seconds/minute = 1800 seconds.
2. **Calculate the total charge:** Q = I * t = 2 A * 1800 s = 3600 C.
3. **Look up the electrochemical equivalent (ECE) of copper:** This value is typically found in chemistry handbooks or online resources. Let's assume the ECE of copper is 0.0329 mg/C.
4. **Calculate the mass of copper deposited:** m = Q * ECE = 3600 C * 0.0329 mg/C = 118.44 mg.
**Faraday's Second Law:**
This law states that the **masses of different ions liberated at the electrodes** when the **same amount of electricity (Q)** is passed through **different electrolytes** are **directly proportional to their chemical equivalents (CE)**. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
```
m1 / m2 = CE1 / CE2
```
where:
* m1 and m2 are the masses of the deposited/liberated substances
* CE1 and CE2 are their respective chemical equivalents
**Example 2:**
* You electrolyze silver nitrate (AgNO3) and copper sulfate (CuSO4) solutions simultaneously with the same amount of charge (Q).
* You need to determine the ratio of the masses of silver and copper deposited.
**Steps:**
1. **Look up the chemical equivalents of silver and copper:** Let's assume the CE of silver (Ag) is 107.87 g/eq and the CE of copper (Cu) is 31.78 g/eq.
2. **Apply the second law equation:** m_Ag / m_Cu = CE_Ag / CE_Cu = 107.87 g/eq / 31.78 g/eq ≈ 3.4.
Therefore, the mass of silver deposited will be approximately 3.4 times the mass of copper deposited under the same conditions.
These are just two examples of calculations involving Faraday's laws. Remember, you'll need additional information like current, time, electrochemical equivalents, and chemical equivalents to perform these calculations effectively.
Molar conductivity, denoted by the symbol Λm, is a measure of a solution's ability to conduct electricity, specifically, the conductance of a solution containing one mole of the electrolyte placed between electrodes with a unit area and a distance of one unit length. It is influenced by several key factors:
**1. Concentration of the electrolyte:**
* Molar conductivity generally **increases with dilution** (decreasing concentration). This is because as the solution is diluted, the distance between ions increases, reducing the frequency of collisions and allowing them to move more freely under the influence of an electric field, thus, enhancing conductivity.
[Image of Molar conductivity vs concentration graph]
**2. Nature of the electrolyte:**
* The **degree of dissociation** of the electrolyte plays a crucial role. Strong electrolytes, which dissociate completely in solution, have a higher number of ions per unit volume, leading to higher molar conductivity compared to weak electrolytes, which dissociate only partially.
* The **size and charge of the ions** also influence conductivity. Smaller and highly charged ions have greater mobility and contribute more significantly to conductivity than larger or less charged ions.
**3. Temperature:**
* Molar conductivity generally **increases with temperature**. This is because as the temperature rises, the solvent molecules move faster and collide with the ions more frequently, imparting kinetic energy to the ions and increasing their average velocity. This, in turn, enhances their ability to carry current, leading to higher conductivity.
It's important to note that the relationship between molar conductivity and concentration is not linear. As the concentration approaches zero (infinite dilution), the molar conductivity reaches a limiting value, known as **limiting molar conductivity (Λ⁰m)**. This value represents the maximum conductivity achievable for the electrolyte and is independent of concentration.
Kohlrausch's law of independent migration of ions states that in a solution containing electrolytes, each ion contributes individually to the total conductivity of the solution and moves independently of the others present, unaffected by the presence of other ions. This law can be applied in various ways, including:
1. Determination of Molar Conductivity: The law allows for the calculation of the molar conductivity of an electrolyte solution by summing the ion contributions together. This helps to understand the electrical conductivity of the solution, which is essential in various chemical and biological applications.
2. Study of Electrolytes Behaviour: The law provides insights into the behavior of ions in the solution. It helps to understand how these ions interact with each other and with the solvent. This information is necessary in various fields such as industrial processes, environmental studies and health sciences.
3. Determining the Degree of Dissociation: The law can be used to determine the degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes by measuring their molar conductivity at different concentrations. The dissociation constant can then be calculated for different solvent conditions. This information is useful in chemical equilibrium studies.
4. Calculation of Ion Concentrations: Kohlrausch's law can be used in the determination of ion concentrations in solutions. By measuring the molar conductivity and knowing the molar conductivity values of individual ions, it is possible to calculate their concentrations using the law. This information is necessary in fields such as pharmacology and environmental studies.
Overall, Kohlrausch's law has significant applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, environmental, and health sciences.
The molar conductivity of electrolytes is influenced by the concentration of the solution. Here are some key points to understand the effect of concentration on molar conductivity:
1. Generally, the molar conductivity of an electrolyte decreases as the concentration increases.
2. This behavior is explained by the phenomenon of ion-ion interactions or the association of ions when the concentration increases.
3. Initially, at low concentrations, the ions are far apart from each other, resulting in minimal ion-ion interactions. This allows for higher mobility of the ions and a higher molar conductivity.
4. As the concentration increases, the ions come closer to each other, leading to a greater likelihood of ion-ion interactions or association. This hinders the mobility of the ions, reducing the molar conductivity.
5. At higher concentrations, the molar conductivity approaches a limiting value called the limiting molar conductivity (Λ°). This value represents the maximum molar conductivity attainable for the electrolyte under the given conditions.
6. The decrease in molar conductivity with increasing concentration can be described by Kohlrausch's law, which states that the molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the contributions of the individual ions in the solution.
7. In dilute solutions, where ion-ion interactions are minimal, the molar conductivity is mainly determined by the individual ion mobilities. As the concentration increases, the contributions from individual ion mobilities decrease due to increased ion-ion interactions.
8. Strong electrolytes, which undergo complete ionization in solution, show a more pronounced decrease in molar conductivity with increasing concentration compared to weak electrolytes.
In summary, as the concentration of an electrolyte increases, the molar conductivity tends to decrease due to increased ion-ion interactions or association. However, at very low concentrations, the molar conductivity is higher, indicating greater ion mobility.
Video Two on organic synthesis was a live TV show highlighting key concepts in organic synthesis
- Electrode potential refers to the potential difference or voltage between an electrode and its surrounding solution/electrolyte.
- It is a measure of the tendency of an electrode to gain or lose electrons, which determines its ability to undergo oxidation or reduction reactions.
- The electrode potential is influenced by various factors, including the nature of the electrode material, concentration of ions in the solution, temperature, and pressure.
- The standard electrode potential (E°) is the electrode potential measured under standard conditions, which include a concentration of 1 mole per liter, temperature of 298 Kelvin, and atmospheric pressure of 1 bar.
- Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is often used as a reference electrode for measuring electrode potentials. Its electrode potential is defined as zero.
- Electrons flow from the electrode with a lower potential to the electrode with a higher potential, following the direction of the electrochemical reaction.
- The difference in electrode potentials of two electrodes is related to the cell potential (Ecell) of an electrochemical cell, which can be used to determine the spontaneity and feasibility of a redox reaction.
- A positive electrode potential indicates a tendency for reduction, while a negative electrode potential indicates a tendency for oxidation.
- Electrode potential can be measured using various techniques, such as potentiometry, voltammetry, and electrochemical cells.
Please note that these are just summarized notes. If you require more in-depth information on any specific aspect, please let me know!
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is an important reference electrode used in electrochemistry. It serves as a baseline for comparing the electrode potentials of other half-reactions. The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in a solution with a hydrogen gas atmosphere at a fixed pressure.
The standard reduction potential of the SHE is defined as 0.00 V at all temperatures. This means that other reduction potentials can be measured relative to the SHE. By convention, the reduction potential of the SHE is considered positive when a half-reaction has a higher potential to be reduced compared to the SHE, and negative when it has a lower potential.
The half-reaction for the SHE is the reduction of protons (H+) to hydrogen gas (H2). This reaction takes place as follows:
2H+ + 2e- -> H2
The SHE is often used in electrochemical cells as a reference electrode, with another half-reaction occurring at a different electrode. The potential difference between the SHE and the other electrode is measured to determine the half-cell potential of the other electrode.
In practical situations, it is difficult to have a true SHE. Therefore, other reference electrodes such as the silver/silver chloride electrode are commonly used instead. However, these reference electrodes are calibrated using the SHE and have their own set standard reduction potentials.
The SHE is a crucial reference in electrochemistry as it allows for the determination of the standard reduction potentials of other half-reactions and the prediction of the feasibility of redox reactions. It provides a consistent reference point for measuring and comparing electrode potentials, which helps in understanding the principles and behaviors of electrochemical processes.
This is a zoom recorded video that will introduce A level students to THERMOCHEMISTRY. It was created to enhance learning during the Covid-19 Lockdown. Please like and share and subscribe to our you tube channel for more such videos.
Common terms used in electrolysis and explanation of the changes that take place during electrolysis
Common Terms Used in Electrolysis:
Electrolyte: A substance that conducts electricity due to the presence of free ions. These ions can be dissolved in a solvent (like aqueous solutions) or molten.
Electrode: An electrical conductor in contact with an electrolyte. There are two types:
Anode: The positive electrode where oxidation occurs. Electrons flow out of the anode.
Cathode: The negative electrode where reduction occurs. Electrons flow into the cathode.
Electrolysis: The process of using electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. An external power source provides the energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction.
Electrolysis products: The substances formed at the electrodes during electrolysis. These products depend on the specific reaction occurring.
Electrolytic cell: A device used to carry out electrolysis, consisting of electrodes, an electrolyte, and a power source.
Changes During Electrolysis:
Electrolysis involves several key changes:
Electrical energy to chemical energy: The external power source provides electrical energy, which is converted into chemical energy to drive the non-spontaneous reaction.
Oxidation at the anode: Anions from the electrolyte lose electrons at the anode, undergoing oxidation. This can involve the electrode itself being oxidized or the oxidation of ions in the electrolyte.
Reduction at the cathode: Cations from the electrolyte gain electrons at the cathode, undergoing reduction.
Movement of ions: Ions in the electrolyte migrate towards the oppositely charged electrode to maintain electrical neutrality.
Formation of electrolysis products: The products of the oxidation and reduction reactions at the electrodes form the final electrolysis products.
Example: Electrolysis of water (H₂O):
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl)
Anode: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻ (Chlorine gas is produced at the anode)
Cathode: 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻ (Hydrogen gas is produced at the cathode)
Overall reaction: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (decomposition of water)
Note: This is a simplified example. The specific reactions and products depend on the nature of the electrolyte and the applied voltage.
Modes of conduction of substances, common terms used in electrolysis
## Modes of Conduction in Substances:
There are three main modes of conduction observed in different substances:
**1. Metallic Conduction:**
* **Description:** Involves the movement of **free electrons** within a metallic lattice. These electrons are not bound to any specific atom and can move freely throughout the metal.
* **Examples:** Metals like copper, aluminum, and silver are good conductors of electricity due to the presence of a large number of free electrons.
**2. Ionic Conduction:**
* **Description:** Occurs in **electrolytes** (molten salts or ionic solutions) where **ions** move through the solution carrying the charge.
* **Examples:** Aqueous solutions of salts like NaCl or molten salts like NaCl (liquid) conduct electricity through the movement of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
**3. Electronic Conduction in Semiconductors:**
* **Description:** Involves the movement of both **electrons** and **holes** (the absence of an electron in the valence band) in semiconductors. The conductivity can be controlled by applying external factors like doping or electric fields.
* **Examples:** Materials like silicon and germanium exhibit semiconducting behavior, where their conductivity can be tailored for various applications in electronics.
## Common Terms Used in Electrolysis:
* **Electrolyte:** A substance that conducts electricity due to the presence of free ions.
* **Electrode:** An electrical conductor that is in contact with an electrolyte.
* **Anode:** The positive electrode where oxidation occurs.
