Understanding the Excel Interface
Posted 2024-07-26 04:31:22
0
10K
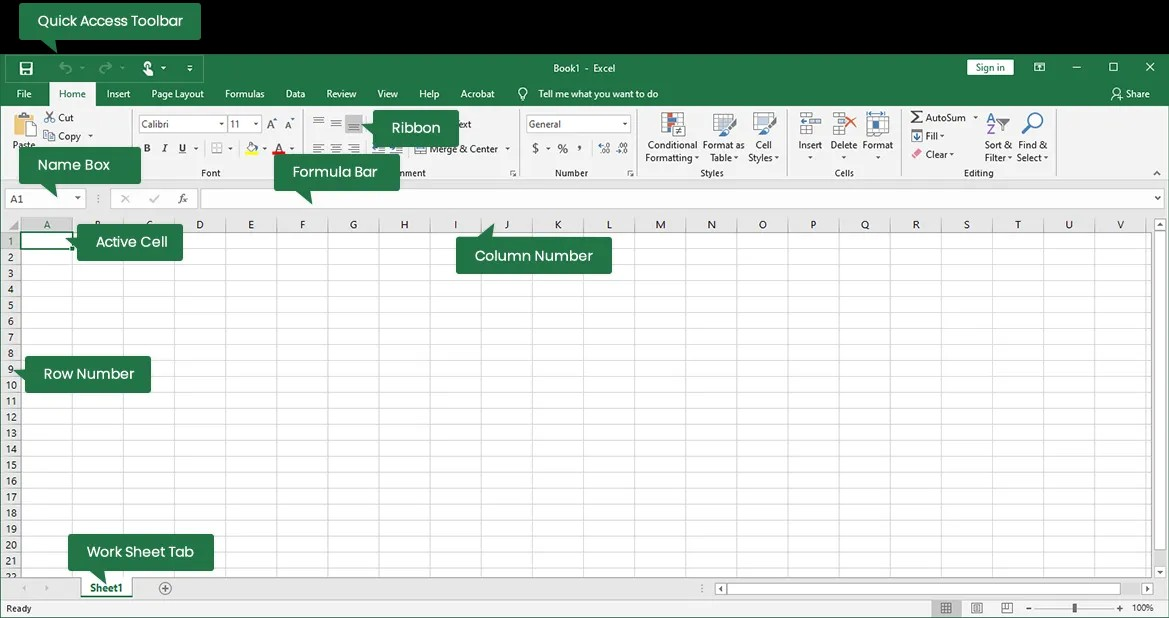
Excel's interface is designed to be user-friendly, but it can seem overwhelming at first. Let's break it down into its core components:
Basic Components
- Workbook: The main file containing one or more worksheets.
- Worksheet: A sheet within a workbook where you input and analyze data.
- Cell: The intersection of a row and column where data is entered.
- Row: A horizontal line of cells identified by numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Column: A vertical line of cells identified by letters (A, B, C, etc.).
Interface Elements
- Title Bar: Displays the workbook name and Excel application name.
- Quick Access Toolbar: Customizable toolbar for frequently used commands.
- Ribbon: Contains tabs (Home, Insert, Page Layout, etc.) with groups of commands.
- Name Box: Shows the address of the active cell.
- Formula Bar: Displays the contents of the active cell (data or formula).
- Worksheet Tabs: Allow you to switch between different worksheets.
- Scroll Bars: Used to navigate through the worksheet.
- Status Bar: Shows information about the worksheet, such as number of selected cells.
Key Areas of the Ribbon
- Home: Basic formatting, editing, and cell alignment.
- Insert: Add tables, charts, pictures, shapes, and more.
- Page Layout: Control page margins, orientation, themes, and scaling.
- Formulas: Insert functions, names, and perform calculations.
- Data: Sort, filter, analyze data, and create data connections.
- Review: Proofing, comments, protection, and changes tracking.
- View: Customize worksheet appearance, zoom, and display options.
Navigating and Using Excel
- Selecting Cells: Click on a cell to make it active. Drag to select a range of cells.
- Entering Data: Type data directly into the active cell or formula bar.
- Using Formulas: Start with an equal sign (=), then enter functions or cell references.
- Formatting: Apply fonts, colors, number formats, and cell styles.
- Creating Charts: Visualize data with various chart types.
- Sorting and Filtering: Organize data based on specific criteria.
Would you like to delve deeper into a specific area of the Excel interface or learn how to perform a particular task?
I can provide more detailed explanations, examples, and step-by-step instructions.
Here are some possible topics:
- Basic data entry and formatting
- Creating and using formulas
- Creating charts
- Data analysis tools
- Excel shortcuts
Search
Categories
- Technology
- Education
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Read More
MARKING GUIDE FOR UMTA UCE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 2024
MARKING GUIDE FOR UMTA UCE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 2024
Find scholarships and study in the United States
There are countless scholarships available in the United States, offered by various institutions,...
Intro to Classes and Objects python Show drafts
Classes: The Blueprints
Imagine you're building a house. You wouldn't just start hammering and...
CBTI UCE BIOLOGY MOCK EXAM PAPER 1
CBTI UCE BIOLOGY MOCK EXAM PAPER 1



