Education
Sub Category
How do cacti, lotus and pine trees survive and thrive in their habitat? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's explore how clouds are formed through this simple activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What happens if we tie a poly bag around a leaf and leave it overnight? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we prove that air is present all around us? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What kind of energy do moving objects have? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What kind of energy does a stretched rubber band, or a compressed spring have? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we check our pulse? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's learn how to measure length and width of objects!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's find out the correct way to measure length of objects!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Energy can be transformed from one from to another. Let's understand that with a simple activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's explore the characteristics of the images formed by a plane mirror!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What happens if you strike two metal spoons inside water? Do you hear them striking, or not? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's draw a ray diagram to understand the path of light when it reflects off a mirror!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What are clothes made up of? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What is energy? How is it related to work? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's look at one method of obtaining fabric from fiber!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Activity: https://youtu.be/Hc4kDe-Fptw
Timestamps
Practice this concept - “link to exercise”
Master the concept of “topic name” through practice exercises and videos - Link to topic
Check out more videos and exercises on “unit name” - Link to unit
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “subject” name, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “class and subject name” here - Link to the course
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
What happens when white light passes through a prism! Something, beautiful! Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Activity: https://youtu.be/omAdc2ImbMM
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Have you ever seen an iron nail attract other iron pieces! Well, be prepared!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Can a charged object attract neutral objects? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's draw a ray diagram to identify the path of light when it refracts through a glass slab, and also learn about Snell's law!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Activity: https://youtu.be/nehTPPI1sE0
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Is the magnetic strength of a magnet constant throughout its length or does it vary at the ends? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What happens when you bring two north poles of a magnet close to each other, and what happens when you bring north and a South Pole close to each other? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some salt can be dissolved in water at a certain temperature of water. But can more or less be dissolved if we change the temperature of water?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's draw a ray diagram to identify the path of light through a prism!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some substances are attracted to a magnet and some aren't. Let's look at some examples!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Unlocking the Invisible Dance: Exploring the Wonders of Magnetic Field Lines!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's see if the ice cubes in a glass sink or float, when we pour some water into it!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's have a look at a simple electrical circuit in action!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's understand how do converging and diverging beams look like!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's explore the characteristics of the images formed by a concave mirror for objects placed at different positions!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we purify salt water solution? Let's say we want to obtain pure water form the solution, how do we do that?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What happens when you rub twi straws with a cloth and bring them close? Something, very interesting! Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
If we keep a magnetised needle near a current carrying wire, it deflects! But why?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What happens when we leave a glass of cold water resting on a table for some time? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What are the different types of forces? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Activity: https://youtu.be/Ii0t3FsrGmc
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
When you freely suspend a magnet, it always point in a fixed direction! What direction is that? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's identify which one's a physical change and which one's a chemical change!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How do we separate the large insoluble solid particles from water?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Water vapor can change back to its state. What is it called? Let's watch it happen!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some changes happen after a definite period while some can happen at any point in time. Let's look at examples for the same!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Light doesn't pass through all materials. Materials can be categorised according to that property!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
There are two types of mixtures. Let's see what are they!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we separate dissolved salt from water? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
From Light to Shadow: Let's navigate the world of Umbra and Penumbra
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Here's the activity: https://youtu.be/6Nrq1_fWShI
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some changes can be reversed, while some can't be. Let's look at examples of the same!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some changes are slow and some are fast. Let's look at some examples for each of them!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Some objects and some sink. Objects can be categorised according to that property!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
A force is made up of two things - direction and magnitude. Let's see how!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we separate two solids from each other?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we separate water from dissolved salt?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Here's the activity: https://youtu.be/XxKDL5RN_eo
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How does water reach the top of a plant or a tree? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Here's the activity: https://youtu.be/Z6vUxC_qmRE
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's understand the concept of pressure through a simple activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How can we separate water and tiny insoluble particles in it?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's carry out a simple activity and actually see iron rusting!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How do the wires conduct electricity? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Rutherford discovered the structure of the atom! Let's understand his model through a simple activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Heat transferred depends on specific heat as well! Let's understand that through this activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
How does heat transfer in solids? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Here's the activity:https://youtu.be/VL1GB4wi7Zs
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor PandeyDescription
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Why do we feel warm when we are near a heat source? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Will the level of the water inside the bottle rise if I keep it in boiling water?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
How does pressure change when different force is applied on the same contact area?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
The level of water rises when an object is submerged into it. But by how much? Is there any relation between the volume of object and the volume of water displaced?
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's explore the relation between buoyant force and displaced liquid!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Why do things feel lighter when they are under water? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Why does a ship float and a tiny piece of metal sink? Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Here's the activity: https://youtu.be/sBlln7G9TPk
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's find out if light travels in a straight line through an interesting activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's see if a magnet behaves the same when a metal plate comes in between!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Let's see gases expanding in front of our eyes using simple materials!
Here's the explanation:
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Which one's a physical change and which one's a chemical change? We have two cases here, dissolved salt in water and burning magnesium. Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Which one's a physical change and which one's a chemical change? We have two cases here, Dissolving sugar and burning sugar. Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Which one's a physical change and which one's a chemical change? We have two cases here, deformation of a solid and spoilage of food. Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's look at a cool example of refraction!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
What produces a sound? Let's understand that through a small activity!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's test if vinegar, oil, water, liquid detergent etc. show any change in the color of a red and blue litmus paper.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Which one's a physical change and which one's a chemical change? We have two cases here, heating iron and rusting of iron. Let's find out!
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's solve a question on electric field due to a dipole.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Vibhor Pandey
Let's practice solving board type numerical from Electricity chapter
More free lessons & practice: https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class10t
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Wheatstone bridge is a special circuit consisting of 5 resistors. When the resistances in the adjacent arms have the same ratio, no current flows through the middle resistor! This is called a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
It's used in calculating unknown resistances using a meter-bridge set up.
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's learn the functions & parts of fore, mid & hindbrain.
https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-10-biolo
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Is there a pattern in how the flowers are arranged in plants? What are the different types of floral arrangements? Watch this video to learn about inflorescence.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Nivedhitha Suresh
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra 2
NEXT Video:
Factoring with Polynomial Division:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=imJCLnDubuA
How to factor a polynomial of degree 3 with grouping. This method works great for 3rd degree polynomials that can be grouped.
THIS DOES NOT ALWAYS WORK: To learn more about factoring a cubic polynomial continue watching our playlist on factoring or skip to the next video:
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
This will be a review of how fractions cancel. Understanding these basic rules now will make everything easier later on in the course when things get more complicated.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
Multiplying fractions is the easiest thing to do with fractions! This will be a quick review of how fractions multiply. We'll use this throughout the algebra course.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
Subtraction is a very poorly behaved operation. It isn't commutative and it isn't associative. But we can force it to be have by turning subtraction into addition!
a - b = a + (-b)
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
The associative property tells us that is doesn't matter how we group addition or multiplication. The property can be written like this:
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
a(bc) = (ab)c
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we learn the commutative property of addition and multiplication. The commutative property tells us that it doesn't matter which order we add or multiply in. We can right this rule like this:
a + b = b + a
ab = ba
Although this rule is very simple its very important!
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we'll review important sets of numbers:
Natural Numbers
Integers
Rational Numbers
Real Numbers
Complex Numbers
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
Welcome to the Algebra course. We'll get started by introducing variables and seeing examples of them in simple equations.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
We prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram are perpendicular if and only if the sides of the parallelogram are the same length.
http://www.rootmath.og | Linear Algebra
The definition of orthogonal: Two vectors are orthogonal when their dot product is zero.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
A brief example of using the dot product definition of the angle between two vectors to find that angle.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
The dot product helps us define the angle between two vectors. In this video we use the law of cosines and the dot product to help us define the angle between two vectors.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
We learn the definition of the dot product and we see an example. In the next video we will see how this definition helps us to define the angle between two vectors.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
We learn some basic properties of vectors like commutativity and associativity of addition, along with others.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
This is a proof that vector addition is commutative and associative. The proof relies on the same properties for the real numbers.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
We derived the length of vectors with 2 and 3 components using the Pythagorean Theorem. Now will will extend the notion of vector length to higher dimensions.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
In this video we'll define R^n. This will hopefully put us on the same page for notation that is coming up in the course.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
In this video we'll derive a formula for finding the length of a 3-dimensional vector. We'll also briefly discuss how to find the length of a vector with more than 3 components.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
We'll look at how to graph vectors with 3 components using 3-dimensional axes.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
u - v = u + (-v)
Since we know how to add vectors and multiply by negative one, we can also subtract vectors. Vector subtraction has geometric significance that we will utilize in a later video.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
When you multiply a vector by a scalar you simply multiply each component by that scalar. Since we can multiply a vector by -1 we can have -v. With this we have the tools we need to talk about vector subtraction (next video)
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
Vectors are added by adding corresponding components. Graphically we add vectors with a "head to tail" approach.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
To find the length of a vector we simply use the Pythagorean Theorem. The components of a vector form the base and height of a right triangle. The length of the vector is simply they hypotenuse of that triangle.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
Another example of using critical numbers to help us gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between a function and it's derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
Another example of using critical numbers to examine the relationship between a function and it's derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
Another example of using critical numbers to help us gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between a function and it's derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
Another example of using critical numbers to help us gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between a function and it's derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
We use critical numbers to help us gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between a function and it's derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
We'll look at the definition of a critical number and how we can find them.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
An example that will expand on our understanding of the relationship between extrema and the derivative.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
In this video we'll introduce extrema (maximum and minimum points) and analyze them in terms of slope and the derivative
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
A more difficult problem involving the rate of change of a man's shadow as he walks away from a lamp post.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
In this problem we related the rate of the rotation of a security beam to the rate at which the beam moves across the floor.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
An introduction to a very interesting problem. I definitely recommend you watch this video before moving on to part 2.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
This problem is very similar to filling a pool but with an added consideration. This is a very typical related rates problem for a Calculus 1 class. You may find a problem like this on a test or exam.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
This will be a basic related rates problem. We'll try to relate the rate at which water is entering to the pool to the rate at which the water level is rising.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
An introduction to related rates and an overview of the example problems to come
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
We use implicit differentiation to take the derivative of arcsec(x).
