HTML Table Borders: A Closer Look
Δημοσιευμένα 2024-09-06 01:25:50
0
11χλμ.
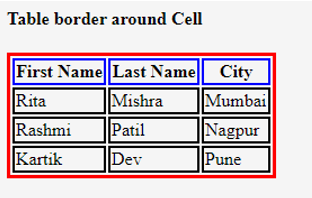
HTML table borders are used to outline the individual cells and rows within a table, making it visually distinct and easier to read. The border attribute is used to specify the width of the border.
Basic Usage
HTML
<table border="1">
</table>
In the example above, the border="1" attribute creates a border with a width of 1 pixel around each cell and row.
Adjusting Border Width
You can customize the border width by changing the value of the border attribute. For instance:
border="2": Creates a border with a width of 2 pixels.border="0": Removes the border completely.
Example with Different Border Widths
HTML
<table>
<tr>
<th>Product</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Product A</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Product B</td>
<td>$200</td>
</tr>
</table>
<table border="2">
<tr>
<th>Product</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Product A</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Product B</td>
<td>$200</td>
</tr>
</table>
Border Styles
While the border attribute primarily controls the width, you can also style the border using CSS properties like:
border-style: Specifies the style of the border (e.g.,solid,dashed,dotted).border-color: Sets the color of the border.border-width: Allows you to set different widths for the top, right, bottom, and left borders.
Example with CSS Styling
HTML
<table border="1" style="border-style: dashed; border-color: blue;">
</table>
Additional Considerations
cellspacing: Controls the space between cells.cellpadding: Sets the space between the cell content and the cell border.border-collapse: Determines whether borders should collapse or separate.
By understanding these concepts and using the provided code examples, you can effectively customize the borders of your HTML tables to enhance their appearance and readability.

Αναζήτηση
Κατηγορίες
- Technology
- Εκπαίδευση
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Παιχνίδια
- Gardening
- Health
- Κεντρική Σελίδα
- Literature
- Networking
- άλλο
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Διαβάζω περισσότερα
Versions of the Linux Operating System
Linux is a versatile and open-source operating system kernel that serves as the foundation for a...
Quotations (<blockquote>, <q>)
Quotes are used to display text that is a direct quote from another source. In HTML, there are...
Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals, households, businesses, and geographic...
The Ten Commandments of Computer Ethics
The Ten Commandments of Computer Ethics were created by the Computer Ethics Institute to guide...