* **Cathode:** The negative electrode where reduction occurs.
* **Electrolysis:** The process of using electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
* **Electrolysis products:** The substances formed at the electrodes during electrolysis.
* **Electrolytic cell:** A device used to carry out electrolysis, consisting of electrodes, an electrolyte, and a power source.
* **Aqueous electrolysis:** Electrolysis involving water as the electrolyte.
* **Electroplating:** The deposition of a metal onto the cathode from a metal-containing solution.
* **Electrorefining:** The purification of a metal by removing impurities that go into the solution during electrolysis.
Understanding these terms and the different modes of conduction is crucial for comprehending the principles and applications of electrolysis in various fields like electroplating, battery technology, and chemical production.
This video was a live show on UBC-Star Tv in which students were introduced to the dos and donts of organic synthesis
describes distribution law of a solute between immiscible solvents and calculated examples . For A-level UACE Exams.
## Distribution Law: Understanding Solute Partitioning Between Immiscible Solvents
The **distribution law**, also known as **Nernst's partition law**, describes the **equilibrium distribution of a solute between two immiscible solvents**. In simpler terms, it explains how a solute will distribute itself between two non-mixing liquids at a constant temperature.
**Key Points:**
* **Immiscible solvents:** These are liquids that don't dissolve in each other, like oil and water.
* **Solute:** The substance that dissolves in both solvents.
* **Equilibrium:** A state where the concentration of the solute in each solvent remains constant over time, even though the molecules continue to move between the layers.
**The Law:**
The distribution law states that the **ratio of the equilibrium concentrations of a solute in two immiscible solvents is constant at a constant temperature**. This constant ratio is called the **distribution coefficient** or **partition coefficient**, denoted by **K<sub>d</sub>**.
**Mathematically:**
```
K_d = C₁ / C₂
```
where:
* C₁ is the concentration of the solute in solvent 1
* C₂ is the concentration of the solute in solvent 2
**Factors Affecting Kd:**
* **Nature of the solute:** Solutes with more affinity for one solvent will have a higher concentration in that solvent, leading to a larger Kd value.
* **Nature of the solvents:** The polarity and ability of solvents to interact with the solute influence the distribution.
* **Temperature:** Kd can change slightly with temperature, although the change is often negligible for most A-Level applications.
**Applications:**
* **Extraction:** Separating a desired compound from a mixture by selectively dissolving it in one solvent and separating the layers.
* **Chromatography:** Utilizing the differing distribution behavior of components to separate them in a mixture.
* **Understanding drug action:** Predicting how drugs distribute between different compartments in the body based on their lipophilicity (affinity for fats).
**Calculated Examples:**
**Example 1:**
A solution of benzoic acid is shaken with water and benzene. After reaching equilibrium, the concentration of benzoic acid in the benzene layer (0.1 M) is found to be ten times higher than its concentration in the water layer (0.01 M). Calculate the distribution coefficient (Kd) for benzoic acid between benzene and water.
```
K_d = C_benzene / C_water = 0.1 M / 0.01 M = 10
```
**Example 2:**
A dye has a Kd value of 5 between chloroform and water. If 10 mg of the dye is dissolved in 10 mL of chloroform, how much dye will be present in 100 mL of water after reaching equilibrium?
* We can assume the initial concentration of the dye in chloroform (C_chloroform) is 1 mg/mL (10 mg / 10 mL).
* We need to find the equilibrium concentration in water (C_water).
```
K_d = C_chloroform / C_water
5 = 1 mg/mL / C_water
C_water = 0.2 mg/mL
```
Therefore, at equilibrium, 0.2 mg/mL x 100 mL = 20 mg of the dye will be present in the water layer.
**Remember:** These are just basic examples. A-Level UACE Exams might involve more complex scenarios and calculations related to distribution law, requiring a deeper understanding of the concepts and their applications.
Describes the chemistry of transition elements; vanadium, chromium and cobaltVanadium and its compound- characteristics of vanadium as transition element- important compound of vanadium such as vanadium pentoxide in contact process.Chromium and its compounds-properties of chromium as transition element- reaction of chromium with air, water, acids, and sodium hydroxide- half reduction equations for chromates and dichromate- inter-conversion of chromates and dichromates- isomerism in chromium (III) chloride hexahydrate, CrCl3.6H2O -hydrolysis of chromium (III) compounds- qualitative analysis of chromium (III) ionsCobalt and its compounds-properties of cobalt as a transition elementqualitative analysis of cobalt (II) ions
## Chemistry of Vanadium, Chromium, and Cobalt (A-Level Chemistry)
These three elements are all **transition metals** located in Group 5, 6, and 7 of the periodic table, respectively. They share some general properties of transition metals, including:
* **Variable oxidation states:** They can exhibit multiple oxidation states due to the availability of electrons in their d-orbitals.
* **Formation of colored compounds:** Their d-orbitals can participate in bonding, leading to various colors in their compounds.
* **Ability to form complexes:** They can form complex ions with various ligands, influencing their properties and reactivity.
Here's a detailed look at the individual chemistry of each element:
**Vanadium (V):**
* **Oxidation states:** +5, +4, +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Vanadium pentoxide (V₂O₅): Used as a catalyst in the Contact process for sulfuric acid production.
* Vanadyl sulfate (VO(SO₄)): Used in photography and as a mordant in dyeing.
* **Properties:**
* Exhibits various colors depending on the oxidation state.
* Vanadium(V) compounds are strong oxidizing agents.
* Forms oxoacids like vanadic acid (HVO₃).
**Chromium (Cr):**
* **Oxidation states:** +6, +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Sodium dichromate (Na₂Cr₂O₇): Used as an oxidizing agent in various reactions.
* Potassium chromate (K₂CrO₄): Used as a pigment and corrosion inhibitor.
* Chromium(III) chloride hexahydrate (CrCl₃•6H₂O): Used as a mordant in dyeing and tanning leather.
* **Properties:**
* Chromium(VI) compounds are strong oxidizing agents and can be carcinogenic.
* Chromium(III) is the most stable oxidation state and forms many stable complexes.
* Exhibits various colors depending on the oxidation state and ligand environment.
**Cobalt (Co):**
* **Oxidation states:** +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl₂): Used as a desiccant and catalyst.
* Cobalt(II) sulfate (CoSO₄): Used in electroplating and pigments.
* Vitamin B₁₂: Contains cobalt(III) and is essential for human health.
* **Properties:**
* Forms many stable complexes with various ligands.
* Exhibits different colors depending on the oxidation state and ligand environment.
* Cobalt(II) compounds are often used as catalysts.
**Additional points to consider:**
* **Redox reactions:** All three elements can undergo redox reactions, involving changes in their oxidation states.
* **Complex formation:** Vanadium, chromium, and cobalt can form complexes with various ligands, influencing their properties like color, stability, and reactivity.
* **Industrial applications:** These elements and their compounds have numerous applications in various industries, including catalysis, pigments, dyes, and electroplating.
**Remember:** This is a general overview, and A-Level chemistry might delve deeper into specific aspects like reaction mechanisms, spectroscopic analysis, and industrial processes related to these elements. It's recommended to consult your textbook or other resources for more detailed information.
Reaction of alkyl halide with hot potasium hydroxide in ethanol to form alkenesAlkyl halides react with alkalis to form alcoholsPotassium cyanides react and increase the carbon chains with alkyl halidesAlkyl halides couples in presence of sodium and ethyl ether to form alkanes with twice the carbon atoms as the parent chainAlkyl halides Form Gridnard’s reagents when reacted with magnesium and dry ether
Classification of aminesboiling and melting points of aminesolubility of aminesbasicity of aminespreparation of amines from alkyl halides, cyanides, nitroalkanesHofmann's degredation
## Amines: Comprehensive Notes
**1. Classification:**
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH₃) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified into four primary types based on the number of alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom:
* **Primary (1°):** One alkyl/aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., CH₃NH₂ - Methylamine)
* **Secondary (2°):** Two alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., (CH₃)₂NH - Dimethylamine)
* **Tertiary (3°):** Three alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., (CH₃)₃N - Trimethylamine)
* **Quaternary (4°):** All four positions around the nitrogen atom are occupied by alkyl/aryl groups, resulting in a positively charged cation (e.g., [(CH₃)₄N⁺]Cl⁻ - Tetramethylammonium chloride)
**2. Physical Properties:**
* **Boiling and Melting Points:**
* Generally increase with increasing chain length of the alkyl/aryl groups due to stronger London dispersion forces.
* Branching in the chain can decrease boiling and melting points due to a decrease in surface area and weaker intermolecular interactions.
* Amines generally have lower boiling and melting points compared to similarly sized alcohols due to the absence of hydrogen bonding in amines.
* **Solubility:**
* Lower amines (primary and secondary) exhibit good water solubility due to the ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
* Solubility in water decreases with increasing size and branching of the alkyl/aryl groups due to the dominance of hydrophobic interactions over hydrogen bonding.
* Tertiary and quaternary amines with no N-H bonds are typically less soluble in water but may show solubility in organic solvents.
**3. Basicity:**
Amines exhibit basic character due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. This lone pair can accept a proton from acids, forming a positively charged ammonium ion. The basicity of amines follows the trend:
**Tertiary > Secondary > Primary > Ammonia**
Several factors influence the basicity of amines:
* **Inductive effect:** Electron-donating groups (e.g., alkyl groups) attached to the nitrogen atom increase basicity by pushing electron density towards the nitrogen, making it more willing to accept a proton.
* **Steric hindrance:** Bulky groups around the nitrogen atom hinder the approach of a proton, decreasing basicity.
**4. Preparation:**
Amines can be synthesized through various methods, some of the most common being:
* **Alkylation of ammonia or amines:** Reaction of ammonia or amines with alkyl halides under suitable conditions (e.g., heating with KOH).
* **Reduction of nitriles:** Conversion of nitriles (R-CN) to primary amines (R-CH₂NH₂) using reducing agents like LiAlH₄ or catalytic hydrogenation.
* **Reduction of nitroalkanes:** Conversion of nitroalkanes (R-NO₂) to primary, secondary, or tertiary amines depending on the reaction conditions and reducing agent used.
* **Gabriel synthesis:** Synthesis of primary amines from phthalimide using strong bases and alkyl halides.
**5. Hofmann Degradation:**
This reaction allows the conversion of a primary amide to a primary amine with one fewer carbon atom. The process involves treating the amide with bromine (Br₂) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), leading to rearrangement and cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond.
**6. Applications of Amines:**
Amines have diverse applications in various fields, including:
* **Pharmaceuticals:** Many drugs, such as antidepressants, decongestants, and antihistamines, contain amine groups.
* **Dyes and pigments:** Amines are used in the production of various dyes and pigments used in textiles, paints, and plastics.
* **Polymers and resins:** Amines are essential components in the synthesis of various polymers like nylon and resins used in adhesives and coatings.
* **Agrochemicals:** Some herbicides and insecticides contain amine functionalities.
* **Surfactants:** Quaternary ammonium salts are used as cationic surfactants in detergents and fabric softeners.
**7. Safety Considerations:**
Amines can exhibit various toxicities depending on their structure and properties. It is crucial to handle them with appropriate safety precautions, including wearing gloves, eye protection, and working in well-ventilated areas. Some amines may be flammable or corrosive, and proper handling procedures should be followed.
reaction of amines with acidsreaction of amines with alkanoyl halidesreaction of primary amines with carbonyl compoundsmeans of distinguishing between classes of amines
1. Reaction of Amines with Acids:
When amines react with acids, they undergo acid-base reactions to form salts. The amine acts as a base and accepts a proton (H+) from the acid. The resulting salt is formed by the ammonium cation (RNH3+) and the anion of the acid.