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
We use implicit differentiation to take the derivative of the inverse sine function: arcsin(x).
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We learn how to take the derivative of the natural log of x.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We take the derivative of the equation of a circle.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We get a feel for how we might take a derivative implicitly and we get the intuition of why implicit differentiation is really just uses the chain rule.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We now learn how the product rule and chain rule can take the place of the quotient rule.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We learn the quotient rule
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
This is a more advanced example of using the chain rule. In this video we need to use the chain rule twice in a row in order to find the complete derivative. Don't let the title fool you, its not difficult, its just a more advanced example that you should know how to do!
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
Our second example of using the chain rule. In this video we will take the derivative of sin(x^2 + 1) using the chain rule. Also remember:
"Derivative of the outside, repeat the inside, times by the derivative of the inside."
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
We use the chain rule to take the derivative of e^(2x).
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
Same chain rule, different notation. We'll look at a popular way of viewing the chain rule.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We learn the chain rule using function notation. This will be the most important rule we have for taking derivatives.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We learn how to take the derivative of a product by using the product rule.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
The derivative of all 6 trig functions.
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
We must use the limit definition of the derivative to find the derivative of sin(x)
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
Power Rule- the easiest thing since counting
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
The derivative of a constant is 0
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
This is the third example where will will use the definition to take the derivative of a function. More importantly we will explore the relationship between a function and it's derivative. It is essential that you understand this relationship!
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
This is the second example where will will use the definition to take the derivative of a function. More importantly we will explore the relationship between a function and it's derivative. It is essential that you understand this relationship!
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
This is the first example where will will use the definition to take the derivative of a function. More importantly we will explore the relationship between a function and it's derivative. It is essential that you understand this relationship!
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
Our third and final example of finding the slope of a tangent line by using the definition of the derivative.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
We look at the square root of x and find the slope of the tangent line when x is one. This is another example of finding the slope of a tangent line using the definition of the derivative.
We will find the slope of the tangent line by using the definition of the derivative.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus
In this video we discover the derivative by attempting to find the slope of a tangent line. We'll see that the derivative is just a limit involving slope.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/problem-solving
Solving a problem involving a circle, secant lines and tangent lines. This problem will lead directly to learning the definition of a derivative.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/problem-solving
Solving an interesting limit problem involving radicals
http://www.rootmath.org | calculus 1
A look at the geometry of a limit we looked at previously.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
Examining the geometry of the trig functions sec(x) and tan(x)
I mention that I couldn't find information. I do not mean to imply that the information isn't out there (it certainly is), I just couldn't find it after doing some brief searches so I decided to just toy with these ideas on my own. I hope this encourages you to do the same!
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/trig-limits
Proof of the lim(sinx/x) = 1
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/continuity-and-one-sided-limits
An example of forcing a piece-wise function to be continuous.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/continuity-and-one-sided-limits
Continuity is a requirement for many theorems, we'll look at how it is defined.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/continuity-and-one-sided-limits
An example to test our understanding of one sided limits.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/continuity-and-one-sided-limits
A quick explanation of one sided limits
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/epsilon-delta-limit-definition
This is an advanced example of proving a limit using the epsilon-delta definition.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/epsilon-delta-limit-definition
An example of using the definition of a limit to prove the limit.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/epsilon-delta-limit-definition
An understanding of the Epsilon Delta definition of a limit.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/epsilon-delta-limit-definition
A look at intervals and notation involved in the Epsilon Delta definition of a limit.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/trig-limits
Solving two limits of trig functions.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/trig-limits
Often times a few special trig limits are proven in class. We'll look at one that we'll prove later, and one that we can prove now.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
Solving limits involving complicated fractions. Please see the lesson page for practice exercises: http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
Rationalization (getting rid of square roots), a new technique for solving limits. Please visit the lesson page for practice exercises: http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
Square Roots: Positive or Negative?
http://forum.rootmath.org/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=22
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
Factoring, a new technique for solving limits analytically. Please visit the lesson page for practice exercises: http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/solving-limits
http;//www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/properties-of-limits
We'll learn properties of limits (what we can and can't do with limits). We'll start to take these for granted in future videos when we solve limits.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/limits-that-fail-to-exist
Our third example of a limit that does not exist. This limit does not exist because the function oscillates as x approaches 0 and so the limit does not exist.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/limits-that-fail-to-exist
A limit does not exist when it 'grows without bound.' Intuitively, if a function keeps getting bigger as you approach the limit value then the limit does not exist.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/limits-that-fail-to-exist
Some limits don't exist. The absolute value of x over x, |x|/x, has no limit as x approaches 0. This is because there is a jump in the graph at zero, or a jump discontinuity. This causes the value of the function to differ at the two sides of the jump and so the limit fails to exist.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/estimating-limits-numerically
Introduction to the limit of a function. We cover how to find a limit by estimating it numerically and we explain why limits are useful. This technique will be made more precise in later videos where we find that our estimate and the exact value are the same.
http://www.rootmath.org
http://www.rootmath.org/calculus/intro-to-limits
An introduction to limits. We'll explore the concept of a limit in basic terms.
http://www.rootmath.org | Calculus 1
An overview of the Calculus Course to come.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
This is the second example of finding a least common denominator by first finding a Least Common Multiple. This technique is useful for 'small' or 'easy' numbers.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we find a least common denominator by first finding a Least Common Multiple. This technique is useful for 'small' or 'easy' numbers.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
An introduction to adding fractions. We'll look at the easy case of adding fractions with a common denominator and we'll also see why we can't add fractions with different denominators.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we learn that certain fractions are equal to 1. This will be very useful later when we want to find common denominators.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we learn how to multiply fractions. Multiplying fractions is the easiest thing you can do with fractions so it's the first thing we'll learn.
http://www.rootmath.org | Algebra
In this video we get a basic understanding of fractions. We learn what a numerator and denominator is and what pieces of information they tell us.
This lesson walks through 12 climate types of the world. Organized into 9 climates classified by latitude and 3 climate types that can be found at any latitude, Mr. Rueschhoff explains each climate, where they are found, the climate factors that contribute to their creation, and their associated biome.
Climates discussed are Tropical Wet; Tropical Wet/Dry; Humid Subtropical; Humid Continental; Mediterranean; Marine West Coast; Sub-Arctic; Tundra; Icecap; Arid, Semi-Arid; and the Highland Climates.
Together with the previous lesson on the Five Factors of Climates and Biomes, viewers should be able to up their finger on the globe and have a good idea of what it is like there in terms of climate.
While accessible to anyone, this lesson is specifically written to address the educational standards of the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography studies course.
The lesson builds upon our look at latitude's impact on seasons and adds four more factors to explain how the Earth's climate is created. In addition to Latitude--the most important factor--are Elevation, Wind Currents, Ocean Currents, and Topography.
The lesson reviews how latitude greatly influences temperature on Earth and introduces how Elevation also has an impact on temperature of regions on Earth. Next, the lesson introduces Wind and Ocean Currents. It explains how convection drives our winds and creates the Hadley Cell and Inter-tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) that has a profound impact of climate in the tropics and creates the conditions for some the world's largest deserts.
Influenced by these Wind Currents are the Ocean Currents which are in a constant cycle of warm and cold water exchange between the equator and poles. Why the waters off of the west coast of a continent are usually cool while waters off the east coast are warm are explained. (Hint, it has to do with the Coriolis Effect). The role that El Nino and the North Atlantic Drift have in shaping the climate of the Americas and Europe are discussed as is the impact of Continentality.
The lesson concludes by discussing Topography's role in our climate--chiefly due to the Rainshadow Effect.
