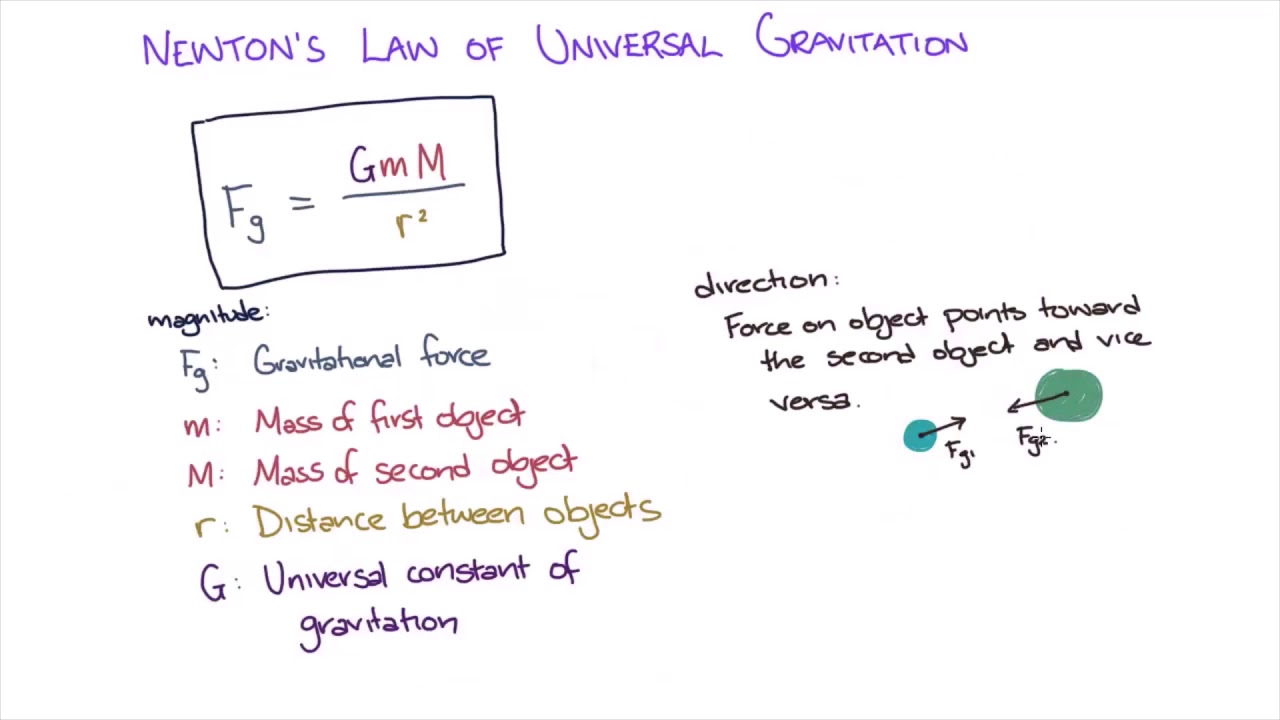
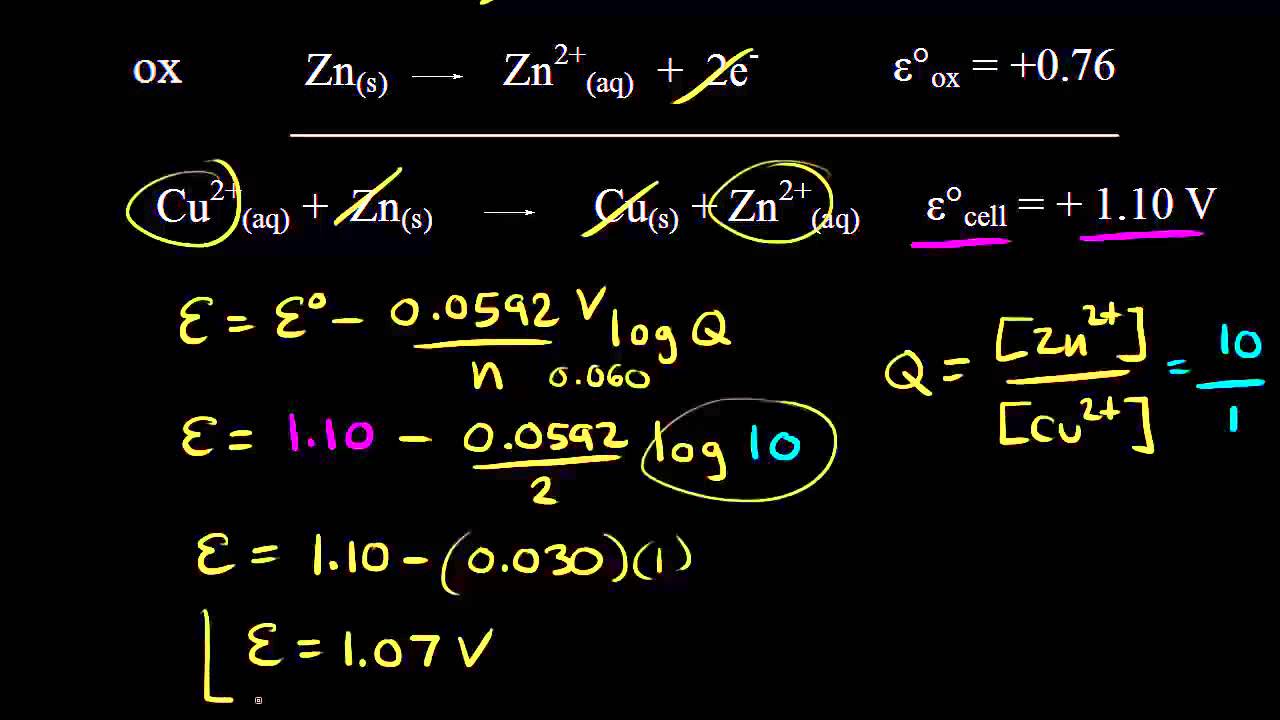Exponential Equation
An exponential equation is an equation in the form of y = ab^x, where a and b are constants and x is the variable.
The variable x is typically the exponent, and the base b is usually a constant greater than 1. The constant a is the initial value or y-intercept of the exponential function.
Exponential equations are used to model relationships where the value of y grows or decays exponentially with respect to x. They are commonly used in finance, population growth, radioactive decay, and other natural phenomena.
The general form of an exponential equation is:
y = ab^x
where:
- y is the dependent variable or output
- x is the independent variable or input
- a is the initial value or y-intercept
- b is the base or growth/decay factor
Examples of exponential equations:
1. Population Growth:
y = 1000 * 1.03^x
where the initial population is 1000 and it grows at a rate of 3% per year.
2. Radioactive Decay:
y = 500 * 0.9^x
where an initial amount of 500 radioactive particles decays at a rate of 10% per hour.
3. Compound Interest:
y = 1000 * (1 + 0.05)^x
where an initial investment of $1000 grows at an annual interest rate of 5%.












![Exponential growth and decay models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_PDGqdVjyig/maxresdefault.jpg)