Understanding the IF Function
Posted 2024-09-03 03:12:25
0
8K
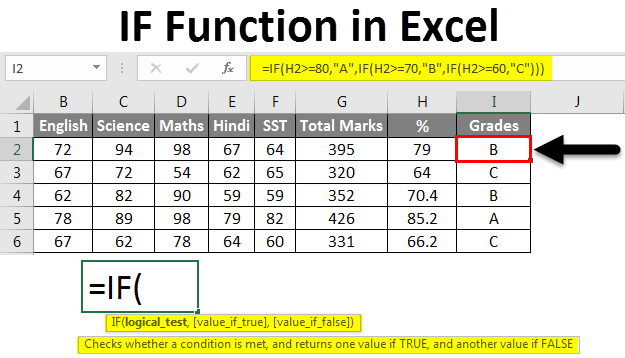
step-by-step guide on using the IF function in Excel, incorporating best practices and addressing potential issues:
Step 1: Understanding the IF Function
- The IF function is a logical function that evaluates a condition and returns one value if the condition is true, and another value if the condition is false.
- Its syntax is:
=IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
Step 2: Defining the Logical Test
- The logical test is the condition you want to evaluate. It can be a simple comparison (e.g., A1 > B1) or a more complex formula.
- Use comparison operators like:
=(equal to)>(greater than)<(less than)>=(greater than or equal to)<=(less than or equal to)<>(not equal to)
Step 3: Specifying Values
value_if_true: The value Excel will return if the logical test is true.value_if_false: The value Excel will return if the logical test is false.- These values can be:
- Numbers
- Text
- Other formulas or functions
- Empty cells ("" or
NULL)
Step 4: Entering the IF Function
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Type
=to start a formula. - Type
IFfollowed by an opening parenthesis. - Enter the logical test within quotation marks if it's text, or directly if it's a cell reference or formula.
- Type a comma to separate the logical test from the value_if_true.
- Enter the value_if_true (if the logical test is true).
- Type a comma to separate the value_if_true from the value_if_false.
- Enter the value_if_false (if the logical test is false).
- Close the parenthesis and press Enter.
Example:
If you want to determine whether a student's grade is "Pass" or "Fail" based on a minimum passing score of 70, you could use the following formula:
Excel
=IF(A2>=70, "Pass", "Fail")
In this example, A2 is the cell containing the student's grade. If the grade is greater than or equal to 70, the formula returns "Pass"; otherwise, it returns "Fail."
Additional Tips:
- Nested IF functions: You can nest multiple IF functions within each other to evaluate more complex conditions.
- Use absolute references (e.g.,
$A$2) if you need to keep the cell reference constant when copying the formula. - Consider using AND and OR functions to combine multiple logical tests within a single IF function.
- Test your formula with different input values to ensure it's working as expected.

Site içinde arama yapın
Kategoriler
- Technology
- EĞİTİM BİLGİLERİ
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Read More
Choosing Kindness in the Face of Anger: A Path to Transformation
Imagine standing at the crossroads of an emotional storm. Someone’s words or actions have...
Variables, Assignments, and Identifiers
Variables
Variables are used to store data that can be used and manipulated throughout...
Global attributes (id, class, style, title)
Global attributes are attributes that can be applied to any HTML element. They provide additional...
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
These are information systems that manage and process data from business transactions. A...