While useful to all audiences, this lesson is specifically designed to address elements of the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography Studies Course.
This video lesson explains why we have seasons on Earth. Specifically, it examines the Earth-Sun relationship. Viewers will learn it isn't just that the Earth rotates every 24 hours or even that it revolves around the Sun ever 365.25 days. Rather, what is special is that the Earth is titled that means that the Sun's energy (solar insolation) is distributed unevenly on the Earth's surface.
The big takeaway--beyond the fact that the Earth's seasons are caused by the Earth's revolution and tilt--is that latitude is an extremely important factor in determining what makes up the characteristics of a location.
Mr. Rueschhoff uses models to show the stages of this Earth-Sun relationship throughout the year to explain what Solstices and Equinoxes are. He concludes by breaking latitude into three bands (High, Middle, and Low) and explain how these three latitude bands have uniquely different seasons--it's not just Spring, Summer, Fall, and Winter!
A lesson that can be viewed and appreciated by all, but is specifically designed to address standards in the Texas Education Knowledge Standards (TEKS) for the World Geography studies course.
This video lesson looks at external factors that shape the Earth's landforms: weathering, erosion, and deposition. This examination of physical geography and geology aspects of the world includes looking at the differences between chemical and physical (or mechanical) weathering, how rain, wind, ice (glaciers), and even gravity moves sediment, and then how deposition of sediment creates landforms such as river deltas as well as produces fertile areas such as the North European Plain through the deposition of loess.
In addition, a review of what soil is and how it is created is included as well as how these processes create sedimentary rock.
This lesson is designed to not only inform all audiences, but also to focus on the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography studies course.
CORRECTION: AT 8:58, I stated that if there is just one Continental Plate you would have Convergent Subduction. I meant to say OCEANIC Plate. Sorry.
Ever heard someone say you're "making a mountain out of a molehill?" Well, I don't actually know what a molehill is (actually, I think I do), but in this lesson, we will examine the Earth's forces that creates its mountains--namely Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics.
This lesson begins by looking at the composition of the Earth and discover that its core, mantle, and crust make it much more like a baseball, than a blue marble that some have called it.
We then look at the outside of the Earth and find that it also has stitches, just like a baseball. Here we learn of Alfred Wegner's examination of the Earth which used records of fossils and rock formations to assert that the continents move--giving rise to the theory of Continental Drift.
While the geology community thought that Wegner was crazy, Harry Hess joined the Navy and through the use of sonar mapped the ocean floor and with carbon dating of the ocean crust, discovered Wegner was right and explained how the continents move through a process not unlike a lava lamp (interested, gotta watch the video--hint, it's through convection of the magma in the asthenosphere).
The lesson then looks at the three major ways that tectonic plates will move in relation to each other: divergence, convergence, and transform boundaries and discover that these moving plates create landforms such as mountains and volcanoes--and even rift valleys.
Because of the different densities, the lesson points out that if there is an oceanic crust involved in a collision of tectonic plates, it will cause something called Convergent Subduction which creates the subduction zone of the Ring of Fire. And if there are two continental plates, it creates Convergent Folding which is the process that continues to create the Himalaya Mountains and Mt. Everest.
All of the movement of these plates, creates a great deal of stress on the crust creates cracks, called faults which is where Earthquakes occur. And the lesson examines how tsunamis are created through underwater earthquakes.
Last, the lesson concludes discussing the Hot Spots that have created the Hawaii Islands as well has turned Yellowstone into a Supervolcano.
This lesson is designed for anyone, but is focused on meeting the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography studies course in the State of Texas.
This lesson walks students through the basic landforms on the Earth. This includes plains, mountains, hills, plateaus, peninsulas, islands, archipelagos, valleys, and canyons. The importance of rivers and the deltas and alluvial plains they create are examined.
The lesson also discusses the difference between oceans, seas, gulfs, and bays. The importance of straits are discussed and how they are the mirror opposite of isthmuses. The difference between lakes and reservoirs--despite usually all called lakes--is pointed out.
Beyond discussing the definitions, as fluid as they might be, the lesson discusses the ways that many of these landforms have been created. This includes the weathering, erosion, and deposition of sediment by wind, water, ice (glaciers), and even gravity. The role that plate tectonics in oceanic and continental plate convergence--either convergent subduction or convergent folding--has in creating landforms such as mountains is shown.
While this lesson can be enjoyed by all audiences, it is designed to meet various standards of the Texas Education Knowledge Standards (TEKS) for the World Geography studies course.
This lesson introduces the viewer to the Four Earth Systems: Atmosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere.
The lesson explains how each system is made up of sub-components and how each system interacts with the other three systems--all supporting life on Earth.
The Carbon Cycle and Water Cycle are described and the Life Cycle is introduced.
This lesson is designed to satisfy elements of the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography studies course.
This lesson looks at the way that countries seek to influence each other. In other words, how countries use power.
Calling upon Mr. Rueschhoff's over 23 years of military service his Master's Degree in Military Studies, he describes the Sources of National Power and the Instruments of National Power. These are concepts used by strategic planners in capitals around the globe.
First, the term power is defined and the concept of the Balance of Power is introduced and its role in keeping world peace.
Then, the lesson looks at what makes a nation powerful through the Sources of National Power which are its physical geography, economics, people, national will, and national direction.
But being powerful isn't enough, it is about how you use this power and Mr. Rueschhoff explains that countries use the DIME: Diplomacy, Information, Military, and Economics. These are the Instruments of National Power. Countries will use a blend of these four instruments to avoid war, gain territory, increase trade, resolve conflicts, and form alliances.
The organizations and alliances that are discussed are the United Nations, European Union, NATO, and OPEC.
While useful to all audiences, this lesson is specifically made to address standards of the World Geography studies course in the Texas Education Knowledge Standards (TEKS).
This is part 2 of our Agriculture and Economies lesson. In part 1, we went over the agricultural and industrial revolutions that made our economies possible.
In this lesson, we go over the 4 Economic Activities (Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary) and the types of Natural Resources. Then, we go over the types of economic systems. We meet Adam Smith and Karl Marx and discuss Free Market, Command (Socialism & Communism), and Mixed Economies. We also briefly discuss Mercantilism and we describe traditional economies.
While all audiences can benefit from this lesson, it is specifically written for a World Geography studies course satisfying multiple standards within the Texas Education Knowledge Standards (TEKS).
This is part one of a two-part lesson that outlines how the agricultural and industrial revolution have shaped our world and our economic systems.
This lesson focuses on the Neolithic Revolution when mankind first discovered agriculture, the Enclosure Movement that spurred the 2nd Agricultural Revolution and the Industrial Revolution, and the Green Revolution.
Useful for all audiences, this lesson was specially designed to be used in Texas classrooms and addresses standards found in the World Geography studies and World History TEKS when it discusses the differences between Subsistence and Commercial Agriculture and the effects of the Industrial Revolution.
This video lesson builds on the discussion about developing and developed countries in the Population Geography lesson. In this lesson, Mr. Rueschhoff describes the United Nation's Human Development Index, how it is determined, and how it can be used to describe countries of the world.
Each of the HDI's dimensions is discussed: Long, Healthy Living, Knowledge, and Standard of Living. This includes explaining the difference between Gross National Income, Gross National Product, and Gross Domestic Product.
Mean and Expected Schooling is discussed as are literacy rates when discussing the knowledge dimension of the UN's HDI.
The lesson concludes with Mr. Rueschhoff showing the population pyramids of a developed country, developing country, and a newly industrialized country and how these relate to the UN's HDI categories.
Thumbnail photograph was used under a Creative Commons license from NigerTZai (BY-SA 4.0).
This lesson introduces the basics of population geography including population demography and population pyramids. Push and Pull factors of migration are also examined.
Specifically, birth rate, fertility rate, mortality rate, and infant mortality rates are defined and different types of population pyramids are examined with how they can help show the developmental status of different countries.
This lesson is provided to satisfy selected standards in the Texas Education Knowledge Standards for the World Geography studies course.
This lesson explores culture: defining what culture is, what are its basic elements, and how it shapes our world today.
Concepts such as ethnocentrism, ethnicity, cultural hearths, cultural diffusion, cultural divergence, cultural convergence, acculturation, and enculturation are explained for the viewers. In addition, the role that technology and innovation have in making culture dynamic is discussed.
As culture is not only dynamic, but also symbolic, language as a mirror of culture is examined. Aspects of language are defined such as language families, dialects, and how lingua francas are used in the world.
While applicable to anyone who is wishing to better understand what culture is and what it entails, this lesson is provided to specifically address elements of the Texas Education Knowledge Standards of the World Geography studies course.
😍😍😍
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
This is part of the IB's NEW physics syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later.