Example: RNH2 + HCl → RNH3+Cl-
2. Reaction of Amines with Alkanoyl Halides:
Amines can also react with alkanoyl halides (acyl halides) to form amides. The halogen atom attached to the alkanoyl halide is replaced by the amine group, resulting in the formation of an amide bond.
Example: RNH2 + RCOX → RCONHR + HX (where X = halogen atom)
3. Reaction of Primary Amines with Carbonyl Compounds:
Primary amines can react with carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes or ketones, to form imines or Schiff bases. In this reaction, the nitrogen of the primary amine forms a double bond with the carbon of the carbonyl group.
Example: RCH=O + RNH2 → RCH=NHR + H2O
Means of distinguishing between classes of amines:
There are several methods to distinguish between different classes of amines, including:
1. Solubility: Primary amines are generally more soluble in water compared to secondary and tertiary amines due to the presence of a hydrogen atom on the nitrogen, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
2. N-Methylation: Primary amines can be methylated by treatment with methyl iodide and a base to form a tertiary amine. Secondary amines can also be methylated to form quaternary ammonium salts.
3. Reaction with Nitrous Acid: Primary amines react with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form a diazonium salt, which is an unstable compound. Secondary and tertiary amines do not react with nitrous acid. This reaction can be used as a distinguishing test.
4. Boiling Point: Tertiary amines generally have higher boiling points compared to primary and secondary amines due to the presence of more alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, which increase intermolecular forces.
5. Chromatographic Methods: Techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or gas chromatography (GC) can be used to separate and analyze different classes of amines based on their different retention times or chromatographic behavior.
chemistry of period 2 elements and diagonal relationships for Advanced Level students
The period 2 elements in the periodic table include lithium (Li), beryllium (Be), boron (B), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), fluorine (F), and neon (Ne). These elements display a wide range of chemical properties and behaviors due to variations in their atomic structure and electron configurations.
1. Lithium (Li): Lithium is the lightest metal in the periodic table and is highly reactive. It readily loses its outermost electron to form a Li+ cation, making it a strong reducing agent. Lithium compounds are used in batteries, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Beryllium (Be): Beryllium is a lightweight alkaline earth metal. It is strong, lightweight, and resistant to high temperatures, making it valuable in industries such as aerospace and nuclear power. Beryllium oxide is used as a ceramic material and a thermal conductor.
3. Boron (B): Boron is a metalloid with both nonmetallic and metallic properties. It forms covalent bonds and exhibits variations in hybridization, resulting in a diverse range of compounds. Boron compounds have numerous applications, including as fertilizers, flame retardants, and as a component in borosilicate glass.
4. Carbon (C): Carbon is a nonmetal that forms the basis of organic chemistry. It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form a large variety of compounds with other elements. Carbon compounds include hydrocarbons, such as methane and ethane, as well as complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and DNA.
5. Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is a diatomic nonmetal that makes up about 78% of Earth's atmosphere. It is relatively inert and forms strong triple bonds between nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen compounds are important in fertilizers, explosives, and as a coolant in various applications.
6. Oxygen (O): Oxygen is a highly reactive nonmetal that readily forms compounds, including oxides. It is essential for respiration and combustion processes. Oxygen also plays a crucial role in the ozone layer of the Earth's atmosphere.
7. Fluorine (F): Fluorine is the most electronegative element and is highly reactive. It is a diatomic nonmetal that reacts with almost all other elements, often resulting in the release of energy. Fluorine compounds are used in toothpaste, refrigerants, and in the production of plastics.
8. Neon (Ne): Neon is a noble gas and has a completely filled valence electron shell. It is chemically inert and does not readily form compounds. Neon is commonly used in neon signs due to its bright orange-red glow when an electric current passes through it.
These period 2 elements demonstrate a wide range of chemical behaviors and applications, from highly reactive metals (such as lithium) to non-reactive noble gases (such as neon). Their properties and reactivities are a result of their electronic configurations and atomic structures.
Here are some examples of reactions involving period 2 elements:
1. Lithium and water: Lithium reacts vigorously with water to produce lithium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The reaction is highly exothermic and liberates a large amount of heat.
2. Beryllium and oxygen: Beryllium reacts with oxygen to form beryllium oxide. This reaction is highly exothermic and releases a large amount of heat.
3. Carbon and oxygen: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. This reaction occurs during combustion processes and is responsible for the production of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
4. Nitrogen and hydrogen: Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia in the Haber process. The reaction is catalyzed by an iron catalyst and occurs at high temperature and pressure.
5. Oxygen and hydrogen: Oxygen reacts with hydrogen to form water. This reaction occurs during combustion processes, and it is also an important component of the water cycle.
6. Fluorine and metals: Fluorine reacts vigorously with metals to form metal fluorides. This reaction is highly exothermic and can result in the release of toxic fluorine gas.
7. Beryllium and acids: Beryllium reacts readily with acids to form beryllium salts and hydrogen gas. This reaction can release hydrogen gas, which may pose a hazard.
8. Boron and halogens: Boron reacts with halogens, such as chlorine and fluorine, to form boron halides. These compounds are often used as reagents in organic chemistry reactions.
9. Carbon and water: Carbon can react with water to produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of chemical reactions that period 2 elements can participate in. The reactivity and behavior of each element are related to its electronic structure and valence electron configuration.
Physical chemistry for A level students especially for those for UACE exams in Uganda
Acid-base indicators are substances that undergo a color change in response to changes in the pH of a solution. They are often used in chemical experiments and titration procedures to determine the endpoint of an acid-base reaction. Different indicators have different pH transition ranges and colors, allowing for the identification of the pH range during a titration.
pH titration curves, on the other hand, are graphical representations of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of a titrant added during a titration. In an acid-base titration, a solution of known concentration (titrant) is slowly added to a solution of unknown concentration (analyte) until the reaction between the two is complete. The pH titration curve plots the pH of the solution being titrated against the volume of titrant added.
The shape of a pH titration curve depends on the nature of the acid and base involved in the reaction, as well as their relative concentrations. The curve typically starts at a low pH when only the acid is present, rises gradually as the titrant is added, and eventually undergoes a rapid change near the equivalence point, where stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have reacted. After the equivalence point, the curve levels off and remains at a high pH when only excess base is present.
The behavior of the pH titration curve depends on the strength of the acid and base being titrated. For strong acids and strong bases, the curve is relatively steep around the equivalence point, resulting in a sharp endpoint and a well-defined titration. For weak acids and weak bases, the curve will be smoother and have a more gradual change around the equivalence point, making it more difficult to determine the exact endpoint of the titration.
By using acid-base indicators in titrations, the color change of the indicator can be used to visually identify the endpoint of the titration. The indicator is chosen based on its pH transition range, which is the pH range over which the indicator changes color. For example, phenolphthalein is often used as an indicator in acid-base titrations, as it changes from colorless to pink in a pH range of 8.2 to 10.0. By observing the color change of the indicator, the endpoint of the titration can be determined, indicating that the reaction is complete.
In summary, acid-base indicators are substances that change color in response to changes in pH, allowing for the observation of endpoint during titrations. pH titration curves, on the other hand, are graphical representations of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of titrant added during a titration. They depict the behavior of pH during a titration and can be used to determine the equivalence point and the strength of the acid and base involved.
physical chemistry; hydrolysis of salts for A-level students
In chemistry, hydrolysis of salts refers to the reaction of a salt with water, resulting in the formation of an acidic or basic solution. Salts are ionic compounds formed from the neutralization of an acid and a base. When a salt dissolves in water, it dissociates into its component ions, which can either be acidic, basic, or neutral.
The hydrolysis of salts can be classified into two categories: acidic hydrolysis and basic hydrolysis, depending on the nature of the salt and the pH of the resulting solution.
1. Acidic hydrolysis: This type of hydrolysis occurs when the salt formed from a weak acid and a strong base is dissolved in water. The anion of the salt acts as a base and reacts with water to produce hydroxide ions and the corresponding acid. For example, when ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis according to the equation:
NH4Cl + H2O ⇌ NH3 + HCl
The ammonium ion (NH4+) acts as an acid and donates a proton to the water, forming ammonium hydroxide (NH3) and hydronium ion (H3O+). The chloride ion (Cl-) acts as a base and accepts a proton from water, forming hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hydroxide ion (OH-).
2. Basic hydrolysis: This type of hydrolysis occurs when the salt formed from a strong acid and a weak base is dissolved in water. The cation of the salt acts as an acid and reacts with water to produce hydronium ions and the corresponding base. For example, when sodium acetate, NaC2H3O2, is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis according to the equation:
NaC2H3O2 + H2O ⇌ Na+ + C2H3O2- + H3O+ + OH-
The sodium ion (Na+) and acetate ion (C2H3O2-) remain unchanged, while water reacts with a small fraction of acetate ions to form acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and hydroxide ion (OH-). At the same time, water reacts with a small fraction of hydronium ions to form hydronium ion (H3O+) and hydroxide ion (OH-).
In summary, hydrolysis of salts can either produce acidic or basic solutions, depending on the nature of the salt and the pH of the resulting solution. Understanding the hydrolysis of salts is important in various chemical and biochemical processes, including the buffering capacity of biological fluids and the maintenance of pH in water treatment processes.
worked examples to thermodynamics question
this academic video for Advanced level students taking chemistry for UACE exams; it describes equilibrium constant Kc and its application with several worked examples.
In chemistry, equilibrium refers to a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction are equal. This means that the concentration of reactants and products remain constant over time, even though the reactions continue to occur. At equilibrium, the system is said to be in a dynamic balance.
The equilibrium constant, denoted by Kc, is a numerical value that represents the ratio of the concentrations of products to the concentrations of reactants, with each concentration raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation. The equilibrium constant expression is written as:
Kc = [C]^c [D]^d / [A]^a [B]^b
Where A, B, C, and D represent the reactants and products, and a, b, c, and d represent their stoichiometric coefficients.
The equilibrium constant is a measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds toward the formation of products. It is a constant at a given temperature and is independent of the initial concentrations of the reactants. The value of Kc reflects the relative concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant provides information about the position of equilibrium.
- If Kc > 1, it indicates that the equilibrium favors the products. This means that at equilibrium, the concentration of the products is higher compared to the concentrations of the reactants.
- If Kc < 1, it suggests that the equilibrium favors the reactants. At equilibrium, the concentration of the reactants is higher compared to the concentrations of the products.
- If Kc = 1, it signifies that the reactants and products are present in roughly equal concentrations at equilibrium.
The equilibrium constant provides insights into the direction in which a reaction will proceed or which species will be present in greater abundance at equilibrium. It also allows for predictions about the effect of changes in concentration, temperature, or pressure on the position of equilibrium.
reactions of amines in A-level organic chemistry
Certainly! Amine chemistry refers to the branch of organic chemistry that focuses on the study of compounds containing amine functional groups (-NH2). Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups.
Amines can be classified into three main types based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom:
1. Primary Amines: These are amines where one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. They have the general formula R-NH2.
2. Secondary Amines: In secondary amines, two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. They are represented by the general formula R2-NH.
3. Tertiary Amines: Tertiary amines have three alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Their general formula is R3-N.
Amine chemistry plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, materials science, and biochemistry. Amines can participate in various reactions, such as substitution, oxidation, reduction, condensation, alkylation, and acylation.
Some notable reactions involving amines include:
1. Amine substitution: Amines can undergo substitution reactions with various electrophiles, wherein the amino group is replaced by another atom or group. This allows for the introduction of different functional groups onto the amine molecule.
2. Amine oxidation: Amines can be oxidized to form amine oxides or further oxidized to form nitro compounds. This reaction is commonly achieved using oxidizing agents such as peroxides or metal oxides.
3. Amine reduction: Amines can be reduced to form secondary or tertiary amines, or even to primary amines from nitro compounds. Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation can be used for these reactions.
