Understanding Quadratic Equations:
Сообщение 2024-08-30 06:49:57
0
10Кб
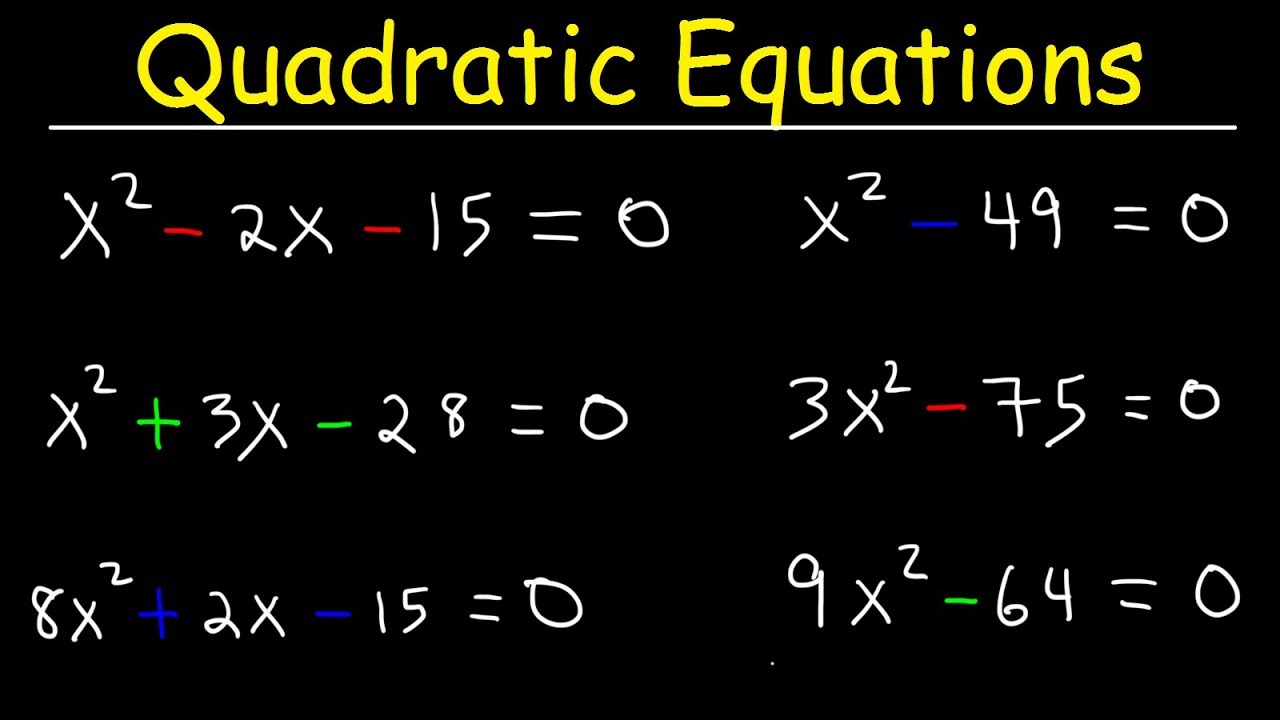
- A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree 2. It can be expressed in the general form:
where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0.
ax² + bx + c = 0
Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations:
-
Factoring:
- Factor the quadratic expression into two linear factors.
- Set each factor equal to zero and solve for x.
- Example:
x² - 5x + 6 = 0 (x - 2)(x - 3) = 0 x = 2 or x = 3
-
Completing the Square:
- Convert the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial.
- Take the square root of both sides and solve for x.
- Example:
x² - 6x + 2 = 0 x² - 6x + 9 = 7 (x - 3)² = 7 x - 3 = ±√7 x = 3 ± √7
-
Quadratic Formula:
- Apply the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / (2a) - Substitute the values of a, b, and c from the quadratic equation.
- Simplify and solve for x.
- Apply the quadratic formula:
Example:
Solve the equation: 2x² - 3x - 5 = 0
Method 1: Factoring
- We cannot factor this equation into two linear factors.
Method 2: Completing the Square
- Divide the equation by 2 to simplify:
x² - (3/2)x - (5/2) = 0 - Add (3/4)² to both sides to complete the square:
x² - (3/2)x + (9/16) = (9/16) + (5/2) (x - 3/4)² = 49/16 x - 3/4 = ±7/4 x = 3/4 ± 7/4 x = 5/2 or x = -1
Method 3: Quadratic Formula
- Substitute a = 2, b = -3, and c = -5 into the formula:
x = (-(-3) ± √((-3)² - 4(2)(-5))) / (2(2)) x = (3 ± √49) / 4 x = (3 ± 7) / 4 x = 5/2 or x = -1
Choosing the Best Method:
- Factoring is often the quickest method if it's possible.
- Completing the square is useful when the quadratic equation is not easily factored.
- The quadratic formula is always applicable, even if factoring or completing the square is difficult.
I hope this explanation helps! Feel free to ask if you have any more questions.


Поиск
Категории
- Technology
- Образование
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Больше
Using the <span> Tag for Styling
The <span> tag is a generic HTML element that is often used to group inline elements...
S.4 CHEMISTRY WAKATA PRE MOCK QUESTIONS 2
https://acrobat.adobe.com/id/urn:aaid:sc:EU:85bd6cfc-45b5-4737-b430-d0e1fce698e9
Know Your Worth, Control Your Emotions, and Never Settle
In a world that often pushes us to conform, understanding your value, mastering your emotions,...
Branching Basics and Multi-Branch Statements in Python
Branching is a fundamental concept in programming that allows your code to make decisions and...
ASSHU ANKOLE MOCK S.6 PHYSICS PAPER 1 GUIDE 2024
ASSHU ANKOLE MOCK S.6 PHYSICS PAPER 1 GUIDE 2024