*If you have exams in May 2024 or Nov 2024, then you should look at the videos I have for that - see the OLD syllabus section at: https://www.youtube.com/@OSC1990
Let's explore the translocation through phloem
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's learn how transpiration helps water transport in xylem
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore xylem and phloem (transport in plants)
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore respiration sites and what ATPs are.
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Lets explore cellular respiration (Aerobic & anaerobic)
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore the photosynthesis process.
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore Autotrophs, holozoic, saprotrophs & parasites
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore the various life processes that keep us alive.
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
How is the juicy fruit in mangoes and grapes formed? How are the seeds, which can grow into a new plant, formed? This video answers these questions.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Nivedhitha Suresh
This is Animation video on Phototropism and Geotropism
The ability to accurately observe, dissect and record an organism is a key skill for biology students. Many students are intimidated by the idea of making a scientific drawing, and struggle to develop their skills in this area.
This video will guide you through how to complete a dissection and scientific drawing of a flower. We recommend using Alstroemeria, as they are regularly available in supermarkets. However, there is an alternative version in which students follow in the footsteps of Darwin, making careful observations and dissections of primulas. Primulas are available in garden centres through much of the late autumn, winter and spring months, and flower in the garden in spring.
0:00 Credits
0:17 Step 1 - remove sepals
0:45 Step 2 - remove petals
1:11 Step 3 - remove stamens opposite sepals
1:54 Step 4 - remove stamens opposite petals
2:21 Step 5 - bissect the ovary
2:58 Step 6 - identify the line of symmetry in the flower
3:16 Step 7 - slice along the line of symmetry
3:32 Step 8 - continue slicing through the petals
4:00 Step 9 - arrange the parts for drawing
4:21 Step 10 - observe the flower parts
4:55 Step 11 - produce anatomical flower drawing
Follow our channel for biology practicals and more.
Teaching and technical notes plus student sheets: https://www.saps.org.uk/dissection
#saps #alevelbiology #flowers
Watching gas bubble up from a pondweed as it photosynthesises can be a great demonstration or student practical. When placed closer to a light , the rate of bubbling will speed up, and as the pondweed is taken further away, the bubbles will slow down again – an instant and visual indicator of the importance of light in photosynthesis.
This video demonstrates how best to use this protocol with your students in the lab, which species of pondweed can be used, how to care for pondweeds and a short explanation on the physiology that allows pondweed to bubble.
A great lab practical for investigating photosynthesis and respiration at GCSE and A-level / post-16. The bubbles produced by pondweed can be counted and the rate of bubbling can serve as an indication of the rate of photosynthesis, or the gas can be collected in a pipette or microsyringe and the amount measured. Students can investigate the effects of either light intensity or the wavelength (colour) of light on photosynthesis.
0:00 Introduction
0:59 Different types of pondweed
3:35 Keeping pondweed healthy
5:37 Setting up the bubbling pondweed practical
10:04 Why does pondweed bubble?
12:03 Summary
Full teaching notes are available at https://www.saps.org.uk/pondweed
#scienceexperiment #photosynthesis #plantscience #saps
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
Are you preparing for your IB maths exams? We've got you covered! OSC Study features exams created by IB experts in mathematics, showing you every step of every solution. Try it out for free here: https://app.oscstudy.com/
We're so excited to be able to share our exams with you!
Cheers, Mitch
This video shows oxidation reduction reactions and explains the formation of the products.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a weak base strong acid titration.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the measurement of the pH of aqueous solutions of ionic compounds.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a weak acid strong base titration.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the standardization of an unknown solution of NaOH with KHP with experimental data.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows for the standardization of an unknown solution of NaOH with KHP without experimental data.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows the titration of a sample of standardized HCl with an unknown solution of NaOH to determine its molarity.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
This video shows titration of a solution of HCl using a pH probe and CBL.
NCSSM, a publicly funded high school in North Carolina, provides exciting, high-level STEM learning opportunities. If you appreciate this video, please consider making a tax-deductible donation to the NCSSM Foundation. Thank you! https://www.ncssm.edu/donate
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under creative commons CC-BY-NC-SA http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video is an exploration of what buffers are and buffer capacity. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAf1/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for a strong acid strong base titration. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfa/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the relative hydrogen ion concentrations is a solution of HCl , CH3COOH, and a CH3COOH-CH3COONa buffer by comparing the rate of reaction with CaCO3. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfb/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the addition of a strong acid and a strong base to water as part of the buffer activity lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfc/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the addition of HCl and NaOH to a 0.10 M CH3COOH/ CH3COONa buffer as part of the buffer activity lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAff/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for phosphoric acid. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfg/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for sodium carbonate. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfh/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the mass percent of sodium hypochlorite in household bleach. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfJ/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the shifting of the FeSCN2+ equilibrium in the LeChatelier's Principle lab. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfx/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of spectrophotometric data to determine the Ksp for silver chromate. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfw/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of pH data to determine the Ksp of Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2.
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfv/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of data to determine the K sp of Ca(OH)2 in water and a solution of CaCl2. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfu/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of titration data to determine the equilibrium constant for the hydrolysis of an ester. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAft/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video is the introduction to Chapter 14 of the web course. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAfs/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the technique of an acid-base titration. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiJ/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the collection of data to determine the specific heat of a metal. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAgU/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the yield of NaCl from the reaction of NaHCO3 and HCl . http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiF/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the conductivity titration of Ba(OH)2 with H2SO4 using a conductivity probe. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiD/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the determination of the mole ratio in an acid-base reaction by measuring the temperature change in the reaction with a temperature probe. The method of continuous variations and a Job's plot is used. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiC/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: Part 2 of 2 videos shows gravimetric determination of a two component mixture of carbonates. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiB/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: Part 1 of 2 videos shows gravimetric determination of a two component mixture of carbonates. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiA/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: Determination of the molar Volume of a Gas at STP. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAid/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the making a solution by measuring a compound and using a volumetric flask. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAib/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the measurement of the conductivity of different concentrations of calcium chloride with a conductivity probe and the determination of the concentration of an unknown solution. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiS/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: Introduction to chapter 3: Atomic and Molecular Structure. dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiz/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the freezing of a sample of t-Butanol. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAix/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the simple distillation of methanol and its separation from a nonvolatile dye. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiv/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the chemical change that occurs during the thermal decomposition of Copper Carbonate. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAit/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the crystallization of sodium acetate from a supersaturated solution. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAis/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the chemical change that occurs when magnesium burns. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAiq/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the boiling of a sample of t- butanol. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAip/
Part of NCSSM CORE collection: This video shows the bending of a bimetallic strip when it is heated due to the different rate of linear expansion. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAio/
This video shows different rate of expansion and contraction of a brass ball and ring when they are heated. http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAin/
This video introduces the concept of significant figures in measurement. www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAim/
This video shows the setup of the long term reaction of CuCl2 and an iron nail. www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAil/
This video explains the importance of chemistry in our everyday lives. There is also a demonstration of the reaction between copper metal and nitric acid. www.dlt.ncssm.edu
Please attribute this work as being created by the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This work is licensed under Creative Commons CC-BY http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0
Help us caption & translate this video!
http://amara.org/v/GAik/
How To Do Titrations | Chemical Calculations | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Learn how to carry out titration experiments.
In this video, you will learn what apparatus needs to be used to conduct a titration, including pipettes, burettes and conical flasks.
Titration experiments enable us to work out the exact concentration of an unknown solute, when we know the concentration of another solute. You can calculate the concentration of acids and alkalis through this method.
You may need to use an indicator to help you spot when the acid or alkali has been neutralised.
This video shows you how to carry out the experiment, and then you will also need to know how to do the calculations to actually find the concentration.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
https://www.patreon.com/fuseschool
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
VISIT us at [a]www.fuseschool.org%2C[/a] where all of our videos are carefully organised into topics and specific orders, and to see what else we have on offer. Comment, like and share with other learners. You can both ask and answer questions, and teachers will get back to you.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Biology videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Physics videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Maths videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/fuseschool/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the FuseSchool platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Befriend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This is an Open Educational Resource. If you would like to use the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Lesson - 06 : The Solid State part - 02 (Closed Packed Structures of Solids)
Lesson 6 :The Solid State Part - 03 (Packing Efficiency,Classification of Solids Based on Their..)
Lesson - 6 :The Solid State Part 1 (Properties of Solids Crystal Lattice and Unit Cells)
Lesson - 5 : The Gaseous and Liquid State part -2 (The Gas Laws)
Lesson - 5 : The Gaseous and Liquid State part -1 (Types of Intermolecular Interactions/Forces)
Lesson - 25 Compounds of Carbon containing Halogens (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)
L 3 Basics of periodic classification of elements P 2
L 2 Basics of Atomic Structure Part 1
L 2 Basics of Atomic Structure Part 2
L 3 Basics of periodic classification of elements P 1
Nomenclature & General Principles of Organic Compounds
Atomic Structure
Chemical Bonding
Coordination Compounds
Nomenclature & General Principles of Organic Compounds
Chemical Bonding
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. Do you want the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Mixing a solution of Copper Sulphate with one of sodium carbonate (washing soda) produces a remarkably visual reaction and precipitate!
