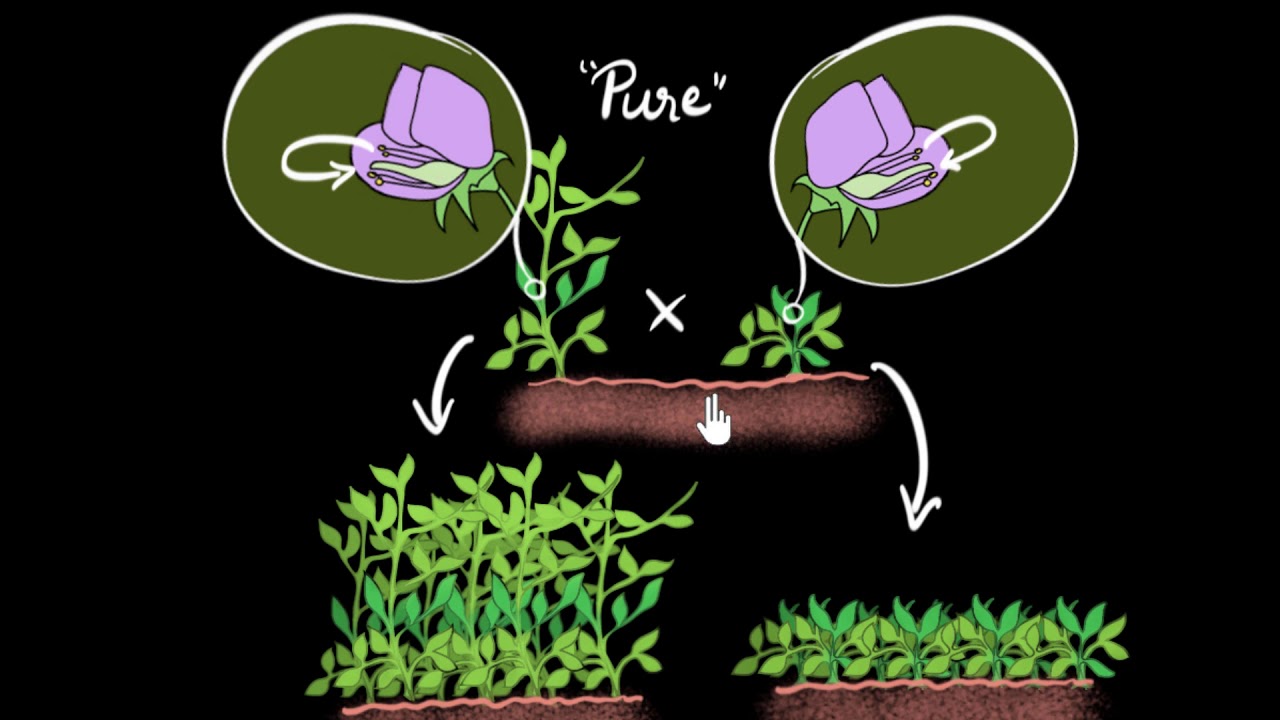
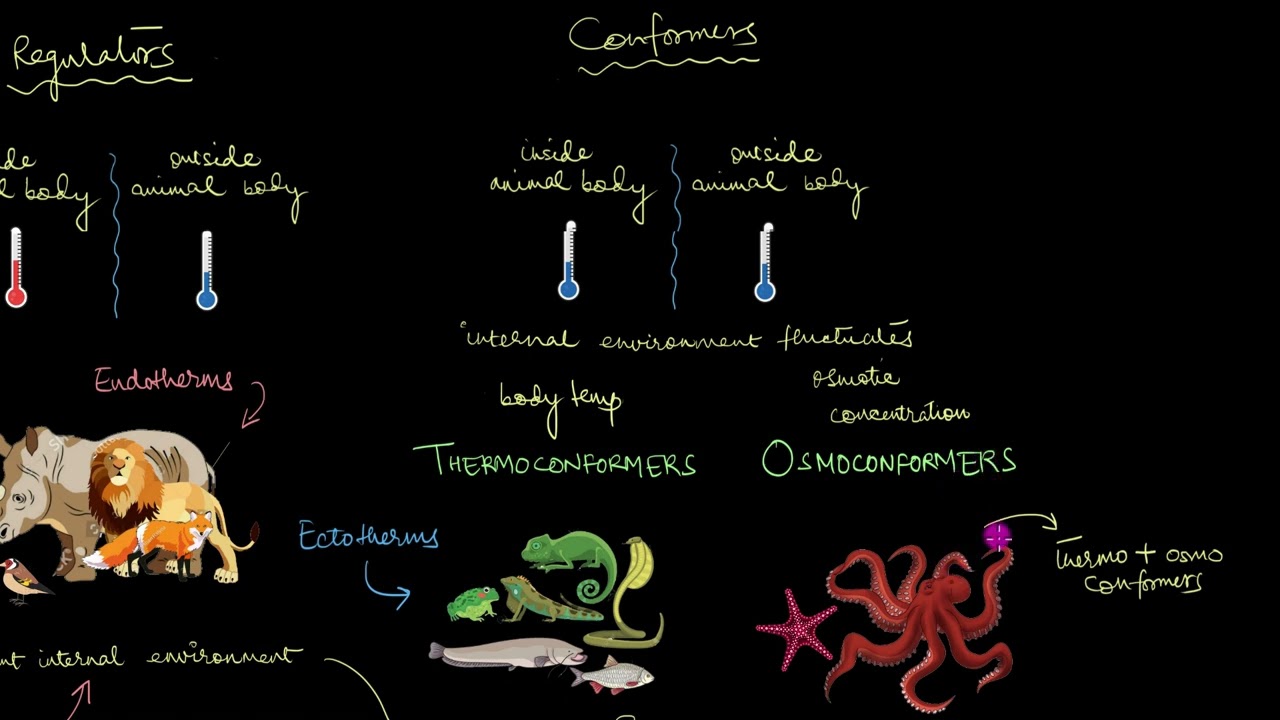
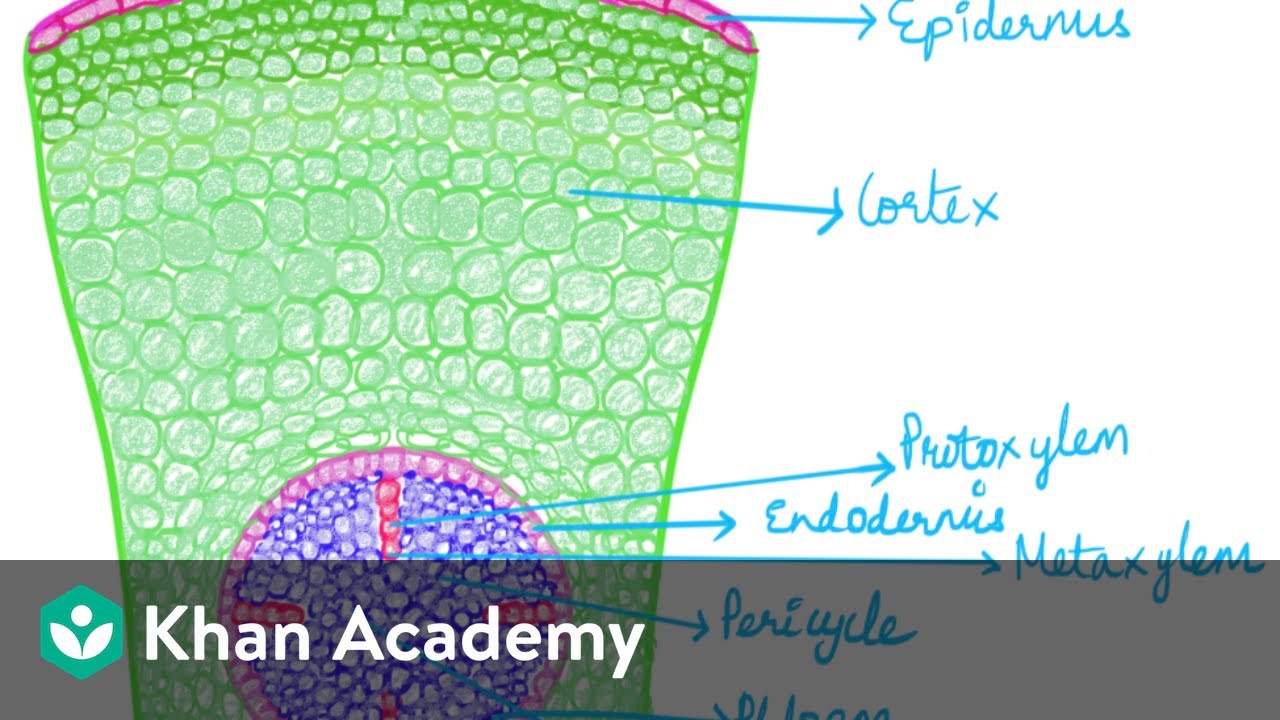
S.6 BIOLOGY LESSON:PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a simple sugar) and oxygen. It is a crucial biological process that occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
During photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by pigments in the chloroplasts, primarily chlorophyll. This energy is used to power a series of chemical reactions that take place in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle).
In the light-dependent reactions, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy carriers are used in the next stage of photosynthesis.
In the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH are utilized to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. This process involves a series of chemical reactions that use enzymes to catalyze the formation of glucose. The glucose produced can be used by the plant as an energy source or stored as starch for later use.
Photosynthesis not only provides energy-rich glucose for the plant but also produces oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is released into the atmosphere and is vital for supporting aerobic respiration in many organisms.
Overall, photosynthesis is an essential process that allows plants, algae, and certain bacteria to convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It plays a crucial role in sustaining plant life and maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Additionally, photosynthesis acts as the primary source of energy for most ecosystems on our planet.