4. Amine condensation: Amines can undergo condensation reactions, combining with other compounds to form imines, enamines, or Schiff bases. These reactions are often used in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and pharmaceuticals.
5. Amine alkylation and acylation: Amines can be alkylated or acylated to form N-alkyl or N-acyl amines, respectively. These reactions involve the addition of an alkyl or acyl group to the nitrogen atom of the amine.
Understanding amine chemistry is crucial for designing and synthesizing new molecules with specific properties and functions. It allows chemists to modify amine-containing compounds for various applications, including drug design, organic synthesis, and materials science.
Rate, rate law, rate equation, the rate constant, the order of reaction with worked examples
Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence those rates. It involves the measurement and analysis of reaction rates, the determination of reaction mechanisms, and the understanding of how reaction rates can be altered.
Here are some important concepts and topics in chemical kinetics at an advanced level:
1. Reaction Rate: The reaction rate represents how fast a reactant is consumed or how fast a product is formed in a chemical reaction. It is typically expressed as the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time.
2. Rate Law: The rate law for a chemical reaction relates the rate of the reaction to the concentrations of the reactants. It is determined experimentally and is expressed as a mathematical equation. The rate law shows the order of reaction with respect to each reactant and the overall order of the reaction.
3. Rate Constant: The rate constant (k) is a proportionality constant in the rate equation that quantifies the relationship between the rate of the reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. It is specific to a given reaction at a given temperature and is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and catalysts.
4. Activation Energy: Activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that must be overcome for reactant molecules to transform into products. The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant to the activation energy and temperature.
5. Reaction Mechanisms: Reaction mechanisms describe the step-by-step sequence of elementary reactions that lead to the overall reaction. Elementary reactions involve the collision or interaction of individual molecules or atoms. Determining the reaction mechanism provides insight into the detailed pathway of the reaction.
6. Reaction Order: The reaction order of a reactant determines how changes in its concentration affect the reaction rate. The reaction order can be zero, first, second, or a combination of these orders. The overall reaction order is the sum of the individual reaction orders.
7. Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. They provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts can significantly influence reaction rates and are extensively used in industrial processes.
8. Temperature and Reaction Rate: Temperature plays a crucial role in determining reaction rates. Increasing temperature generally increases the rate of a reaction by increasing the number of collisions and providing greater kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier.
9. Reaction Rate Laws and Integrated Rate Laws: Reaction rate laws and integrated rate laws describe the relationship between reactant concentrations and time during a chemical reaction. They can be used to determine reaction orders, rate constants, and monitor the progress of a reaction.
10. Reaction Kinetics and Equilibrium: The study of reaction kinetics provides insights into the time-dependent behavior of chemical reactions. It helps in understanding how reaction rates change as a system approaches equilibrium and how reaction conditions can be manipulated to shift the equilibrium position.
These concepts represent a deeper level of understanding in chemical kinetics, and they are often explored in advanced level chemistry courses and research. The study of chemical kinetics is essential for understanding reaction mechanisms, designing efficient chemical processes, and predicting the behavior of chemical systems.
Carbon and its compounds (hydrides, halides, oxides, Carbonic acids);
Silicon and its compounds (reaction of silicon dioxide with sodium hydroxide and hydrogen fluoric acid)
compounds of germanium, tin and lead (oxides, chlorides, nitrates)
mechanism of electrolysis, factors affecting selective discharge, application of electrolysis, extraction of sodium, preparation of sodium hydroxide, Faraday's laws of electrolysis
Here are some examples of applications of electrolysis:
1. Electroplating: Electroplating is a process that uses electrolysis to deposit a layer of metal onto the surface of an object. It is commonly used to enhance the appearance, protect against corrosion, or improve conductivity of objects. For example, jewelry, automotive parts, and electronic components undergo electroplating.
2. Electrorefining of Metals: Electrorefining is the process of purifying impure metals using electrolysis. Impure metal is used as the anode, and a pure metal or graphite rod is used as the cathode. Through electrolysis, the impurities are dissolved into the electrolyte or settle as a sludge, leaving a pure metal at the cathode. This process is used in the refining of copper, lead, and other metals.
3. Electrolytic Cells for Energy Storage: Electrolytic cells, such as electrolyzers, are used to store energy in the form of chemical compounds. For example, during periods of excess renewable energy production, electrolyzers can use the electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. The hydrogen gas can be stored for later use as a fuel source in fuel cells or for powering vehicles.
4. Chlor-Alkali Industry: The chlor-alkali industry relies heavily on electrolysis. In this industry, electrolysis is used to produce chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and alkali metal hydroxides (such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) simultaneously. These compounds have various industrial applications, including the production of bleach, detergents, paper, and textiles.
5. Electrolysis in Water Treatment: Electrolysis can be used for water treatment and disinfection. By applying an electrical current through water, electrolysis can produce disinfecting agents such as chlorine or ozone. These agents can effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens present in water.
6. Electrolysis in Electrochemical Cells: Electrochemical cells, such as batteries and fuel cells, rely on electrochemical reactions driven by electrolysis. For example, rechargeable batteries like lithium-ion batteries use electrolysis during the charging process, allowing the flow of ions between electrodes.
7. Electrolysis in Electrolytic Capacitors: Electrolytic capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for energy storage. These capacitors are constructed using an electrolyte, which undergoes electrolysis during operation. The electrolysis maintains the capacitance and enables energy storage in the capacitor.
These are just a few examples of the numerous applications of electrolysis in various industries and technological advancements. Electrolytic processes involving electrolysis have a significant impact on our daily lives, from manufacturing processes to energy storage and environmental solutions.
the resistance of the electrolyte, the resistivity of electrolyte, the conductivity of electrolytes, molar conductivity, molar conductivity at infinite dilution, conductometric curves
Electroconductivity, in the context of A-Level studies, refers to the ability of a substance or solution to conduct electricity. Here are some key points about electroconductivity at the A-Level:
1. Electrical Conductivity: Electrical conductivity is a measure of how well a substance allows the flow of electric current through it. Materials or solutions that are good conductors have high electrical conductivity, while those that impede the flow of current have low electrical conductivity.
2. Conductivity and Ions: The ability of a substance to conduct electricity is directly related to the presence of mobile charge carriers. In the case of solutions, the presence of ions in solution allows the solution to conduct electricity. In solid conductors, delocalized electrons enable the flow of current.
3. Electrolytes: Substances that readily form ions in solution are called electrolytes. Electrolytes can be strong or weak depending on their ability to ionize completely or partially. Strong electrolytes, such as strong acids or salts, produce a high concentration of ions and thus have high electrical conductivity. Weak electrolytes, on the other hand, produce a lower concentration of ions and have lower electrical conductivity.
4. Ionic Solutions: Ionic solutions, which contain ions in solution, exhibit higher electrical conductivity compared to non-ionic solutions. This is because ions act as charge carriers and facilitate the flow of current.
5. Ionic Compound Dissociation: When an ionic compound dissolves in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions. The dissociation of the compound into ions increases electrical conductivity, as the resulting solution contains mobile ions.
6. Conductivity Measurements: The electrical conductivity of a solution is typically measured using a conductivity meter. This device measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electric current and provides a numerical value for the conductivity.
7. Factors Affecting Conductivity: The electrical conductivity of a solution is influenced by several factors. Temperature, concentration of ions, and the presence of impurities can all affect the conductivity of a solution.
8. Applications: Understanding electroconductivity is important in various applications, such as in the design and operation of electrochemical cells, batteries, circuitry, and conductivity-based sensors. It is also relevant in fields like environmental science, where water quality is assessed based on its electrical conductivity.
These points provide a basic overview of electroconductivity at the A-Level. Further exploration of the topic can involve studying conductivity measurements, conductivity trends across the periodic table, and the relationship between conductivity and electrolysis or galvanic cells.u
Phases and factors affecting the phase of a substance, physical chemistry A-level.
Physical Equilibria, also known as physical phase equilibria, refers to the equilibrium between different physical states of matter such as solid, liquid, and gas. Here are some key points about physical equilibria:
1. Phase Transitions: Physical equilibria involve phase transitions, which are the changes of a substance from one phase to another. Common phase transitions include solidification (from liquid to solid), melting (from solid to liquid), vaporization (from liquid to gas), condensation (from gas to liquid), sublimation (from solid to gas), and deposition (from gas to solid).
2. Equilibrium Conditions: For a physical equilibrium to be established, the rates of the forward and backward phase transitions must be equal. This means that the amount and concentration of each phase remain constant over time.
3. Equilibrium Temperature: Each phase transition occurs at a specific temperature, known as the equilibrium temperature. This temperature depends on the pressure and composition of the system.
4. Phase Equilibrium Diagrams: Phase equilibrium diagrams, such as the water phase diagram or the phase diagram of a substance, provide a graphical representation of the conditions at which different phases coexist in equilibrium. These diagrams show the temperature and pressure ranges for each phase and the boundaries between them.
5. Triple Point: The triple point on a phase equilibrium diagram represents the unique set of conditions (temperature and pressure) at which all three phases (solid, liquid, and gas) of a substance can coexist in equilibrium.
6. Critical Point: The critical point is the temperature and pressure above which a substance can no longer exist as a distinct liquid phase, regardless of pressure. At the critical point, the liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable and merge into a supercritical fluid.
7. Phase Equilibrium Calculations: Thermodynamic models and equations, such as the Clapeyron equation or the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, are used to calculate and predict phase equilibrium conditions. These calculations require knowledge of properties such as enthalpy, entropy, and temperature.
8. Applications: Understanding physical equilibria is important in various fields, including material science, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and atmospheric science. It helps in designing processes, predicting phase behavior, and optimizing the production and use of substances.
Physical equilibria play a crucial role in various natural and technological processes, and studying their behavior is fundamental to understanding the physical properties and transformations of matter.
Describes ionic, covalent, dative bonds, bond polarity and polarization of bonds suitable students taking chemistry at advanced level of education
Ionic bonds:
Ionic bonds are formed between two atoms when one atom donates one or more electrons to another atom. This transfer of electrons leads to the formation of ions - positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. Ionic bonds typically occur between a metal and a non-metal.
Covalent bonds:
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases. Covalent bonds typically occur between non-metals.
Dative bonds (also known as coordinate covalent bonds):
Dative bonds occur when both electrons in a shared pair come from the same atom. In other words, one atom donates both electrons to the bond, while the other atom does not contribute any electrons. Dative bonds can be thought of as a special case of covalent bonds, where one atom supplies both electrons. This type of bonding is commonly found in Lewis acid-base reactions.
Bond polarity:
Bond polarity refers to the unequal sharing of electrons between two atoms in a covalent bond. This unequal sharing occurs when one atom has a higher electronegativity (tendency to attract electrons) than the other atom. The difference in electronegativity leads to a separation of charges, creating a polar bond. The atom with higher electronegativity will have a partial negative charge (δ-) while the other atom will have a partial positive charge (δ+).
Polarization of bonds:
Polarization of bonds refers to the distortion of the electron cloud in a chemical bond due to the influence of external or internal forces. This can occur when a more electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud towards itself, causing an uneven distribution of electron density along the bond. Bond polarization can lead to the formation of partial charges or dipoles within a molecule.
Students taking chemistry at an advanced level of education will study these concepts in greater detail and explore their applications in various chemical reactions, organic chemistry, molecular geometry, and spectroscopy.
Suitable for Advance level students tacking physical chemistry: the video describe how to use Raoult's laws to calculate the composition and vapour pressures of components in the ideal mixtures
General CHS 102 - History and Development of Organic Chemistry....For Private Tutoring:Contact Me: +256787503215
Stoichiometry Calculations involving Equation of Reactions" Pt 1
chemistry of period 3 for Advanced level students
molecular, ionic, atomic and metallic solids
electrode potential, standard electrode potential, factors affecting electrode potential, factors affecting standard electrode potential, standard hydrogen electrode, measurent of electrode potentials, emf cells and calculations.