Website: https://thinktac.in/
Subscribe to our channel:http://www.youtube.com/c/ThinkTac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science.
#Chemicalreaction #ThinkTac #coppersulphate science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Website: https://thinktac.in/
Subscribe to our channel:http://www.youtube.com/c/ThinkTac
#LitmusPaper #DIYLitmusPaper #ThinkTac #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. Make a battery using different metal strips, a separator and different solutions as electrolyte.
Visit our Website: https://thinktac.in/
Purchase our kits - https://www.thinktac.com/avail....able-courses/?catid=
Subscribe to our channel:http://www.youtube.com/c/ThinkTac
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Make your own small fire extinguisher using citric acid and baking soda.
Website: https://thinktac.in/
Subscribe to our channel:http://www.youtube.com/c/ThinkTac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science
#Fireextinguisher #ThinkTac #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Using sulphur powder and lime powder, we make acidic and basic solutions that are diluted enough to be safe and easily tested using litmus papers
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Once an acid-base reaction is done, How do we determine the amount of either one of the reactants?.
We "titrate", that is to measure the concentration of the unknown reactant (called analyte) using a reactant with a known concentration ( called "Titrant"). Let us see how to do this!
Here we use Bromothymol blue , as a reaction indicator
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Make tweezers using ice cream sticks and aluminum strips. Burn a magnesium strip by holding it using the tweezers.
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Magnesium ribbon pieces are immersed in a solution of citric acid to produce hydrogen. This gas is collected in a balloon and see how the balloon floats in the air.
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Mixing a solution of copper sulphate with one of sodium carbonate (washing soda) produces a remarkably visual reaction and precipitate!
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science.
#Precipitation #coppersulphate #thinktac #sodiumcarbonate science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ The ability of a metal to react with other chemicals is an important property of the metal and is called its Reactivity. In this TACtivity, we perform a simple experiment with three metals (Copper, Iron, and Magnesium) to see how their reactivities compare.
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com
.
. You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://my-unlab.web.app/ Using Benedict's reagent, one can detect the presence of glucose in a food substance. The foods we use are milk, cornflour solution, cooked dhal, sugar solution, and salt solution.
Thinktac Videos:
► Subscribe to Thinktac: https://www.youtube.com/thinktac
► Circle us on G+:https://plus.google.com/+thinktac
► Like us on Facebook:https://www.facebook.com/thinktac
Experiential science at school and at home, face-to-face and online, providing materials & resources to create, experiment, tinker, innovate and learn science. science experiments for kids, simple science experiments, easy science experiments, experiments for kids, science experiments at home, science experiments with water, easy experiments, cool science experiments, science experiments for kids at school, easy science experiments for kids, simple experiments for kids, fun science experiments, simple science experiments for class 5, easy science experiments to do at home, science experiments for class 5, easy experiments for kids, easy science #SchoolScienceExhibition, #NewScienceProjects, #ScienceExperimentsForKids, #DIYScience
#NEET #JEE, #JEEADV, #CentumAcademy #JEE2020
This Video Series cater to the needs of aspirants of KVPY, JEE Mains and Advanced. A step by step guide to ace these examinations is what an aspirant needs. CENTUM ACADEMY’s e-learning modules have been designed to help students get a structured approach towards preparation for examinations like KVPY, JEE Mains and JEE Advanced.
You can let us know if you want to get video sessions on specific topics by mentioning the same in Comments Section.
Enjoy Learning!!!
Do also visit
www.centum.learnyst.com for mock tests and topic wise Daily Practice Sheets.
#NEET #JEE, #JEEADV, #CentumAcademy #JEE2020
This Video Series cater to the needs of aspirants of KVPY, JEE Mains and Advanced. A step by step guide to ace these examinations is what an aspirant needs. CENTUM ACADEMY’s e-learning modules have been designed to help students get a structured approach towards preparation for examinations like KVPY, JEE Mains and JEE Advanced.
You can let us know if you want to get video sessions on specific topics by mentioning the same in Comments Section.
Enjoy Learning!!!
Do also visit
www.centum.learnyst.com for mock tests and topic wise Daily Practice Sheets.
Basic Introduction. System Definitions and their types, Surroundings and types of Boundary
This Video Series for those who want to delve a little deep into the world of Geometry. The gems of Geometry .i.e. the theorems and their proofs have been compiled in this series. This series is for students - those who want to explore geometry as well as those who are appearing for Mathematics Olympiads (PRMO, RMO, INMO, IMO) and for Maths enthusiasts.
For more such sessions, please visit:
www.wiki.centumacademy.com
#Olympiads #Geometry #Theorems
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. AS Chem: States of Matter (Gas Laws)
Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Quiz section for MSE 170: Fundamentals of Materials Science.
Recorded Summer 2020
Leave a comment if I got something wrong. Happy to receive feedback.
Checkout our undergraduate journal:
https://sites.google.com/uw.edu/urmse/volumes
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
If you like what you saw here and organic chemistry has started to make a whole lot more sense, head over to [a]www.altacademy.org[/a] for access to:
1. Videos
2. Past Paper Solutions
3. Revision Guides
4. Notes
5. Doubt solving with experts
6. Flashcards
7. An active and global online community
PLUS a whole lot more. Not just for Chemistry, but 5 other A Level subjects.
See you there
[a]www.altacademy.org[/a]
www.instagram.com/altacademyorg
help@altacademy.org
Found this video helpful? Need more help with your A Levels but for more than just Chemistry? Head over to http://www.altacademy.org where we’ve got an elaborate suite of subject videos, revision guides, flash cards and even 1:1 academic support for a number of A Level courses. A2 Chem: Electrochemistry Revision 1
Companion site: http://chemistrywithbilal.com
AS Chemistry 42 Day Revision Challenge
Playlist Link:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLjKGeVMH_gh
Introductory lecture on redox reactions and batteries for MSE juniors.
Recorded Spring 2020
Leave a comment if I got something wrong. Happy to receive feedback.
Checkout our undergraduate journal:
https://sites.google.com/uw.edu/urmse/volumes
Learn the basics about Avogadro's number - The Mole. What is Avogrado's number? Why is it called like that and what relation does it have to the mole? Find more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn the basics about Moles in equations. How do you calculate a mole? How do moles work in equations? Find out more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn the basics about calculating molarity as part of the chemical calculations topic.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about the extraction of salt within the uses of salt, as part of the overall topic of acids and bases.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Class 9 | NCERT | Writing Chemical Formulae | Part 1/1 | English | Class 9 | Atoms and Molecules | Atomic Structure
In this video, we will study about Atoms and Molecules.
To watch more videos of this class, visit this playlist - https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PL4EcHZ6qe-g
About TicTacLearn -
We firmly believe that education is the greatest equalizer of all! But unfortunately, we live in a world where access to quality learning resources is limited and comes with an associated price-tag, effectively perpetuating inequity in the society.
We have set out to change that.
At TICTACLEARN we believe that digital content has the power to reshape the learning spaces in the country and we want to take it one step closer to every learner, educator and parent. With that in mind we have created one of the largest open-source repositories of high-quality, curriculum aligned digital learning resources (~12,000 videos, aligned item bank, etc.) available for everyone, free of cost! Furthermore, we know that educational resources are most effective when in the learners native language, and hence we aim to make our videos available in all major Indian languages.
To watch our videos in other languages, click on the links below:
Hindi: bit.ly/TTL_Hindi
Telugu: bit.ly/TTL_Telugu
Marathi: bit.ly/TTL_Marathi
English: bit.ly/TTL_English
Odia: bit.ly/TTL_Odia About TicTac Learn - We firmly believe that education is the greatest equalizer of all!
But unfortunately, we live in a world where access to quality learning resources is limited and comes with an associated price-tag, effectively perpetuating inequity in the society.
We have set out to change that. At TICTACLEARN we believe that digital content has the power to reshape the learning spaces in the country and we want to take it one step closer to every learner, educator and parent. With that in mind we have created one of the largest open-source repositories of high-quality, curriculum aligned digital learning resources (~12,000 videos, aligned item bank, etc.) available for everyone, free of cost!
Furthermore, we know that educational resources are most effective when in the learners native language, and hence we aim to make our videos available in all major Indian languages.
✤Do Not Forget to Subscribe:
👉 TicTacLearn Hindi: https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnHindi?sub_con
👉TicTacLearn English: https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnEnglish?sub_c
👉TicTacLearn Gujarati: https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnGujarati?sub_
👉TicTacLearn Marathi: https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnMarathi?sub_c
👉TicTacLearn Telugu: https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnTelugu?sub_co
👉TicTacLearn Odia:https://www.youtube.com/c/TicT....acLearnOdia?sub_conf
Crude Oil Fractions & Their Uses | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Learn the basics about the uses of crude oil fractions.
