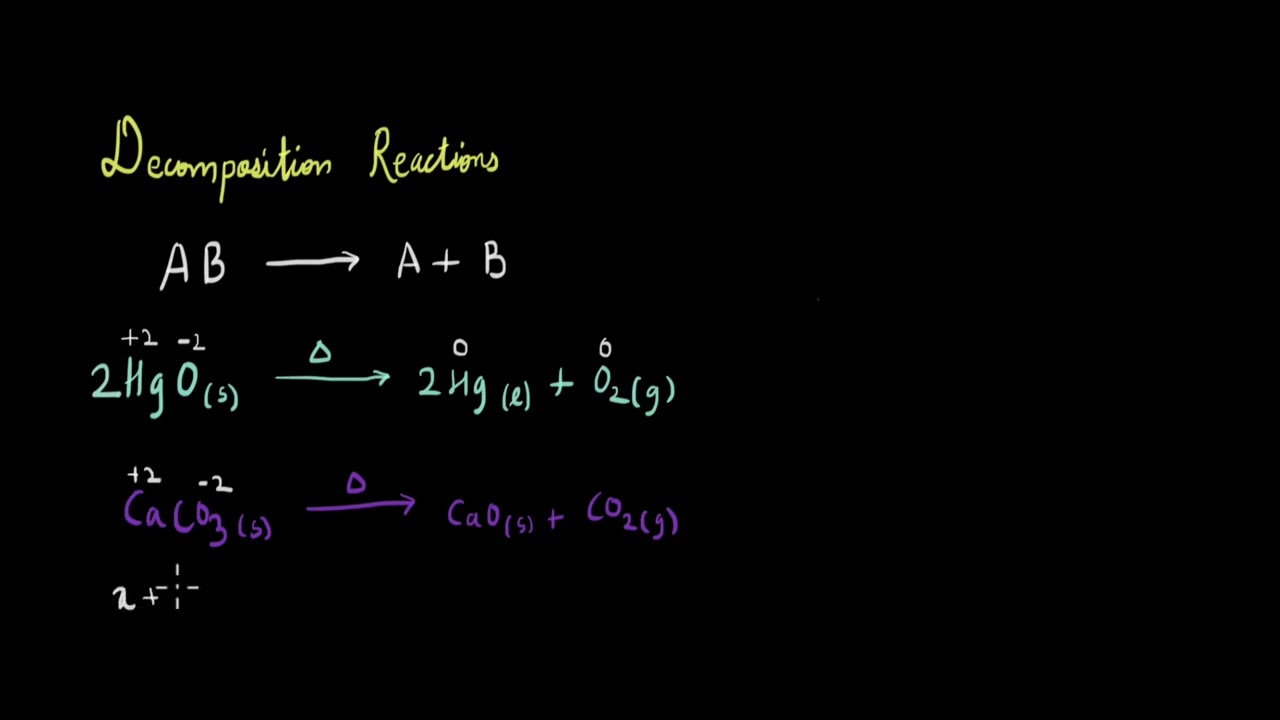
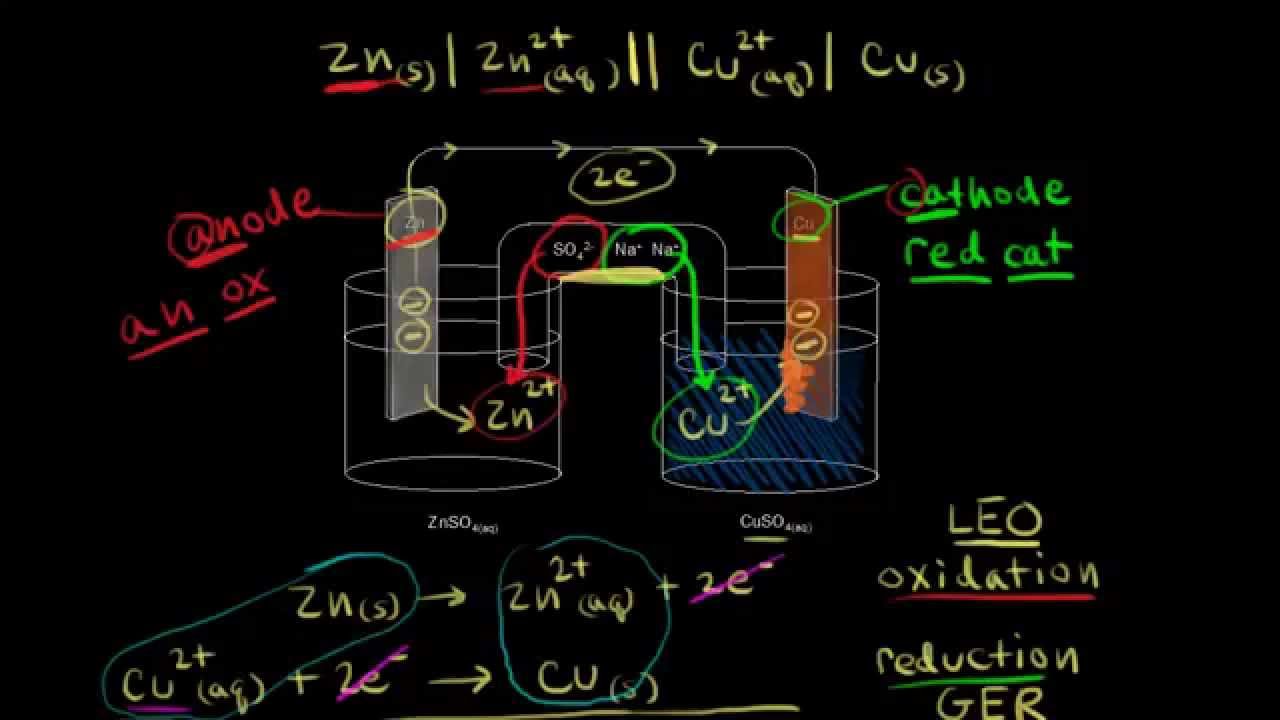
Organic Chemistry Basics
This video introduces one to Organic Chemistry from the basics while also highlighting some of the basic terminologies in Organic Chemistry.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on the study of carbon compounds. Carbon atoms can form stable covalent bonds with other atoms, allowing for the formation of a wide range of complex molecules, including those found in living organisms.
Here are some basic terminologies commonly used in organic chemistry:
1. Carbon (C): Carbon is an element that forms the backbone of organic molecules. It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
2. Hydrocarbon: A hydrocarbon is a molecule consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It is the simplest type of organic compound. There are two main types of hydrocarbons: alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) and alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond).
3. Functional group: A functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms that gives a compound its characteristic chemical properties and reactivity. Examples of functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines.
4. Isomers: Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. There are different types of isomers, such as structural isomers (different connectivity), geometric isomers (cis-trans isomerism), and enantiomers (mirror-image isomers).
5. Alcohols: Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group attached to a carbon atom. They are characterized by the "-ol" suffix in their names. For example, ethanol is a common alcohol.
6. Aldehydes and Ketones: Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O). Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of a carbon chain, whereas ketones have it within the carbon chain.
7. Carboxylic acids: Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are characterized by the "-oic acid" suffix in their names. Examples include acetic acid and formic acid.
8. Amines: Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom attached to carbon atoms or hydrogen atoms. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines based on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
These are just a few basic terminologies in organic chemistry. The subject encompasses many more concepts and reactions, including polymerization, aromatic compounds, stereochemistry, and reactions like substitution, elimination, and addition reactions.