Reaction of alkynes with water
Reaction of alkynes with ammoniacal silver nitrate or ammoniacal copper I chloride
distinguishing between terminal alkynes and those with the tripple bond in the middle of the chain
atomic masses, relative atomic masses, and relative molecular masses
describes physical and chemical properties of cobalt and nickel
Chemistry of Cobalt:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Cobalt has an atomic number of 27 and an atomic weight of 58.933 g/mol. It is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal with a high melting point of 1495°C and a boiling point of 2870°C.
2. Oxidation states: Cobalt can exhibit various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4. The +2 state is the most common and stable, while the +3 and +4 states are less common.
3. Chemical reactivity: Cobalt is a moderately reactive metal, similar to iron. It reacts slowly with oxygen in the air to form cobalt(II) oxide (CoO). It also reacts with a variety of acids and non-metals, such as sulfur and halogens.
4. Cobalt compounds: Cobalt forms a multitude of compounds, such as cobalt chloride (CoCl2), cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2), and cobalt sulfate (CoSO4). These compounds find applications in various fields, including catalysts, pigments, and batteries.
5. Biological importance: Cobalt is an essential element for some living organisms. It is a critical component of vitamin B12 (cobalamin), which is necessary for proper functioning of the nervous system, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production.
6. Magnetic properties: Cobalt is known for its magnetic properties. It is one of the few naturally occurring magnetic elements and can be magnetized to produce permanent magnets.
7. Alloys: Cobalt forms alloys with other metals, such as cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) and cobalt-nickel (Co-Ni) alloys. These alloys have excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, making them useful in applications like aerospace, orthopedic implants, and turbine blades.
Chemistry of Nickel:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Nickel has an atomic number of 28 and an atomic weight of 58.693 g/mol. It is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel has a melting point of 1455°C and a boiling point of 2730°C.
2. Oxidation states: Nickel commonly exhibits two oxidation states, +2 and +3. The +2 state is the more stable and prevalent form.
3. Chemical reactivity: Nickel undergoes slow oxidation in air, forming a thin oxide layer. It is resistant to corrosion and is utilized in various applications where corrosion resistance is crucial, such as stainless steel.
4. Nickel compounds: Nickel forms a range of compounds, including nickel chloride (NiCl2), nickel sulfate (NiSO4), and nickel oxide (NiO). These compounds have applications in electroplating, catalysts, and ceramics.
5. Biological importance: Nickel is not considered an essential nutrient for most organisms but has some biological activity. It is a cofactor for certain enzymes and plays a role in enzymatic processes.
6. Alloy formation: Nickel is widely used in alloy formation. It forms alloys with metals like iron, chromium, and copper, leading to the production of stainless steel, superalloys, and various other alloys with improved mechanical and thermal properties.
7. Industrial applications: Nickel and its alloys find extensive use in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction, due to their excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and heat resistance.
Understanding the chemistry of cobalt and nickel is crucial in fields such as materials science, metallurgy, catalysis, and biochemistry. It enables the development of new materials and compounds, enhances industrial processes, and contributes to advancements in various technological applications.
properties of iron such reaction with air, water, chlorine acid, qualitative analysis,stability of oxidation states 2 and 3
Iron is a transition element that belongs to the d-block in the periodic table. Here are some key aspects of the chemistry of iron:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Iron has an atomic number of 26 and an atomic weight of 55.845 g/mol. It is a silvery-gray metal with a high melting point of 1538°C and a boiling point of 2862°C. Iron is a paramagnetic material, meaning it is weakly attracted to magnetic fields.
2. Oxidation states: Iron can exhibit various oxidation states, but the most common are +2 (ferrous) and +3 (ferric). The +2 state is more stable in aqueous solutions, while the +3 state is more prevalent in solid compounds.
3. Chemical reactivity: Iron is a moderately reactive metal. It readily reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture to form iron oxides. This reaction is known as rusting. Iron also reacts with acids, halogens, and sulfur, among other elements.
4. Iron compounds: Iron forms various compounds, including iron oxide (Fe2O3), iron sulfide (FeS), iron chloride (FeCl2 and FeCl3), and iron carbonate (FeCO3). These compounds find applications in industries like construction, manufacturing, and medicine.
5. Biological importance: Iron is an essential nutrient for most living organisms. It plays a critical role in oxygen transport (through hemoglobin and myoglobin), energy metabolism, DNA synthesis, and enzyme activity.
6. Alloy formation: Iron forms alloys with other elements, such as carbon (to produce steel), nickel (to produce stainless steel), and cobalt (to produce magnets). These alloys have enhanced properties, including improved strength, corrosion resistance, and magnetic properties.
7. Redox reactions: Iron can readily undergo redox reactions, switching between the +2 and +3 oxidation states. This property is crucial in many biological processes and industrial applications.
8. Geological occurrence: Iron is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust. It is commonly found in the form of hematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), and siderite (FeCO3).
Studying the chemistry of iron is crucial in various disciplines, including materials science, environmental science, biology, medicine, and geology. It helps us understand the behavior of iron and its compounds, develop new materials, improve industrial processes, and maintain human health.
physical and chemical properties of manganese, reaction with water, air, oxidation properties of manganese VII, confirmatory tests of manganese II ions
The chemistry of manganese involves the study of the properties, reactions, and compounds of the element manganese (Mn), which belongs to the transition metal group in the periodic table. Here are some key aspects of the chemistry of manganese:
1. Oxidation states: Manganese exhibits various oxidation states ranging from -3 to +7. The most common oxidation states are +2, +4, and +7.
2. Chemical reactivity: Manganese is a moderately reactive metal. It readily reacts with halogens, sulfur, and many other non-metallic elements. It also reacts with acids to produce salts and hydrogen gas.
3. Manganese compounds: Manganese forms various compounds such as oxides (e.g., manganese dioxide), sulfides (e.g., manganese sulfide), halides (e.g., manganese chloride), and complex ions (e.g., permanganate ion).
4. Catalytic properties: Manganese, particularly in its higher oxidation states (e.g., MnO2), exhibits excellent catalytic activity. It is used as a catalyst in many chemical reactions, such as the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
5. Biological importance: Manganese is an essential trace element for many organisms, including plants, animals, and humans. It plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including enzyme activation, energy metabolism, and antioxidant defense.
6. Oxidation-reduction reactions: Manganese can undergo oxidation-reduction reactions by switching between different oxidation states. This ability is utilized in redox reactions and electron transfer processes.
7. Coordination chemistry: Manganese forms complex compounds with ligands in coordination chemistry. These compounds have applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and environmental science.
8. Geological occurrence: Manganese is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. It is commonly found in ores, such as pyrolusite (MnO2) and rhodochrosite (MnCO3).
Studying the chemistry of manganese is important for understanding its properties, applications, and environmental impact. It has wide-ranging implications in fields such as materials science, environmental science, medicine, and industrial processes.
osmotic pressure and calculation
Describes boiling point elevation and calculations
Describes the lowering of osmotic pressure with calculations
Calculating solubility product, common ion effect
Solubility product constant (Ksp) is a thermodynamic equilibrium constant that describes the degree to which a sparingly soluble compound dissolves in water. It is equal to the product of the concentrations of the ions raised to the powers of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation representing the dissolution of the compound. For example, consider the dissolution of a sparingly soluble salt MX at equilibrium:
MX (s) ⇌ M^+ (aq) + X^- (aq)
The solubility product expression for this reaction is:
Ksp = [M^+][X^-]
where [M^+] and [X^-] are the concentrations of the dissolved ions in the equilibrium mixture. The value of Ksp depends only on temperature and is a measure of the maximum amount of dissolved ions that can exist in a saturated solution of the salt.
If the ion concentrations in a particular solution are greater than Ksp, the salt will precipitate out of the solution until it reaches equilibrium again. On the other hand, if the ion concentrations are less than Ksp, the solution is unsaturated and additional salt can dissolve until saturation is reached. The Ksp value allows us to predict the solubility behavior of a salt and also to determine its molar solubility (the concentration of the dissolved ions) at equilibrium.
terminologies in in thermodynamic
Certainly! Here are some additional terminologies used in advanced level thermochemistry:
1. #Enthalpy: The total heat energy content of a system at constant pressure.
2. #InternalEnergy: The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of the particles within a system.
3. #StandardState: The defined set of conditions under which thermodynamic properties are measured and compared.
4. #EnthalpyofFormation: The change in enthalpy that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
5. #EnthalpyofCombustion: The change in enthalpy that occurs when one mole of a substance is completely burned in excess oxygen.
6. #EnthalpyofReaction: The change in enthalpy that occurs during a chemical reaction, typically expressed in kJ/mol.
7. #HeatofSolution: The enthalpy change that occurs when a solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution.
8. #StandardEnthalpyofReaction: The enthalpy change that occurs during a reaction when all reactants and products are in their standard states.
9. #StandardEnthalpyofFormation: The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states, with all substances in their standard states as reactants and products.
10. #BondDissociationEnergy: The energy required to break a specific bond in a gaseous molecule.
11. #EnthalpyDiagram: A graphical representation of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction, showing the potential energy of the reactants and products.
12. #EntropyChange: The change in entropy that occurs during a chemical reaction, usually expressed in J/mol·K.
13. #GibbsFreeEnergyChange: The change in Gibbs free energy that occurs during a chemical reaction, indicating the spontaneity and direction of the reaction.
14. #EquilibriumConstant: The ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations at equilibrium for a chemical reaction, indicating the extent of the reaction.
15. #ThermodynamicCycle: A series of thermodynamic processes that returns a system to its initial state, often used to determine specific energy changes.
These terminologies are commonly used in advanced level thermochemistry to analyze and quantify the energy changes and thermodynamic properties associated with chemical reactions and systems.
preparation alkynes for vicinal dihalidespreparation of ethyne from carbonpreparation of long chain alkynesreaction of alkynes alkynes, ethyne, propynes, butynwith hydrogen chloride and hydrogen bromidesreaction of alkynes, ethyne, propynes, butyne with chlorine and bromines
Preparation of alkenes from alcoholspreparation of alkenes from alkylhalides
## Preparation of Alkenes from Alcohols and Alkyl Halides:
There are several methods for preparing alkenes from alcohols and alkyl halides. Here are the two most common ones:
**1. Dehydration of Alcohols:**
This method involves removing a water molecule from an alcohol to form an alkene. There are two main types of dehydration reactions:
- **Acidic dehydration:** This reaction uses concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid as a catalyst. The alcohol must have at least one beta-hydrogen (a hydrogen atom on the carbon atom next to the hydroxyl group). This reaction follows the **Saytzeff rule**, which states that the more substituted alkene will be the major product.
- **Thermal dehydration:** This reaction uses heat (around 300°C) and often involves passing the alcohol vapor over alumina as a catalyst. This method has fewer regioselectivity issues than acidic dehydration, but it often leads to a mixture of products.
**2. Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides:**
This method involves removing a hydrogen halide (like HCl or HBr) from an alkyl halide to form an alkene. There are also two main types of dehydrohalogenation reactions:
- **E2 elimination:** This reaction uses a strong base, such as potassium hydroxide or sodium ethoxide, as a catalyst. The base abstracts a proton from the beta-hydrogen, while the halide ion leaves, forming an alkene. The major product follows the **Zaitsev rule**, which is similar to the Saytzeff rule.
- **E1 elimination:** This reaction is less common and requires strong heat instead of a base. It typically occurs with tertiary alkyl halides and follows a different mechanism than E2 elimination.