Before watching this video you should watch our video explaining how crude oil is separated into its different length hydrocarbon fractions by utilising the different boiling points of each hydrocarbon fraction.
JOIN US ON PATREON
https://www.patreon.com/fuseschool
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
VISIT us at [a]www.fuseschool.org%2C[/a] where all of our videos are carefully organised into topics and specific orders, and to see what else we have on offer. Comment, like and share with other learners. You can both ask and answer questions, and teachers will get back to you.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Biology videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Physics videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Maths videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/fuseschool/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the FuseSchool platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Befriend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This is an Open Educational Resource. If you would like to use the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about halogenation within the alkanes and alkenes part of organic chemistry.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about condensation polymerisation within the overall organic chemistry topic.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about synthetic polymers when learning about polymers as a part of the organic chemistry topic.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about natural polymers. What are natural polymers? where are they found and how are they structured?
Find out more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn about carbohydrates within the overall topic of organic chemistry.
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
JOIN our platform at [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: [a]www.fuseschool.org[/a]
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about how alcohol is made? What are the steps necessary? And, what happens during the process of fermentation? and is Ethene? Find out in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Learn the basics about alcohols and what they are. SUBSCRIBE to our channel to access many more educational videos. At The Fuse School, teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT. Our OER are available free of charge to anyone. Make sure to subscribe - we are going to create 3000 more!
This video is part of the Chemistry Journey project - a Chemistry Education project by The Fuse School sponsored by Fuse. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseschool
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Google+: http://www.gplus.to/FuseSchool
Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/virtualschooluk
Email: info@fuseschool.org
Website: www.fuseschool.org
This video is distributed under a Creative Commons License:
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs CC BY-NC-ND
Learn the basics about testing alkenes with bromine water. Why is bromine water used to test alkenes? What is bromine water made of? Find out more in this video!
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This video explains displacement reactions where the reaction of various metals with acid is taken as example and a gas is displaced. Here the rate of reaction of different metals with hydrochloric acid has also been compared. It also explains double displacement reaction and neutralization reactions with the help of different examples.
The video shows a demonstration of some physical and chemical changes and also some combination and decomposition reactions
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
This is part of the IB's NEW Biology syllabus, which means you have exams in May 2025 or later. The videos were designed and recorded by Cheryl Hickman
Structure Of The Leaf | Plant | Biology | The FuseSchool
Plants make food through photosynthesis. Using their leaves, plants combine sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make glucose and oxygen. A leaf is like a plant's food factory, collecting all of the components into one place so that photosynthesis can happen.
Let's start with sunlight. The top of a leaf is exposed to the most sunlight, and so the cells specialised for trapping light are on top of the leaf. These specialised cells are called palisade mesophyll cells. They are packed full of chlorophyll - the green chemical that plants used to absorb light. Most leaves have a large surface area so that they can trap as much sunlight as possible.
Moving onto carbon dioxide. This is where the bottom of the leaf comes in. There are little pores on the bottom of the leaf called stomata. The stomata open up so that carbon dioxide can diffuse into the leaf. The stomata are controlled by 'sausage shaped' guard cells, which open up to let carbon dioxide in. The guard cells can also close the stomata, to stop other things inside the leaf, like water, from escaping.
The carbon dioxide comes in from the stomata, and then makes its way up through the leaf, through the gaps in the spongy mesophyll layer in the bottom part of the leaf and heads up to the palisade cells where photosynthesis occurs. Leaves are thin so that the carbon dioxide doesn't have too far to travel.
The final reactant needed for photosynthesis is water. Water comes into the plant through the roots, moves up the stem and enters the leaf through the vascular bundle. The vascular bundle contains a hollow tube specifically for water movement called the xylem. The veins on a leaf are actually the vascular bundle, allowing water to be spread out through the leaf.
The leaves palisade cells now have sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. They are ready to photosynthesis to make glucose and oxygen.
How do leaves manage to let in the wanted things (like water and carbon dioxide) but prevent unwanted things like bacteria getting in and also prevent the reactants from escaping before being used? At the top and bottom of the leaf are epidermis cells. These produce a protective waxy cuticle layer. The waxy cuticle seals up the leaf so that the only way in and out are through the stomata, which are regulated by the guard cells.
So from top to bottom, a leaf's structure:
- Waxy cuticle and epidermis cells
- Palisade cells (where photosynthesis occurs)
- Spongy mesophyll (with vascular bundle running through for water transport)
- Epidermis and cuticle, with stomata and guard cells spread throughout (allowing carbon dioxide in).
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
https://www.patreon.com/fuseschool
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
VISIT us at [a]www.fuseschool.org%2C[/a] where all of our videos are carefully organised into topics and specific orders, and to see what else we have on offer. Comment, like and share with other learners. You can both ask and answer questions, and teachers will get back to you.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Biology videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Physics videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Find all of our Maths videos here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/fuseschool/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fuseschool/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the FuseSchool platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Befriend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
This is an Open Educational Resource. If you would like to use the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
Learn the basics about The Lymphatic System.
This Open Educational Resource is free of charge, under a Creative Commons License: Attribution-NonCommercial CC BY-NC ( View License Deed: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ). You are allowed to download the video for nonprofit, educational use. If you would like to modify the video, please contact us: info@fuseschool.org
SUBSCRIBE to the Fuse School YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
This video is part of 'Chemistry for All' - a Chemistry Education project by our Charity Fuse Foundation - the organisation behind The Fuse School. These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid. Find our other Chemistry videos here:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLW0gavSzhMl
Twitter: https://twitter.com/fuseSchool
Access a deeper Learning Experience in the Fuse School platform and app: www.fuseschool.org
Follow us: http://www.youtube.com/fuseschool
Friend us: http://www.facebook.com/fuseschool
Strong acids/bases dissociate completely whereas weak acids/bases dissociate partially.
In this video, David explains how Louis De Broglie got his Nobel Prize for the idea of matter having a wavelength.
Bond enthalpy is the energy required to break one mole of a specific type of bond in a gaseous molecule. It is usually represented as ΔH or ΔHrxn.
Enthalpy of reaction, also known as heat of reaction, is the change in enthalpy that occurs during a chemical reaction when the reactants are converted into products. It is also represented as ΔH or ΔHrxn.
The relationship between bond enthalpy and enthalpy of reaction can be explained using the concept of bond breaking and bond forming.
In a chemical reaction, bonds in the reactant molecules are broken, and new bonds are formed in the product molecules. The energy required to break the bonds (bond enthalpy) is an endothermic process, as energy needs to be supplied to weaken the bonds.
On the other hand, the energy released when new bonds are formed (bond formation) is an exothermic process, as energy is released during the formation of stronger bonds.
The enthalpy of reaction is the net energy change in the reaction, taking into account the energy required to break the bonds and the energy released when new bonds are formed.
Mathematically, the enthalpy of reaction (ΔHrxn) can be calculated using the bond enthalpies of the bonds broken (ΣΔHbroken) and the bond enthalpies of the bonds formed (ΣΔHformed):
ΔHrxn = ΣΔHformed - ΣΔHbroken
If the sum of the bond energies for the bonds broken is greater than the sum of the bond energies for the bonds formed, then the ΔHrxn will be positive, indicating an endothermic reaction. Conversely, if the sum of the energies for the bonds formed is greater than the sum of the energies for the bonds broken, then the ΔHrxn will be negative, indicating an exothermic reaction.
Using the Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential when concentrations are not standard conditions. Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.About Khan Academy: Tebtalks offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions that are reknown
How to use a table of standard reduction potentials to calculate standard cell potential. Identifying trends in oxidizing and reducing agent strength.
Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/cell-potential/v/using-reduction-potentials?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Missed the previous lesson? https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/oxidation-reduction/batter-galvanic-voltaic-cell/v/nickel-cadmium-battery?utm_source=YT&utm_medium=Desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Chemistry on Khan Academy: Did you know that everything is made out of chemicals? Chemistry is the study of matter: its composition, properties, and reactivity. This material roughly covers a first-year high school or college course, and a good understanding of algebra is helpful.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Subscribe to Khan Academy’s Chemistry channel: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCyEot66LrwWFEMONv
Subscribe to Khan Academy: https://www.youtube.com/subscr....iption_center?add_us
This video talks about how we can use the reduction potential values to construct a galvanic cell.Practice this concept - “:electrochemistryTo get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry", find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - Sure! Let's practice constructing a galvanic cell using reduction potential values.
First, let's choose a redox reaction that has known reduction potential values. A common reaction that is often used in galvanic cells is the reduction of copper ions (Cu2+) by zinc metal (Zn) in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4):
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (reduction half-reaction, E° = +0.34 V)
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- (oxidation half-reaction, E° = -0.76 V)
The reduction potential values (E°) for these half-reactions are given in volts (V). The reduction half-reaction has a positive E° value, indicating it is spontaneous in nature.
