Understanding the IF Function
Veröffentlicht 2024-09-03 03:12:25
0
8KB
step-by-step guide on using the IF function in Excel, incorporating best practices and addressing potential issues:
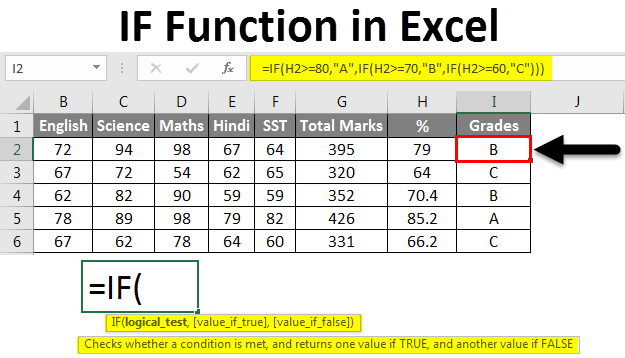
Step 1: Understanding the IF Function
- The IF function is a logical function that evaluates a condition and returns one value if the condition is true, and another value if the condition is false.
- Its syntax is:
=IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
Step 2: Defining the Logical Test
- The logical test is the condition you want to evaluate. It can be a simple comparison (e.g., A1 > B1) or a more complex formula.
- Use comparison operators like:
=(equal to)>(greater than)<(less than)>=(greater than or equal to)<=(less than or equal to)<>(not equal to)
Step 3: Specifying Values
value_if_true: The value Excel will return if the logical test is true.value_if_false: The value Excel will return if the logical test is false.- These values can be:
- Numbers
- Text
- Other formulas or functions
- Empty cells ("" or
NULL)
Step 4: Entering the IF Function
- Select the cell where you want to display the result.
- Type
=to start a formula. - Type
IFfollowed by an opening parenthesis. - Enter the logical test within quotation marks if it's text, or directly if it's a cell reference or formula.
- Type a comma to separate the logical test from the value_if_true.
- Enter the value_if_true (if the logical test is true).
- Type a comma to separate the value_if_true from the value_if_false.
- Enter the value_if_false (if the logical test is false).
- Close the parenthesis and press Enter.
Example:
If you want to determine whether a student's grade is "Pass" or "Fail" based on a minimum passing score of 70, you could use the following formula:
Excel
=IF(A2>=70, "Pass", "Fail")
In this example, A2 is the cell containing the student's grade. If the grade is greater than or equal to 70, the formula returns "Pass"; otherwise, it returns "Fail."
Additional Tips:
- Nested IF functions: You can nest multiple IF functions within each other to evaluate more complex conditions.
- Use absolute references (e.g.,
$A$2) if you need to keep the cell reference constant when copying the formula. - Consider using AND and OR functions to combine multiple logical tests within a single IF function.
- Test your formula with different input values to ensure it's working as expected.

Suche
Kategorien
- Technology
- Ausbildung
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Mehr lesen
Range and Nested Loops
Range Function (range())
The range() function is a built-in function in Python used to generate...
Creating your first HTML file
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Choose a Text Editor:
Basic Text Editors: Notepad (Windows), TextEdit...
Executive Information Systems (EIS)
Executive Information Systems (EIS) are specialized information systems designed to support the...
Understanding the Excel Interface
Excel's interface is designed to be user-friendly, but it can seem overwhelming at first. Let's...
Increasing Pressure on IT Experts
Information technology (IT) experts face increasing pressure due to several factors that have...