**Additional points to consider:**
* The specific method used for preparing an alkene depends on the starting material, the desired product, and other factors like availability of reagents and reaction conditions.
* Both dehydration and dehydrohalogenation reactions can be regioselective, meaning that the position of the double bond in the alkene product can be controlled to some extent.
* Safety precautions are essential when working with concentrated acids, strong bases, and organic solvents.
I hope this information helps! Feel free to ask if you have any further questions or need more details on specific aspects of these reactions.
Carbonium ionsreaction of alkenes with hydrogen bromide in presence a peroxideozonolysis of alkenespolymerization of alkenes
reaction of alkenes with chlorine, bromine and iodinereaction of propene, ethene, 2-methylpropene with water, halogens, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid
Alkenes part 1
examples of alkenes, reduction of alkene, reaction of alkenes with dilute potassium permanganate, electrophylic addition reaction, reaction of alkenes with halogens, chlorine, bromine and iodine
Properties of alkeness
sources ofalkenes
Nomenclature of alkanes
Definitions of organic chemistry
Hydrocarbons
Functional groups,
Homologous series
Isomerism
OMG!
#WalterLewin #physics
This video talks about the definition of the enthalpy of atomisation and how it helps calculate the Bond enthalpy, sublimation enthalpy, etc., in various cases.
00:00- Introduction
2:35- Relationship between atomisation enthalpy and bond enthalpy
4:30- Worked example
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Thermodynamics” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 11 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
TV LESSON SS3 is a Lagos state online class for SS3 student in preparation for WAEC.
Subscribe- be the first to view our latest videos
Connect with WazobiaMax TV on social media:
Follow WazobiaMax TV on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/wa...
Follow WazobiaMax TV on instagra m: https://www.instagram.com/w...
Follow #WazobiaMax TV on Twitter: https://twitter.com/wazobiamax
In this video, we look in detail at standard enthalpy change of reaction. I discuss what this means and how to carry out the calculation. I give you two examples to try yourself before taking you through the correct answers. I also explain to you what the units of standard enthalpy change of reaction actually mean.This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
In this video, we look at how to determine the standard enthalpy change of a reaction. First I take you through the experimental procedure. I then explain to you how to correct the results to take into account heat losses from the experimental setup. Finally, I show you how to carry out the calculation.This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
