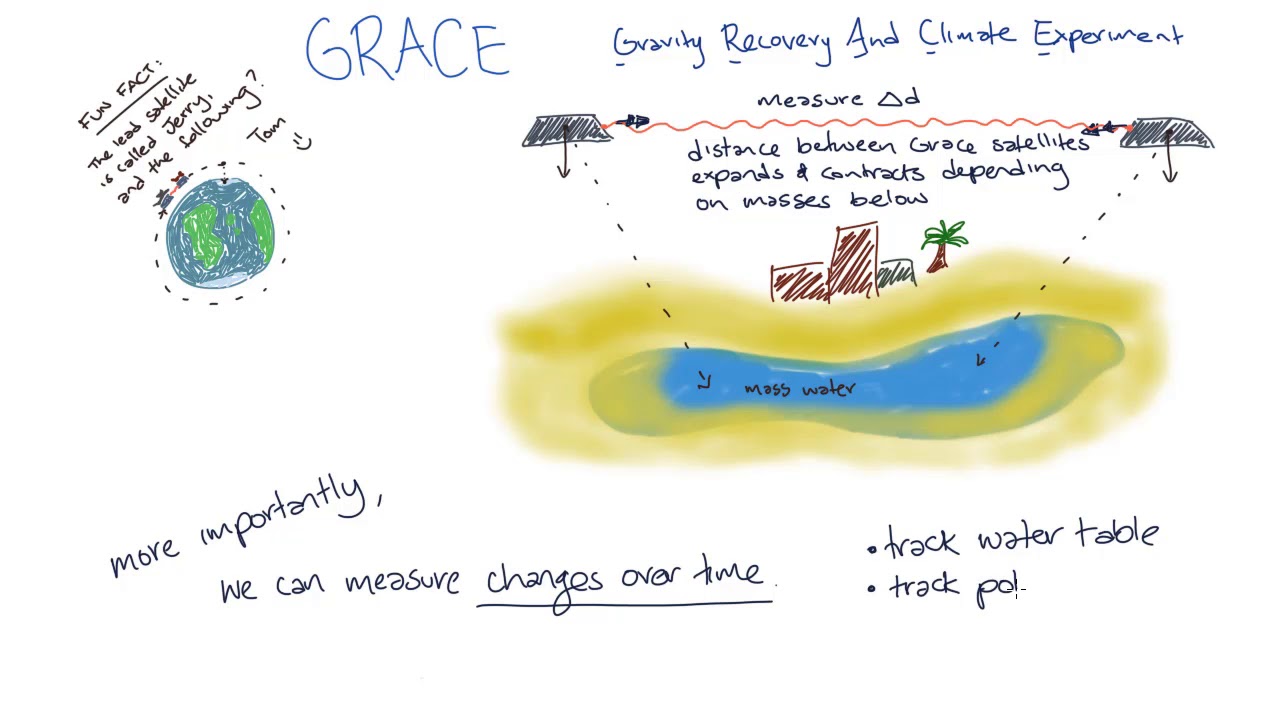
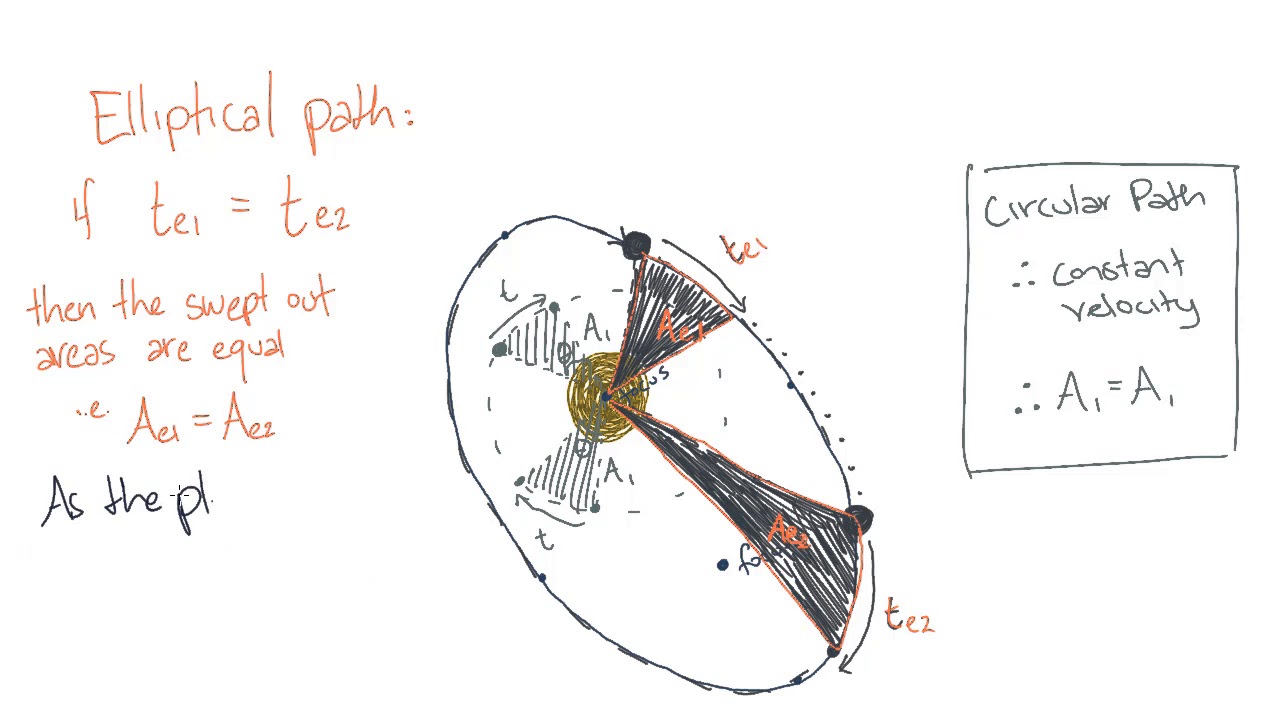
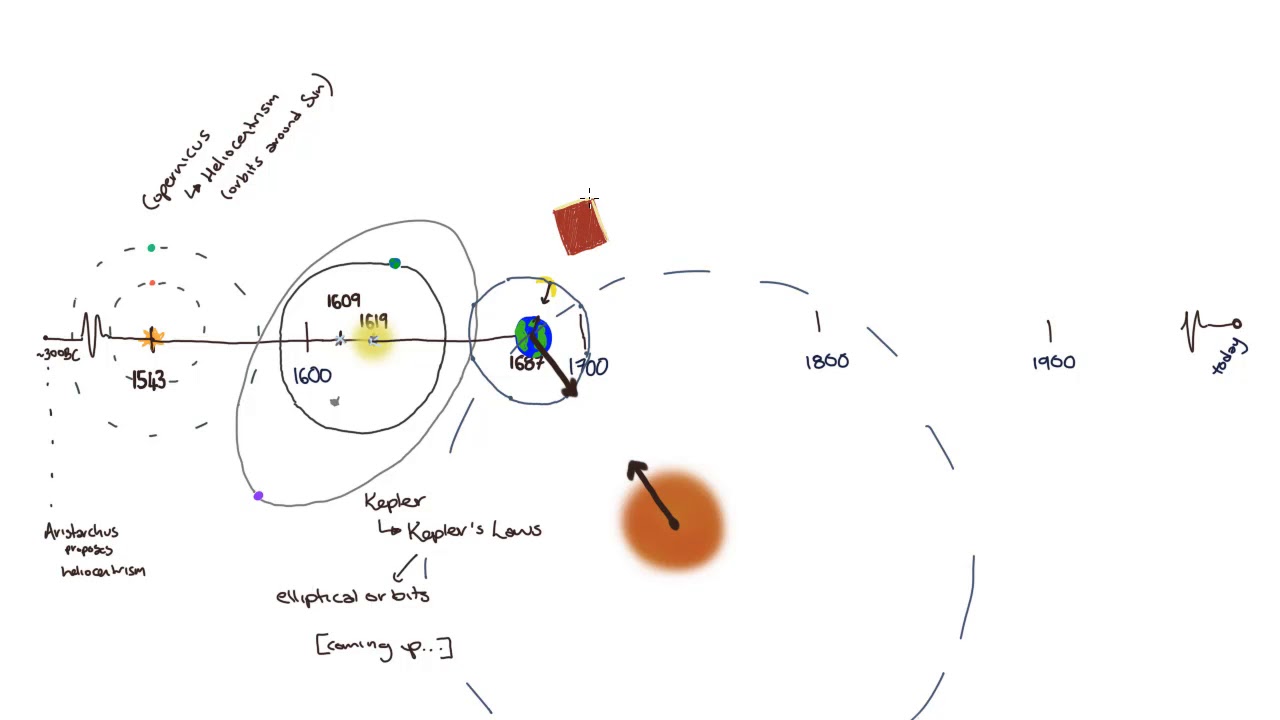
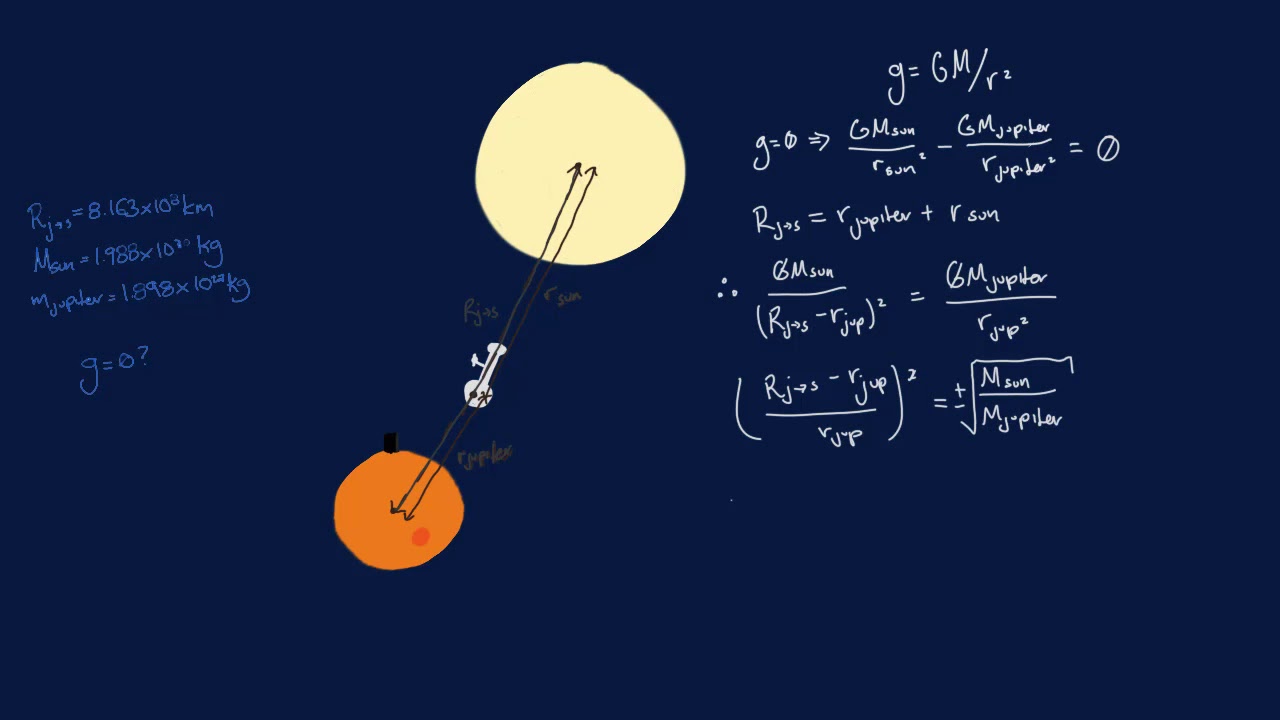S.3 PHYSICS LESSON : EQUATIONS OF LINEAR MOTION
The equations of linear motion are used to understand the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object moving in a straight line. There are four main equations of linear motion, which are:
1. s = ut + 1/2 at^2 - This equation relates the distance traveled s by an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and time t.
2. v = u + at - This equation relates the final velocity v of an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and time t.
3. v^2 = u^2 + 2as - This equation relates the final velocity v of an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and the distance traveled s.
4. s = (u + v) t / 2 - This equation relates the distance traveled s by an object in terms of its initial velocity u, final velocity v, and time t.
Here,
s = distance traveled by the object
u = initial velocity of the object
v = final velocity of the object
a = acceleration of the object
t = time taken for the motion
These four equations can be used to solve a variety of problems related to linear motion. For example, if we know the initial velocity, acceleration, and time taken by an object, we can use the first equation to calculate the distance traveled by the object. Similarly, if we know the initial and final velocities and the acceleration, we can use the third equation to calculate the distance traveled by the object.