MATHEMATICS :BASIC TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. It is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving right triangles.
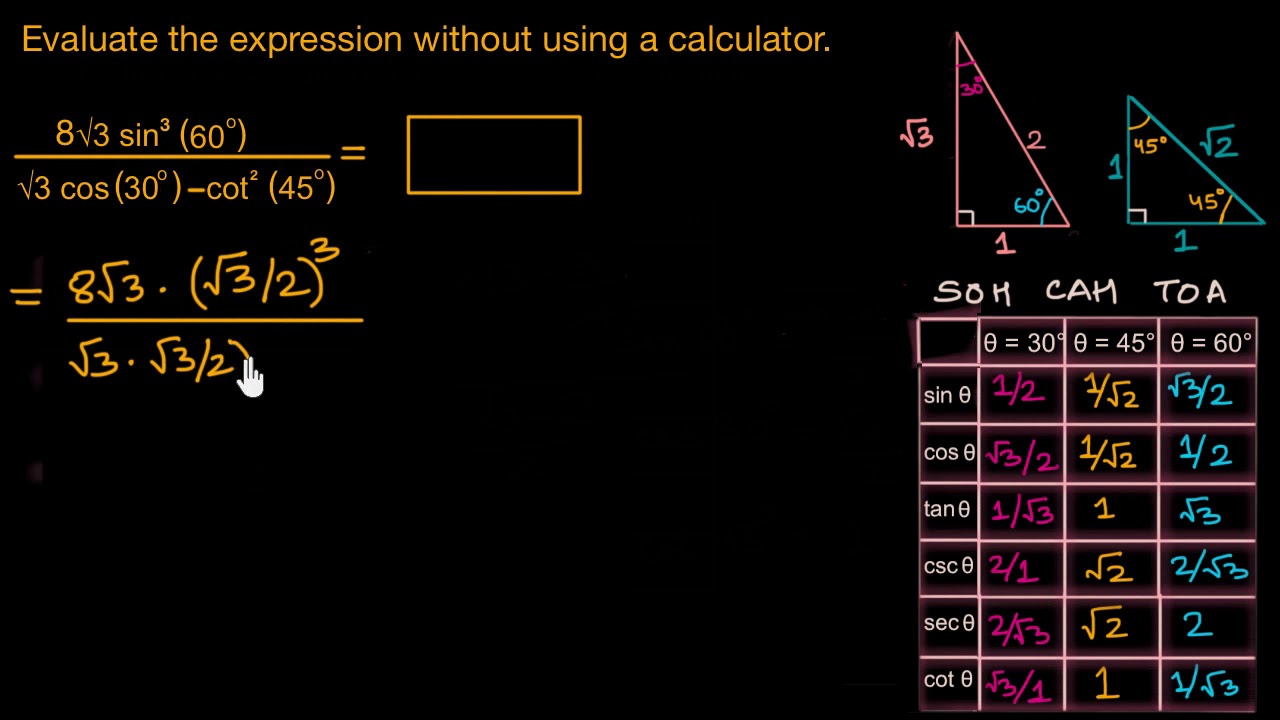
The three basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, and tangent. The sine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The tangent of an angle is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle to the cosine of the angle.
In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle, the base is the side adjacent to the angle, and the height is the side opposite to the angle. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Trigonometric functions can be used to solve various problems involving angles and sides of triangles. For example, if you know one side and one angle of a right triangle, you can use trigonometric functions to find the lengths of the other sides. Similarly, if you know the lengths of two sides, you can use trigonometric functions to find the angles of the triangle.
Trigonometry also involves concepts such as radian measure, which is an alternative way of measuring angles, and the unit circle, which is a circle with a radius of one unit used to define the values of trigonometric functions for all angles.
Overall, basic trigonometry provides tools to analyze and solve problems involving triangles, angles, and sides. It is an important branch of mathematics that has applications in various fields.