You can find all my A Level Chemistry videos fully indexed at https://www.freesciencelessons.....co.uk/a-level-revis
In this video, I explain how to determine the standard enthalpy change of combustion for a liquid fuel. First I show you the method. Then I take you through the calculation. Finally, I explain why the standard enthalpy change of combustion that we determine may be different to published values.
This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
Image credits
Spirit Burner
https://upload.wikimedia.org/w....ikipedia/commons/9/9
Xofc, CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0), via Wikimedia Commons
Hess's law, also known as the law of constant heat summation, is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics that states that the total enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is independent of the pathway taken, as long as the initial and final states are the same. In simpler terms, it doesn't matter how many steps a chemical reaction takes, the overall heat absorbed or released will always be the same.
This law is based on the concept of **enthalpy**, which is a thermodynamic property that combines a system's internal energy and the amount of work it can perform on its surroundings due to changes in pressure and volume. Enthalpy is often denoted by the symbol **H**.
Hess's law has numerous applications in chemistry, particularly in thermochemistry, which deals with the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. It allows chemists to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction even if it cannot be measured directly, by breaking it down into a series of simpler steps for which the enthalpy changes are known.
Here's a visual representation of Hess's law:
[Image of Hess's law diagram]
**Example:**
Consider the combustion of methane (CH₄) to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O):
CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) ΔH = -890.3 kJ
However, it is difficult to measure the enthalpy change for this reaction directly in a single step. Instead, we can break it down into a series of hypothetical steps for which the enthalpy changes are known:
1. Combustion of hydrogen to form water vapor:
H₂(g) + ½O₂(g) → H₂O(g) ΔH = -285.8 kJ (multiply by 2)
2. Condensation of water vapor to form liquid water:
H₂O(g) → H₂O(l) ΔH = -44.0 kJ
By summing the enthalpy changes for these two steps, we can calculate the enthalpy change for the overall combustion reaction:
ΔH = (-285.8 kJ/mol) x 2 + (-44.0 kJ/mol) = -890.6 kJ/mol
This value is in excellent agreement with the experimental value of -890.3 kJ/mol, demonstrating the validity of Hess's law.
Hess's law is a powerful tool that allows chemists to predict the enthalpy changes for a wide variety of chemical reactions, even if they cannot be measured directly. It is a cornerstone of thermochemistry and has numerous applications in fields such as chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental science.