To construct a galvanic cell, we need two half-cells, each consisting of an electrode and an electrolyte solution. The reduction half-reaction will be our cathode (positive electrode), and the oxidation half-reaction will be our anode (negative electrode).
Now, let's assemble the galvanic cell step by step:
1. Start by creating the anode compartment: Place a strip of zinc metal (Zn) into a beaker containing a solution of zinc sulfate (ZnSO4). This is the anode half-cell.
2. Next, create the cathode compartment: Place a strip of copper metal (Cu) into a beaker containing a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4). This is the cathode half-cell.
3. Connect the two half-cells: Connect a wire between the zinc metal in the anode half-cell and the copper metal in the cathode half-cell. This allows the flow of electrons through the wire from the anode to the cathode.
4. Complete the circuit: Connect the two half-cells using a salt bridge. A salt bridge can be made by soaking a piece of filter paper in a salt solution (e.g., KCl) and placing it between the two half-cells. The salt bridge completes the circuit and allows ions to flow between the two half-cells, maintaining electrical neutrality.
5. Observe the flow of electrons: Electrons flow from the zinc anode, where zinc atoms are oxidized, to the copper cathode, where copper ions are reduced. This flow of electrons generates an electric current that can be used to do work.
So, by using the reduction potential values, we have successfully constructed a galvanic cell using a zinc-copper redox reaction
This video talks about the use of Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential for a given cell at a particular temperature (other than the standard conditions).
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Master the concept of “Cell potentials under non-standard conditions” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrochemistry” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-12-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry", find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 12 Chemistry” here - https://www.google.com/url?client=internal-element-cse&cx=004984196166817161901:gt3nscsxv5o&q=https://www.khanacademy.org/science/class-12-chemistry-india&sa=U&ved=2ahUKEwiToa_q0ID-AhVp8jgGHQ-eCtIQFnoECAEQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2TEFUhHpIMyKNfZE-8Jrv_
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
This video explains how molar conductivity varies with dilution in case of both strong and weak electrolytes. It also graphically explains why the increase in the molar conductivity is higher for a weak electrolyte as compared to a strong one.
Master the concept of “Electrolytic cells and electrolysis” through practice exercises and videos - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Electrochemistry” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with Chemistry, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for Class 12 Chemistry here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Colligative properties are properties of a solution that depend solely on the concentration of solute particles in the solvent and not on the nature of the solute. One of the colligative properties is the elevation of boiling point.
The elevation of boiling point is the phenomenon where the boiling point of a solvent is raised when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it. This occurs because the presence of solute particles in the solvent disrupts the intermolecular forces between solvent molecules, making it more difficult for the solvent to vaporize and reach its boiling point.
Some key points about the elevation of boiling point are:
1. Explanation: Dissolving a non-volatile solute in a solvent increases the number of solute particles in the solution. These solute particles create additional obstacles for solvent molecules to overcome in order to escape into the vapor phase during boiling. As a result, more energy is required to reach the boiling point, causing an elevation in the boiling point of the solution compared to the pure solvent.
2. Relationship with Concentration: The extent of the elevation of boiling point is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute particles in the solution. This relationship is described by the equation:
ΔTb = Kb * m
Where ΔTb is the elevation in boiling point, Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant specific to the solvent, and m is the molality of the solute particles in the solution.
3. Colligative Property: The elevation of boiling point is a colligative property because it depends only on the number of solute particles and not on their size or chemical nature. This means that any solute that does not vaporize at the boiling point of the solvent will affect the boiling point similarly, regardless of its identity.
4. Applications: The elevation of boiling point has practical applications. For example, it is utilized in antifreeze solutions, where the addition of solutes (such as ethylene glycol) raises the boiling point of water in vehicle cooling systems. It also plays a role in adjusting cooking times and temperatures at higher altitudes, where the lower atmospheric pressure results in a lower boiling point of water.
It is important to note that the elevation of boiling point is just one of the colligative properties exhibited by solutions, along with other properties like vapor pressure lowering, depression of freezing point, and osmotic pressure. These properties are especially important in fields such as chemistry, biology, and pharmaceuticals and contribute to various applications and processes.
We are familiar with the various concentration terms like molarity, molality, mole fraction and so on. In this video, we will solve few questions on these concepts.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Classification of elements and periodicity in properties” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Solutions” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-12-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
Let's solve a few questions on electronic configurations of elements.
Practice this concept - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Check out more videos and exercises on “Classification of elements and periodicity in properties” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/up-class-11-ch
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Revathi Ramachandran
In this video, we discuss the formal proof of the theorem which says that the equal chords that is the chords with same length subtend equal chord at the center of the circle.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Devashish Phadnis
We discuss the proof of theorem which says that the equal chords of the circle are equidistant from the center.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Devashish Phadnis
In this video we discuss the step deviation method to find mean of grouped data. This method involves assuming mean for the groups and is discussed with an example.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Devashish Phadnis
In this video we discuss the famous Alternate segment theorem which has the statement that "Measure of angle formed by tangent and chord is equal to measure of angle inscribed in the alternate arc". We disucss its proof.
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Devashish Phadnis
In this video we prove the statement for PA x PB = PT^2 or in other words,
Proof: If from an external point P of a circle a tangent segment PT and a secant PAB are drawn, then PA.PB=PT^2
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Devashish Phadnis
In this video, we step into the world of honey bees and find out why some of them don't have fathers, while everyone has grandfathers!
More free lessons & practice: https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class-12
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Sulagna Das
Chapter Name: Sequences and Series
Topic: Solved example
Grade: X
Author: Tushar Sinha
*Geometric Mean
* AM , GM Inequality
________________________________________________________________________________________________
A STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO PREPARE FOR BOARDS & COMPETITIVE EXAMINATIONS
This session can be useful to students of high school of CBSE, ICSE, IGCSE or State Boards, as well as those who are preparing for competitive exams like NTSE, IIT JEE, NEET, KVPY, CET, Olympiads, Bank PO, CLAT, SAT, CAT, GMAT, GRE, UPSC Civil Services Examination, NDA
For more such
a) Sessions and courses,
b) Practice worksheets,
c) MCQ Quiz,
d) Self-Assessment Tests,
e) Query resolution (on video conferencing)
Please visit: https://centum.learnyst.com/learn
Website: https://centumacademy.com/
Follow us for more interesting discussions on
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/centumacademy
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/centumacademy
Twitter: https://twitter.com/centumacademy
#CentumAcademy #Algebra #SequencesAndSeries
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into VSEPR theory and molecular structure. It contains examples and practice problems of drawing lewis structures along with the correct molecular geometry. Structures include the tetrahedral shape, bent, linear, trigonal planar, and trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry as well as their bond angles.
How To Draw Lewis Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NFZtjSeT3XE
VSEPR Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DBrq31w8vC4
Molecular Geometry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Cw0_cJzkSI
Lewis Dot Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ymf3kZePDnU
Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhItoqhHoEE
_________________________________
Octet Rule Exceptions:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=96L6_IwyHRM
Resonance Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9B5FGPDwX_E
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ykSzYl_4vI
Formal Charge Calculations:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_SIjijCouE
Lewis Structures - Mega Review:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PeY_sihSh8E
________________________________
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdJeQUd2g_4
Molecular Orbital Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6tB6E6R_XpQ
Dipole Dipole Forces of Attraction:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zOvnu0KYyxo
Hydrogen Bonding:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZDjJOqOKeCI
Unit Cell Chemistry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HCWwRh5CXYU
_________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
https://www.video-tutor.net/
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
https://www.patreon.com/MathSc....ienceTutor/collectio
This video tutorial provides a basic introduction into organic chemistry. Here is a list of topics:
1. How to draw lewis structures of organic compounds
2. Identifying functional groups - alkanes, alkenes, & alkynes
3. Formal charge calculations
4. Resonance structures
5. Basic IUPAC nomenclature of alkanes
___________________________________
Organic Chemistry - Basic Introduction:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B_ketdzJtY8
Which Bond Is More Polar?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o0-a5HzSzdE
How To Draw Lewis Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6unef5Hz6SU
Condensed Structures to Skeletal Structures:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HRkvjKHFNDA
Functional Groups Review:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9jM8lWxrAE
Primary, Secondary, & Tertiary Functional Groups:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r_Zhb0nQEvE
_________________________________
How To Calculate Formal Charge:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C2l-76VP8s0
Finding Lone Pairs Using Formal Charge:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jlCPY6iXQ1c
Dipole Moment & Electronegativity:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFAU1GMJmnI
Predicting Bond Angles:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPS7zdg8HzY
Valence Bond Theory:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vqx9a2aU99c
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pdJeQUd2g_4
_______________________________
Bond Strength and Bond Length:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSRY95IAwF8
Orbital Overlap and Bond Length:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BatJrR5sblA
Organic Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
https://www.video-tutor.net/orgo-chem.html
Organic Chemistry Exam 1 Playlist:
https://bit.ly/3kJnNXU
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
https://www.patreon.com/MathSc....ienceTutor/collectio
FORM II
MAIN TOPIC : MAP READING
SUB TOPIC : Introduction to map reading
In this video, Supriya solves a word problem based on Arithmetic progressions.
