Reaction of amines
reactions of amines in A-level organic chemistry
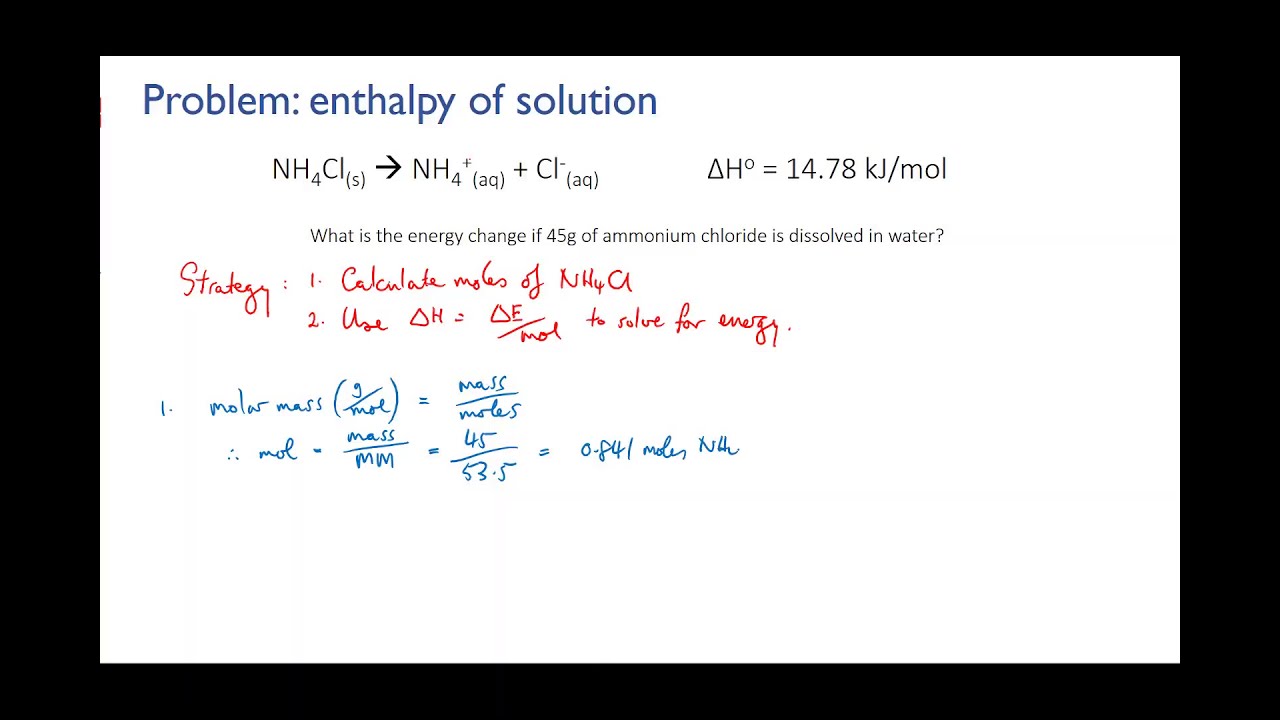
Certainly! Amine chemistry refers to the branch of organic chemistry that focuses on the study of compounds containing amine functional groups (-NH2). Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups.
Amines can be classified into three main types based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom:
1. Primary Amines: These are amines where one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. They have the general formula R-NH2.
2. Secondary Amines: In secondary amines, two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. They are represented by the general formula R2-NH.
3. Tertiary Amines: Tertiary amines have three alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Their general formula is R3-N.
Amine chemistry plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, materials science, and biochemistry. Amines can participate in various reactions, such as substitution, oxidation, reduction, condensation, alkylation, and acylation.
Some notable reactions involving amines include:
1. Amine substitution: Amines can undergo substitution reactions with various electrophiles, wherein the amino group is replaced by another atom or group. This allows for the introduction of different functional groups onto the amine molecule.
2. Amine oxidation: Amines can be oxidized to form amine oxides or further oxidized to form nitro compounds. This reaction is commonly achieved using oxidizing agents such as peroxides or metal oxides.
3. Amine reduction: Amines can be reduced to form secondary or tertiary amines, or even to primary amines from nitro compounds. Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation can be used for these reactions.
4. Amine condensation: Amines can undergo condensation reactions, combining with other compounds to form imines, enamines, or Schiff bases. These reactions are often used in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and pharmaceuticals.
5. Amine alkylation and acylation: Amines can be alkylated or acylated to form N-alkyl or N-acyl amines, respectively. These reactions involve the addition of an alkyl or acyl group to the nitrogen atom of the amine.
Understanding amine chemistry is crucial for designing and synthesizing new molecules with specific properties and functions. It allows chemists to modify amine-containing compounds for various applications, including drug design, organic synthesis, and materials science.