Colligative properties: Elevation of boiling point | Solutions | Chemistry |
Colligative properties are properties of a solution that depend solely on the concentration of solute particles in the solvent and not on the nature of the solute. One of the colligative properties is the elevation of boiling point.
The elevation of boiling point is the phenomenon where the boiling point of a solvent is raised when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it. This occurs because the presence of solute particles in the solvent disrupts the intermolecular forces between solvent molecules, making it more difficult for the solvent to vaporize and reach its boiling point.
Some key points about the elevation of boiling point are:
1. Explanation: Dissolving a non-volatile solute in a solvent increases the number of solute particles in the solution. These solute particles create additional obstacles for solvent molecules to overcome in order to escape into the vapor phase during boiling. As a result, more energy is required to reach the boiling point, causing an elevation in the boiling point of the solution compared to the pure solvent.
2. Relationship with Concentration: The extent of the elevation of boiling point is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute particles in the solution. This relationship is described by the equation:
ΔTb = Kb * m
Where ΔTb is the elevation in boiling point, Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant specific to the solvent, and m is the molality of the solute particles in the solution.
3. Colligative Property: The elevation of boiling point is a colligative property because it depends only on the number of solute particles and not on their size or chemical nature. This means that any solute that does not vaporize at the boiling point of the solvent will affect the boiling point similarly, regardless of its identity.
4. Applications: The elevation of boiling point has practical applications. For example, it is utilized in antifreeze solutions, where the addition of solutes (such as ethylene glycol) raises the boiling point of water in vehicle cooling systems. It also plays a role in adjusting cooking times and temperatures at higher altitudes, where the lower atmospheric pressure results in a lower boiling point of water.
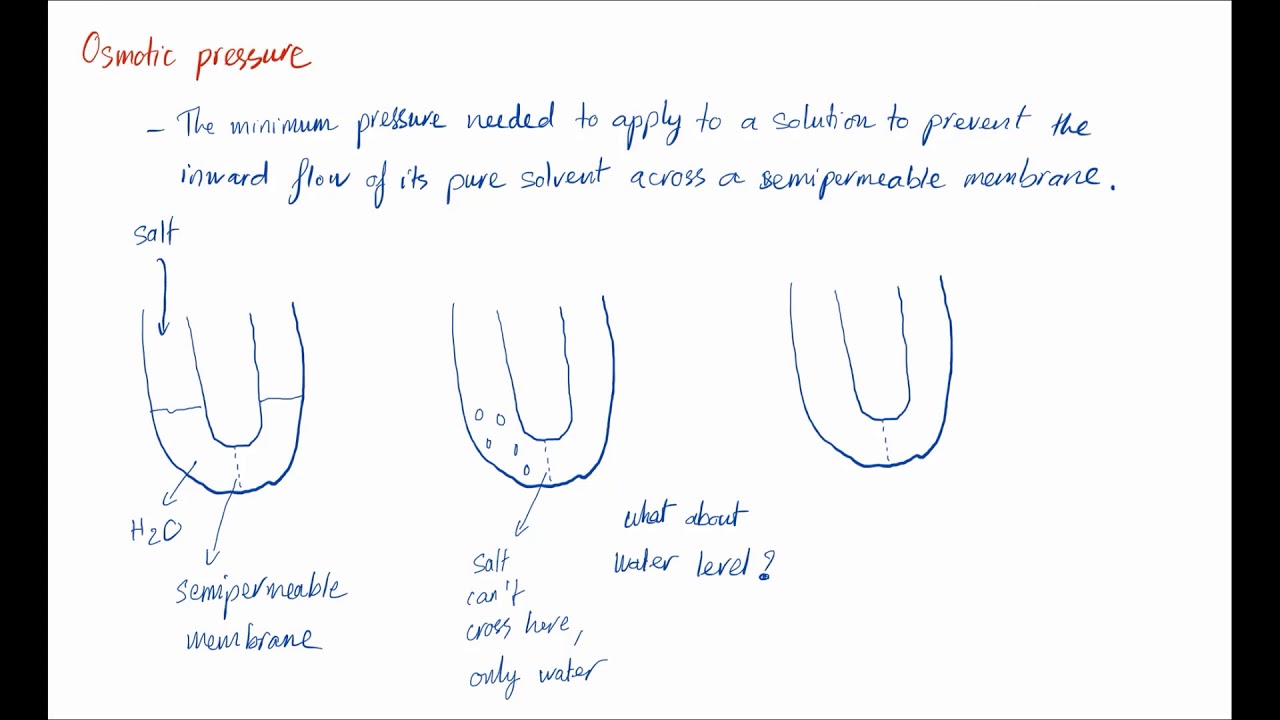
It is important to note that the elevation of boiling point is just one of the colligative properties exhibited by solutions, along with other properties like vapor pressure lowering, depression of freezing point, and osmotic pressure. These properties are especially important in fields such as chemistry, biology, and pharmaceuticals and contribute to various applications and processes.