The dreaded Hess's cycle I hear you cry! Hopefully this video will put those Hess's demons to rest. Take a look to find out how you use a Hess's cycle and how to draw them correctly in order to work out enthalpy of reaction, combustion and formation.
A level Chemistry
Energetics
Enthalpy Change
Exothermic and Endothermic
Reaction Profiles
Combustion
Formation
Standard Conditions
Hess' Law
Bond Energy
Physical Chemistry | Year 1
Let's explore the ideas of redox reactions
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Jitin Nair
❤
❤
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry.
😀
The name of a monatomic cation is simply the name of the element followed by the word ion. Thus, Na+ is the sodium ion, Al3+ is the aluminum ion, Ca2+ is the calcium ion, and so forth.
When naming these cations or compounds containing these cations, it is necessary to specify their charge. Cations and anions combine to form ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are named with the cation first and the anion last. The same convention is used when writing their chemical formulas.
In science, a cation is an ion, or charged particle, with a positive charge. In other words, a cation has more protons than electrons. If you come across the word ion in a chemistry or physics class, cation and anion won't be far behind. An ion is a particle that has an electrical charge.
In standard atomic notation, the name of an element is presented in the form of a symbol with certain super- and sub-scripts. A standard atomic notation shows the symbol, atomic number, mass number and charge (in case of an ion) of the element simultaneously.
The term matter refers to anything that occupies space and has weight—in other words, that element the universe is made of. All matter is made up of substances called elements, which have specific chemical and physical properties and cannot be broken down into other substances through ordinary chemical reactions.
An atom is the basic unit of a chemical element. A typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons (as seen in the VIDEO. Other particles exist as well, such as alpha and beta particles (which are discussed below). The Bohr model shows the three basic subatomic particles in a simple manner
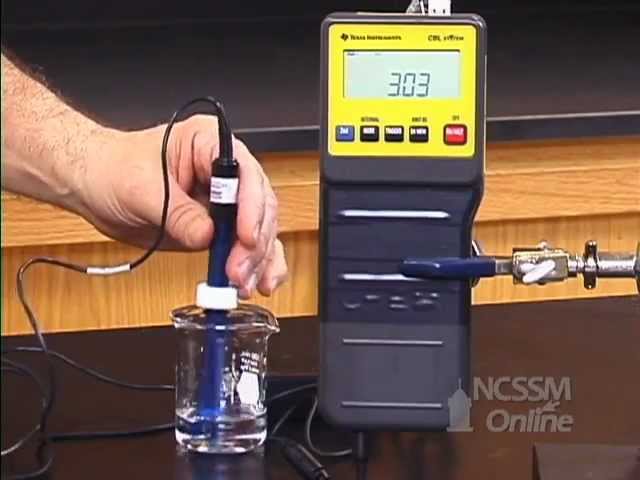
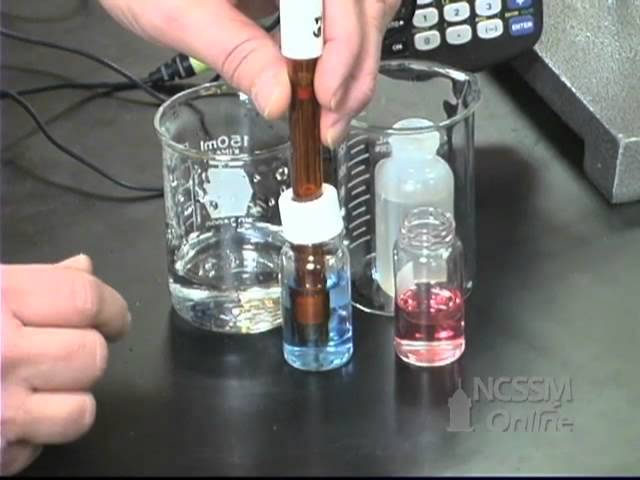





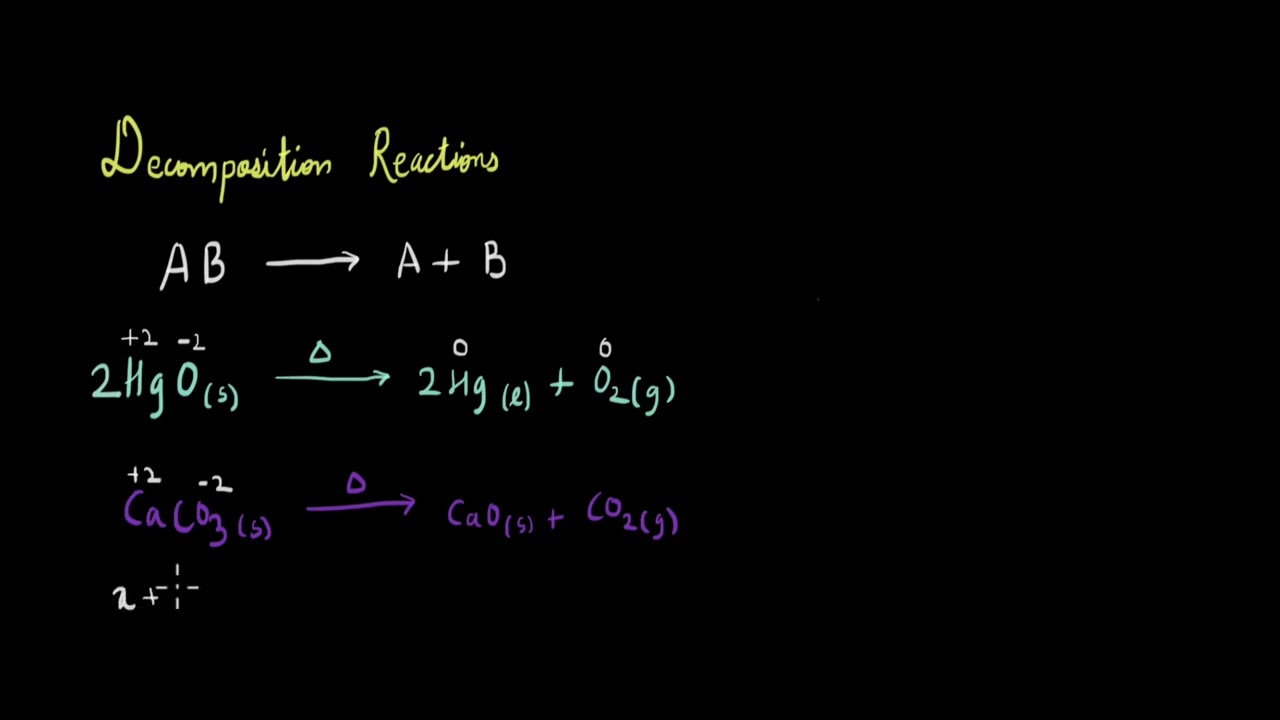


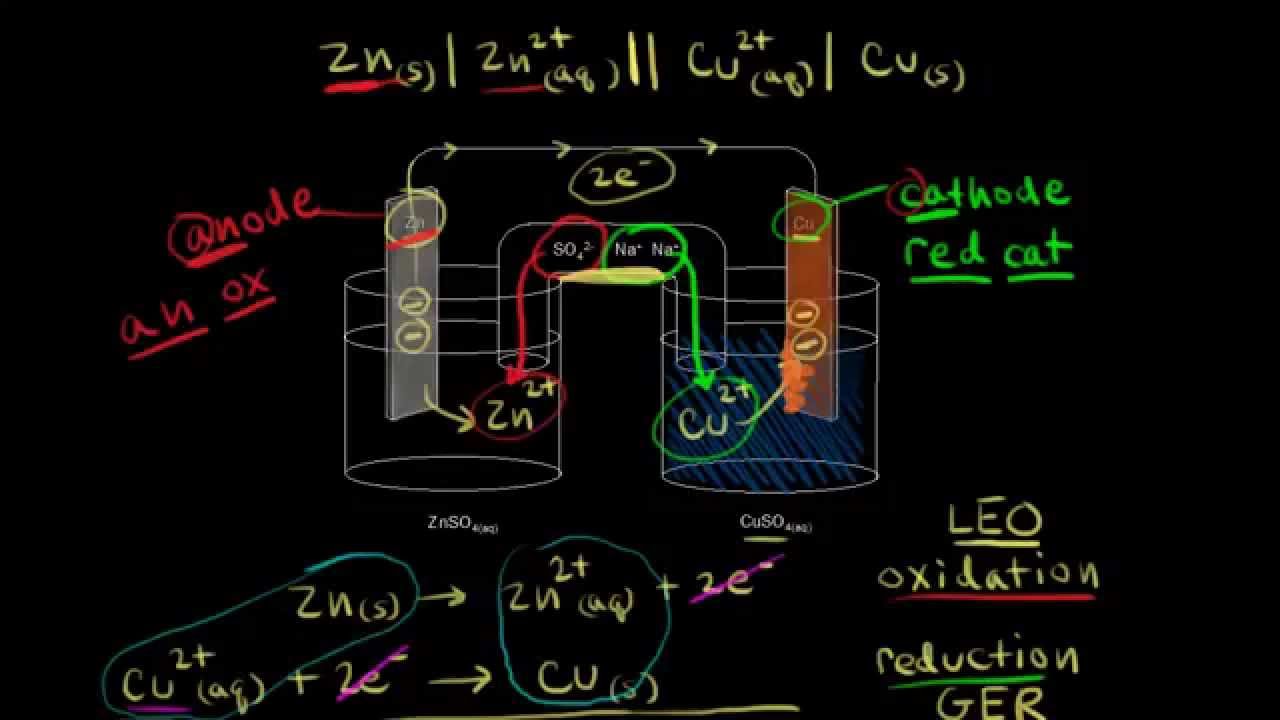













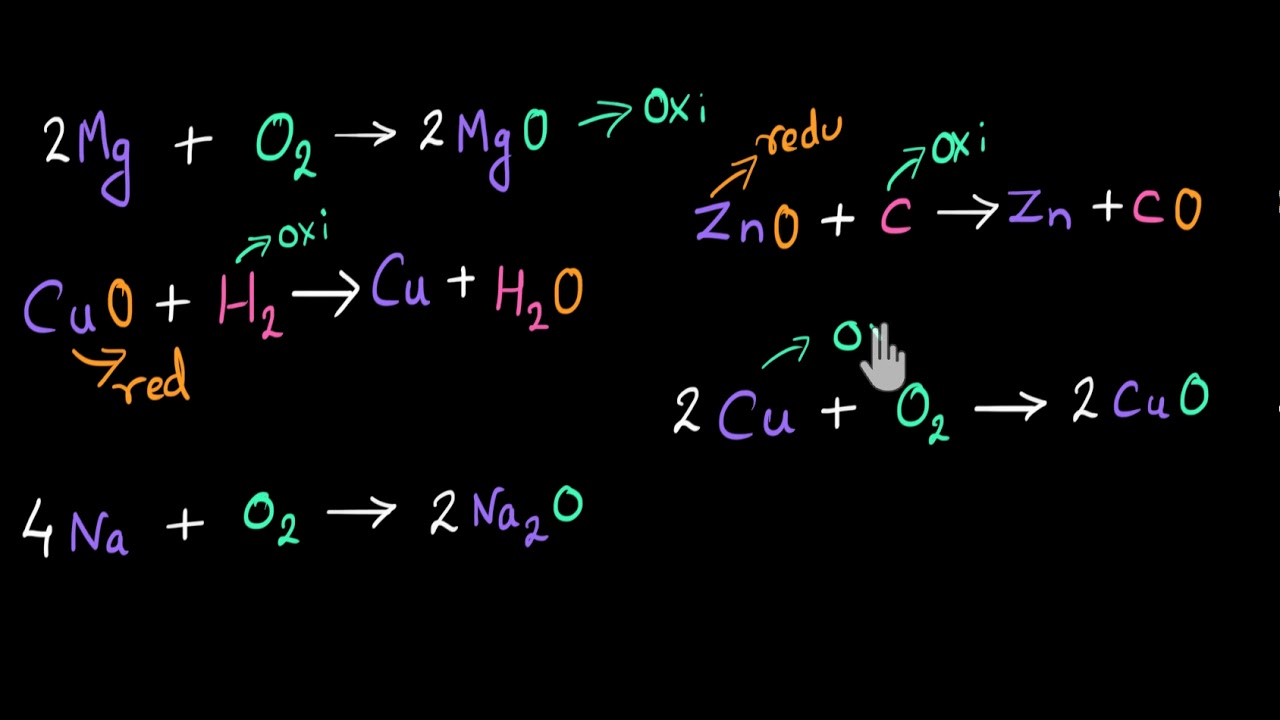







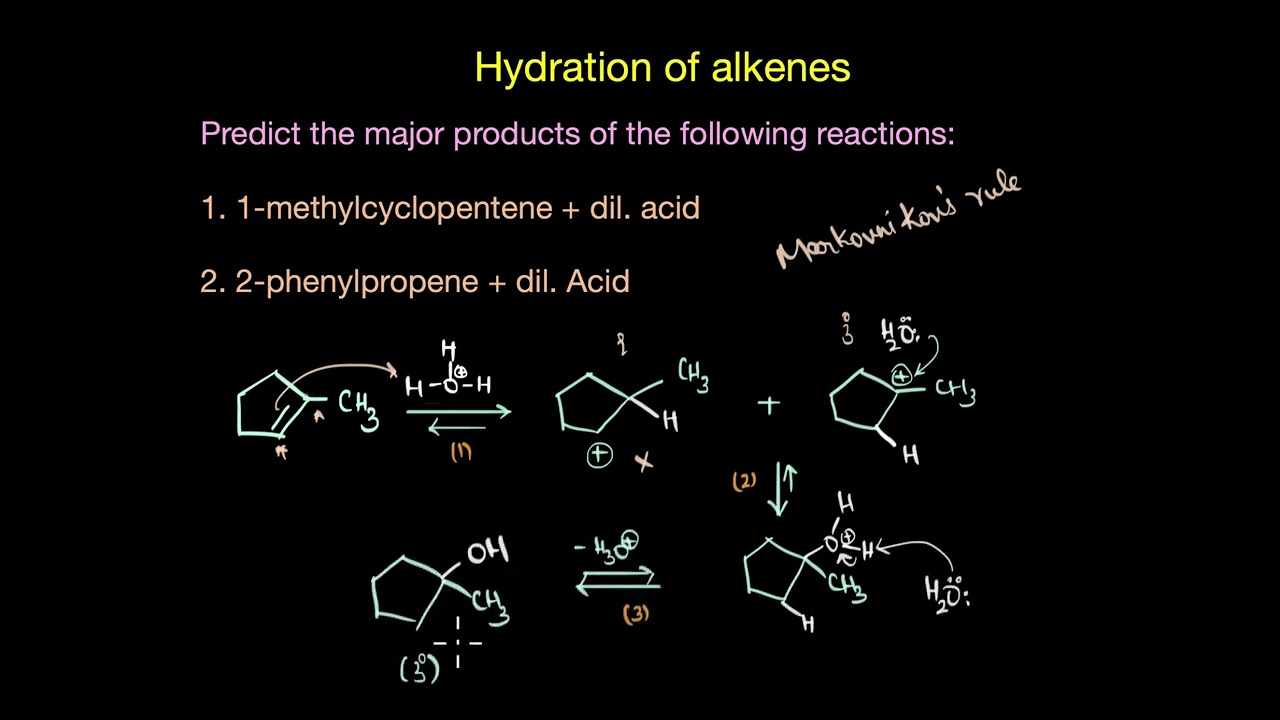

















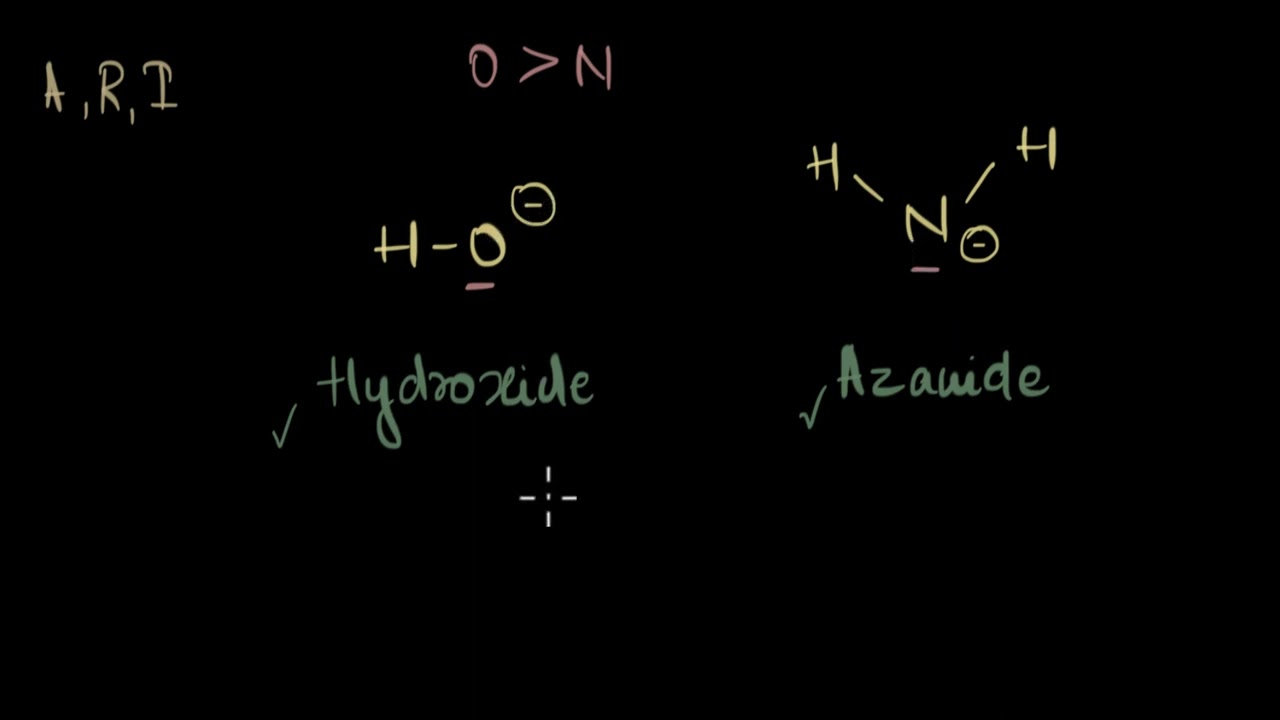

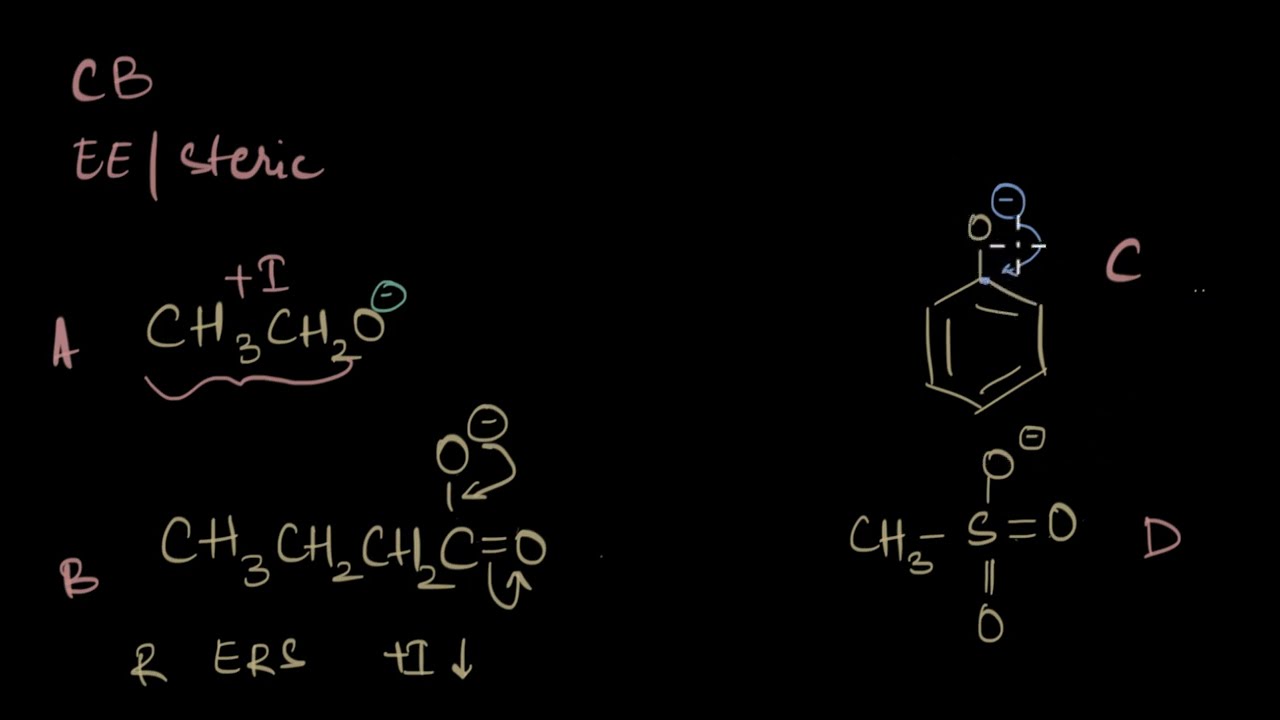
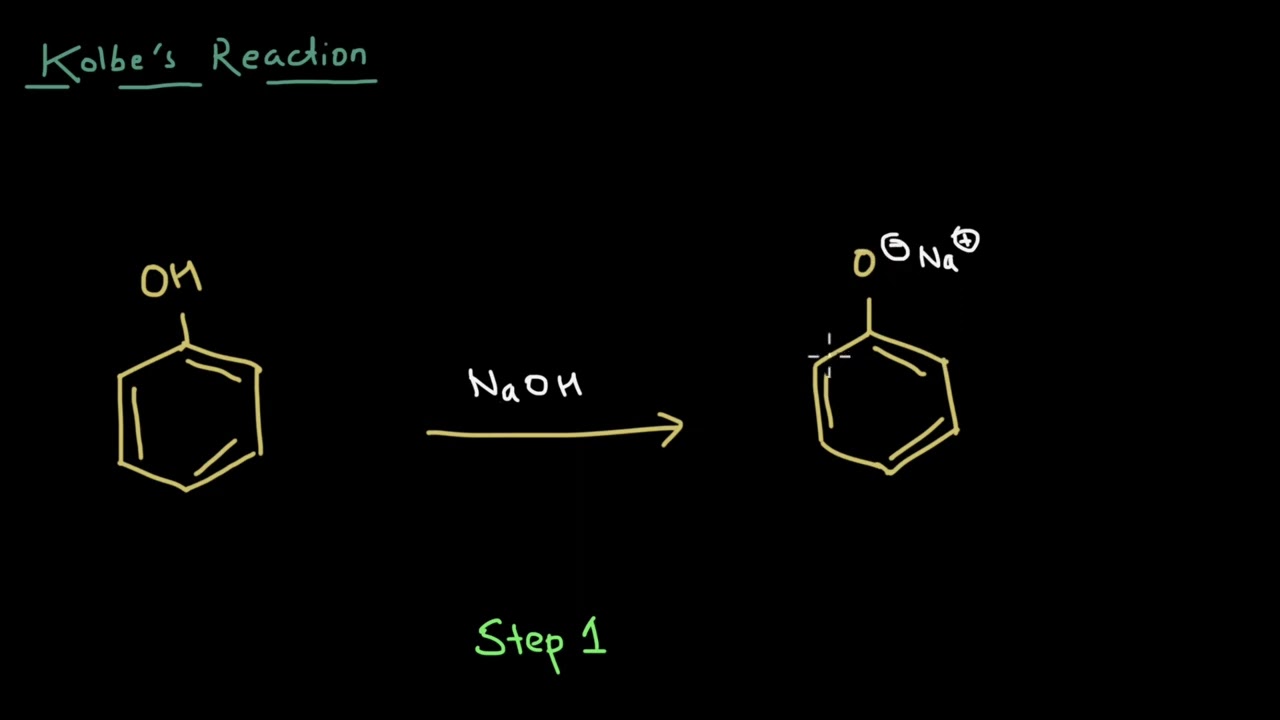

























































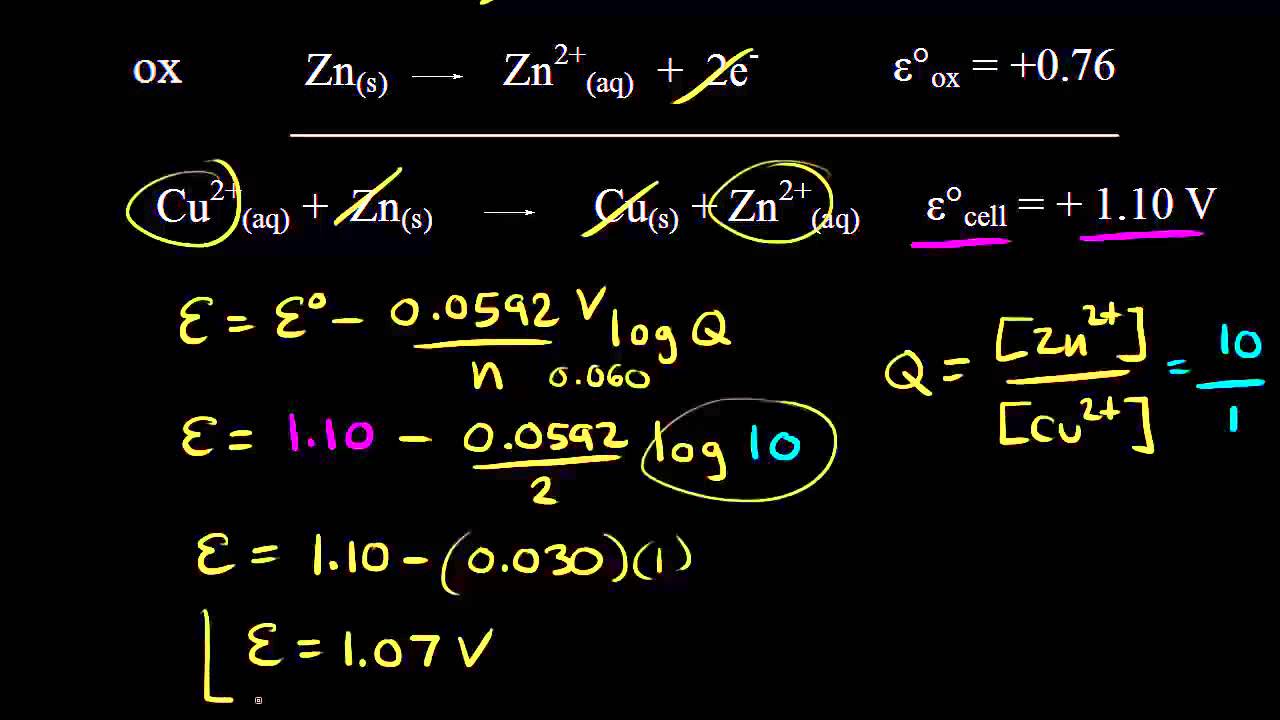
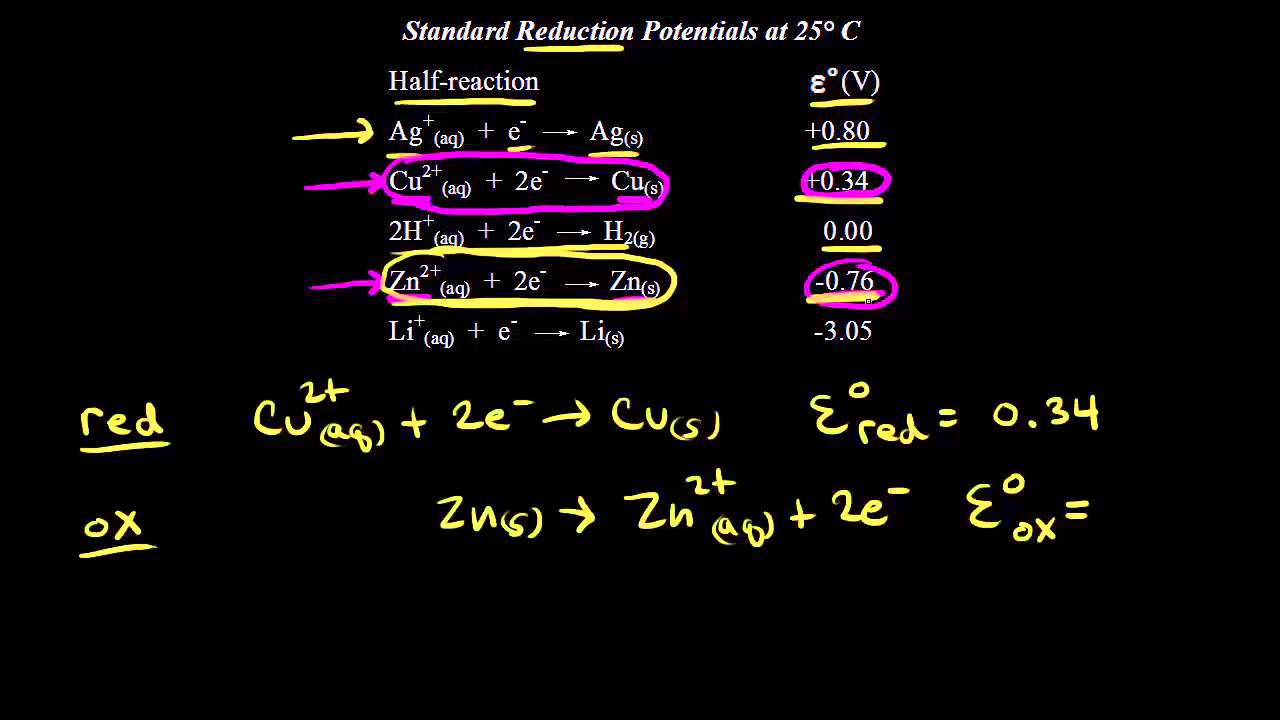













![The Periodic Table of the Elements in Chemistry - [1-2-12]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CTwua04Ykso/maxresdefault.jpg)