Understanding the SUMPRODUCT Function
Posted 2024-09-03 03:25:02
0
10K
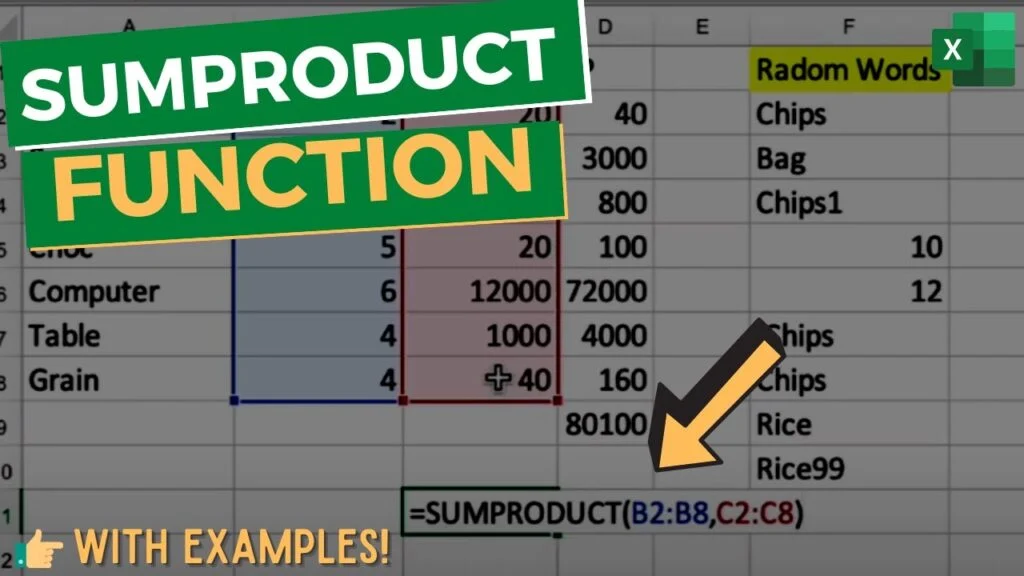
The SUMPRODUCT function in Excel is a powerful tool used to perform array-based calculations without explicitly creating an array formula. It multiplies corresponding elements in two or more arrays and then sums the products.
Basic Syntax:
Excel
=SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
- array1 (required): The first array of numbers or cells.
- array2 (optional): Additional arrays of numbers or cells.
Examples:
-
Multiplying Corresponding Elements and Summing:
- To multiply corresponding elements in columns A and B and sum the products:
Excel
=SUMPRODUCT(A1:A10, B1:B10)
- To multiply corresponding elements in columns A and B and sum the products:
-
Using Criteria:
- To sum the product of values in column B where the corresponding values in column A are greater than 50:
Excel
=SUMPRODUCT((A1:A10>50)*B1:B10)
- To sum the product of values in column B where the corresponding values in column A are greater than 50:
-
Multiple Criteria:
- To sum the product of values in column C where the corresponding values in column A are greater than 50 and column B is less than 100:
Excel
=SUMPRODUCT((A1:A10>50)*(B1:B10<100)*C1:C10)
- To sum the product of values in column C where the corresponding values in column A are greater than 50 and column B is less than 100:
Additional Considerations:
- Array Size: The arrays must be the same size.
- Text Values: If a cell contains text, it will be treated as 0.
- Error Values: If a cell contains an error, the SUMPRODUCT function will return an error.
- Nested Functions: You can use SUMPRODUCT within other functions.
Advanced Usage:
- Conditional Summing: Use SUMPRODUCT to perform conditional summations.
- Weighted Averages: Calculate weighted averages using SUMPRODUCT.
- Frequency Tables: Create frequency tables using SUMPRODUCT.
Example: Weighted Average
To calculate a weighted average of values in column B based on weights in column C:
Excel
=SUMPRODUCT(B1:B10, C1:C10)/SUM(C1:C10)
Key Points to Remember:
- SUMPRODUCT is a versatile function for array-based calculations.
- It can be used for conditional summing, weighted averages, and more.
- Ensure arrays are the same size and handle text and error values appropriately.
- Explore advanced usage for complex data analysis.


Cerca
Categorie
- Technology
- Formazione
- Business
- Music
- Got talent
- Film
- Politics
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Leggi tutto
UACE WAKISSHA FOODS AND NUTRITION 2024
UACE WAKISSHA FOODS AND NUTRITION 2024
Creating your first HTML file
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Choose a Text Editor:
Basic Text Editors: Notepad (Windows), TextEdit...
Understanding the Excel Interface
Excel's interface is designed to be user-friendly, but it can seem overwhelming at first. Let's...
UACE MACIDITA PURE MATHS MOCK EXAM 2024
UACE MACIDITA PURE MATHS MOCK EXAM 2024
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) are legal protections granted to creators and inventors to...



