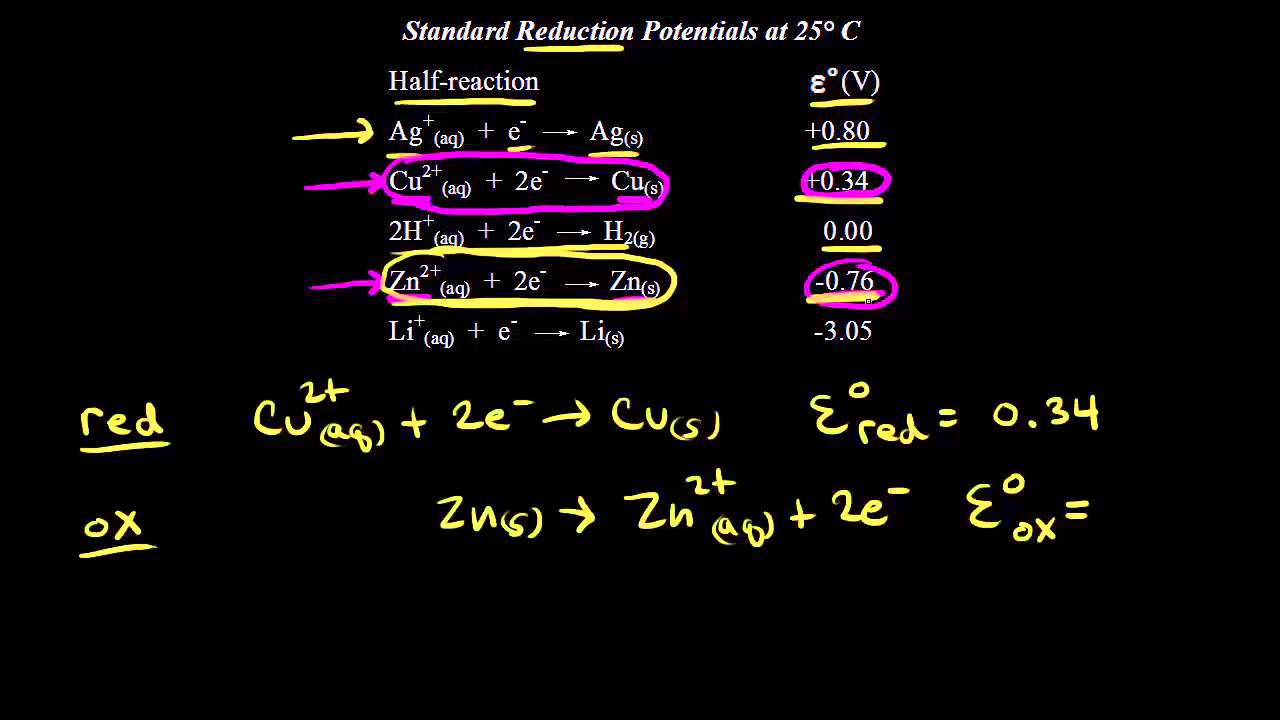
STANDARD HYDROGEN ELECTRODE
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is an important reference electrode used in electrochemistry. It serves as a baseline for comparing the electrode potentials of other half-reactions. The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in a solution with a hydrogen gas atmosphere at a fixed pressure.
The standard reduction potential of the SHE is defined as 0.00 V at all temperatures. This means that other reduction potentials can be measured relative to the SHE. By convention, the reduction potential of the SHE is considered positive when a half-reaction has a higher potential to be reduced compared to the SHE, and negative when it has a lower potential.
The half-reaction for the SHE is the reduction of protons (H+) to hydrogen gas (H2). This reaction takes place as follows:
2H+ + 2e- -> H2
The SHE is often used in electrochemical cells as a reference electrode, with another half-reaction occurring at a different electrode. The potential difference between the SHE and the other electrode is measured to determine the half-cell potential of the other electrode.
In practical situations, it is difficult to have a true SHE. Therefore, other reference electrodes such as the silver/silver chloride electrode are commonly used instead. However, these reference electrodes are calibrated using the SHE and have their own set standard reduction potentials.
The SHE is a crucial reference in electrochemistry as it allows for the determination of the standard reduction potentials of other half-reactions and the prediction of the feasibility of redox reactions. It provides a consistent reference point for measuring and comparing electrode potentials, which helps in understanding the principles and behaviors of electrochemical processes.




![Standard deviation and variance [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QbNf1-R_XVc/maxresdefault.jpg)