Bonding
Describes ionic, covalent, dative bonds, bond polarity and polarization of bonds suitable students taking chemistry at advanced level of education
Ionic bonds:
Ionic bonds are formed between two atoms when one atom donates one or more electrons to another atom. This transfer of electrons leads to the formation of ions - positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. Ionic bonds typically occur between a metal and a non-metal.
Covalent bonds:
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases. Covalent bonds typically occur between non-metals.
Dative bonds (also known as coordinate covalent bonds):
Dative bonds occur when both electrons in a shared pair come from the same atom. In other words, one atom donates both electrons to the bond, while the other atom does not contribute any electrons. Dative bonds can be thought of as a special case of covalent bonds, where one atom supplies both electrons. This type of bonding is commonly found in Lewis acid-base reactions.
Bond polarity:
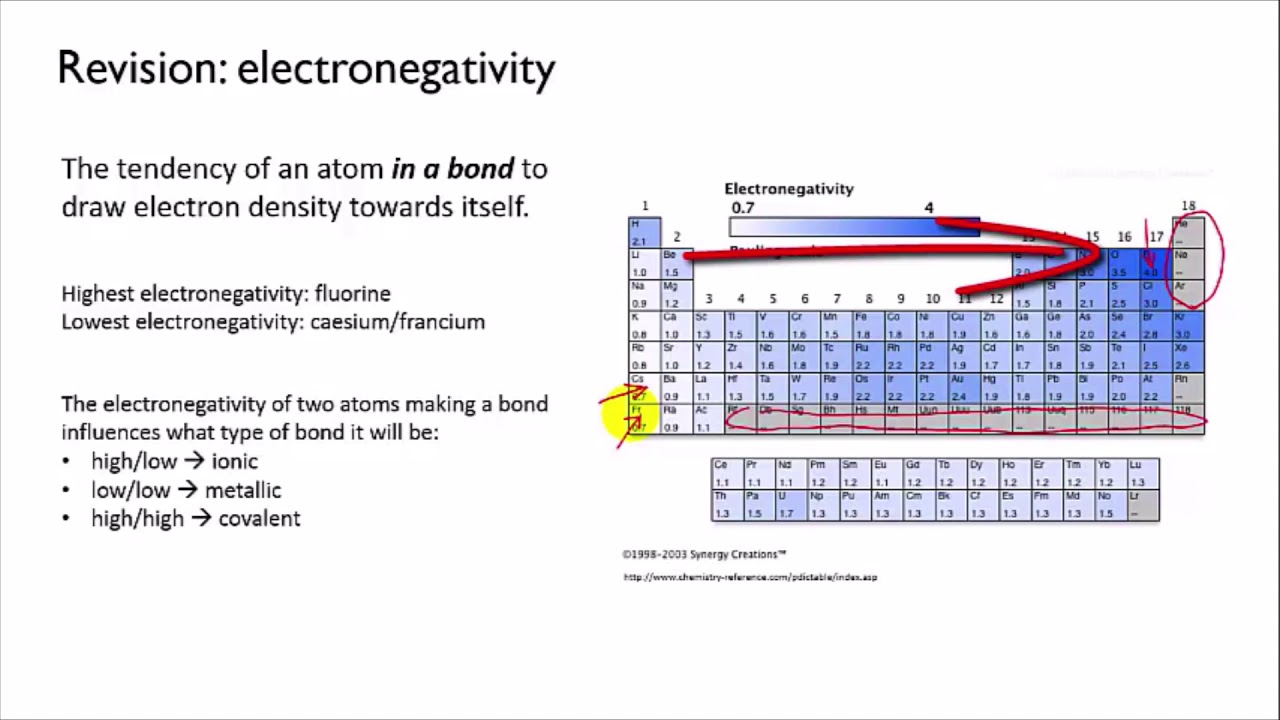
Bond polarity refers to the unequal sharing of electrons between two atoms in a covalent bond. This unequal sharing occurs when one atom has a higher electronegativity (tendency to attract electrons) than the other atom. The difference in electronegativity leads to a separation of charges, creating a polar bond. The atom with higher electronegativity will have a partial negative charge (δ-) while the other atom will have a partial positive charge (δ+).
Polarization of bonds:
Polarization of bonds refers to the distortion of the electron cloud in a chemical bond due to the influence of external or internal forces. This can occur when a more electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud towards itself, causing an uneven distribution of electron density along the bond. Bond polarization can lead to the formation of partial charges or dipoles within a molecule.
Students taking chemistry at an advanced level of education will study these concepts in greater detail and explore their applications in various chemical reactions, organic chemistry, molecular geometry, and spectroscopy.