For more free lessons & practice - https://www.khanacademy.org/ma....th/in-in-grade-10-nc
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Supriya.
In this video, Anmol discusses how we can use zeros of the given polynomial to find the value of the given unknown.
For more free lessons & practice - https://www.khanacademy.org/ma....th/in-in-grade-10-nc
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Anmol.
Let's see which fractions give terminating decimals and which don't - without actually dividing them!
More free lessons & practice https://www.khanacademy.org/ma....th/in-in-grade-10-nc
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Ashish Gupta
Let's use number lines to think about Arithmetic progressions. Bonus: We wouldn't need the nth term formula after this!
More free lessons & practice https://www.khanacademy.org/ma....th/in-in-grade-10-nc
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Ashish Gupta
This video introduces one to Organic Chemistry from the basics while also highlighting some of the basic terminologies in Organic Chemistry.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on the study of carbon compounds. Carbon atoms can form stable covalent bonds with other atoms, allowing for the formation of a wide range of complex molecules, including those found in living organisms.
Here are some basic terminologies commonly used in organic chemistry:
1. Carbon (C): Carbon is an element that forms the backbone of organic molecules. It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
2. Hydrocarbon: A hydrocarbon is a molecule consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It is the simplest type of organic compound. There are two main types of hydrocarbons: alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) and alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond).
3. Functional group: A functional group is a specific arrangement of atoms that gives a compound its characteristic chemical properties and reactivity. Examples of functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines.
4. Isomers: Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. There are different types of isomers, such as structural isomers (different connectivity), geometric isomers (cis-trans isomerism), and enantiomers (mirror-image isomers).
5. Alcohols: Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group attached to a carbon atom. They are characterized by the "-ol" suffix in their names. For example, ethanol is a common alcohol.
6. Aldehydes and Ketones: Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O). Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of a carbon chain, whereas ketones have it within the carbon chain.
7. Carboxylic acids: Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are characterized by the "-oic acid" suffix in their names. Examples include acetic acid and formic acid.
8. Amines: Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom attached to carbon atoms or hydrogen atoms. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines based on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
These are just a few basic terminologies in organic chemistry. The subject encompasses many more concepts and reactions, including polymerization, aromatic compounds, stereochemistry, and reactions like substitution, elimination, and addition reactions.
h In this lesson, you will learn about the periodic table and how it is used in chemistry. We will focus on how the periodic table is organized by atomic number, and discuss how properties of elements are periodic in nature throughout the table due to the electrons in the outer shells of the atoms. We will also discuss atomic mass and valence electrons, including predicting when an atom will gain or lose an electron in a chemical reaction.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements based on their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus). It organizes all the known elements in a specific order which allows for classification and understanding of their properties and relationships.
The table is composed of rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements in the same period share the same energy levels, while elements in the same group share similar chemical properties.
The elements on the periodic table are represented by symbols, and each element has its own unique atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical symbol. The order of elements is based on increasing atomic number, which also corresponds to the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
The periodic table is an essential tool for scientists, students, and researchers as it provides valuable information about elements, such as their atomic masses, electron configurations, and various trends in their chemical behavior.
What is an Atom?
An atom is the basic unit of matter, and it is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms are the building blocks of all matter in the universe. They are composed of three main subatomic particles:
1. Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of the atom.
2. Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also located in the nucleus.
3. Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels.
The protons and neutrons are tightly packed in the central nucleus of the atom, while the electrons move in various energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus defines its atomic number, which, in turn, determines the element to which the atom belongs. The number of electrons typically matches the number of protons, creating a neutral atom.
Atoms can combine to form molecules through chemical bonding, and they can participate in chemical reactions by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. The study of atoms and their interactions is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics and has led to a deeper understanding of the properties and behavior of matter.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Let's learn IUPAC Naming of Organic Compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and functional groups such as halides, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids. We discuss the IUPAC Naming rules with lots of examples!
The factors affecting dynamic equilibrium such as concentration changes, temperature changes, pressure changes, catalysts, nature of reactants, and surface area have various industrial applications. Here are some examples:
1. Haber Process: The Haber Process involves the production of ammonia by combining nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas in a high-pressure, high-temperature reaction. The process takes advantage of Le Chatelier's principle, which states that increasing the pressure and decreasing the temperature favors the production of ammonia, increasing the yield of the reaction.
2. Contact Process: The Contact Process is used to produce sulfuric acid from sulfur dioxide gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. The reaction is exothermic, and increasing the temperature will decrease the yield. However, a catalyst such as vanadium oxide is used to increase the rate of reaction, while maintaining a high yield.
3. Polymerization: In polymerization reactions, a catalyst is used to increase the rate of the reaction, and hence increase the yield of the desired product. For example, Ziegler-Natta catalysts are used in the industrial production of polyethylene, polypropylene, and other polyolefins.
4. Surface Area: In reactions involving solids, increasing the surface area of the solid will increase the rate of reaction. This principle is employed in the manufacturing of fertilizers, where the reactants are ground into fine powders to increase their surface area, resulting in a faster reaction and higher yield.
In general, the understanding and manipulation of dynamic equilibrium is an important tool for chemical industries to optimize chemical reactions and improve the efficiency of their processes.
The effect of pressure on dynamic equilibrium depends on the number of moles of gas present in the balanced chemical equation. Here are the possible effects:
1. No effect: If the number of moles of gas on both sides of the reaction is equal, changes in pressure will have no effect on the position of the equilibrium. This is because altering the pressure will not favor either the forward or reverse reaction.
2. Effect on side with fewer moles: If the number of moles of gas is different on each side of the reaction, changes in pressure can affect the equilibrium position. Increasing the pressure will decrease the volume, and the equilibrium will shift towards the side with fewer moles of gas. Conversely, decreasing the pressure will increase the volume, causing the equilibrium to shift towards the side with more moles of gas.
It is important to note that changes in pressure do not affect the value of the equilibrium constant (K), which remains the same. Also, it is worth mentioning that pressure changes only affect equilibria involving gases, not reactions involving only solids or liquids.
Dynamic equilibrium is a state in which the forward and reverse reactions of a reversible reaction occur at equal rates. The position of the equilibrium can be influenced by certain factors. Here are a few factors that affect dynamic equilibrium:
1. Changes in concentration: If the concentration of one of the reactants or products is increased, the system will try to counteract this change by shifting the equilibrium to the opposite side of the reaction, away from the added substance.
2. Changes in temperature: Changes in temperature can influence the position of the equilibrium in exothermic or endothermic reactions. Increasing the temperature will favor the endothermic reaction, and decreasing the temperature will favor the exothermic reaction.
3. Changes in pressure: Changes in pressure affect the equilibrium position in reactions with gaseous reactants and products. Increasing the pressure will decrease the volume and push the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles, and vice versa.
4. Catalysts: Catalysts have no effect on the position of the equilibrium, but they can increase the rate at which the equilibrium is reached by lowering the activation energy of both the forward and reverse reactions.
5. Nature of reactants: The nature of the reactants involved in a reaction can affect the position of the equilibrium. If reactants are more stable than products, the equilibrium will shift towards the products side and vice versa.
6. Surface area: The surface area of the reactants can affect the rate at which the reaction occurs, thus indirectly affecting the position of the equilibrium.
In summary, the equilibrium position of a reversible reaction is affected by changes in concentration, temperature, pressure, catalysts, nature of reactants, and surface area. Understanding these factors can be useful in predicting and controlling the position of the equilibrium in various chemical reactions.
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions, meaning that the reactants can be converted into products, and the products can also react to form the reactants again. In a reversible reaction, an equilibrium is established where the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time.
Here is an example of a reversible reaction:
A + B ⇌ C + D
In the forward reaction, reactants A and B combine to form products C and D. In the reverse reaction, products C and D react to form the original reactants A and B.
The direction of a reversible reaction is influenced by various factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration. Le Chatelier's principle states that if a change is applied to a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the change.
For example, if the concentration of one of the reactants is increased, the equilibrium will shift towards the side with fewer moles of that reactant to reduce the excess concentration. The reaction will then favor the forward direction. Conversely, if the concentration of a product is increased, the equilibrium will shift towards the side with fewer moles of that product, favoring the reverse reaction.
Similarly, changes in pressure and temperature can also affect the equilibrium position of a reversible reaction. Increasing the pressure will favor the direction with fewer moles of gas, while decreasing the pressure will favor the direction with more moles of gas. Changes in temperature can affect the equilibrium position depending on whether the reaction is exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic (absorbs heat).
Reversible reactions are essential in many chemical and biological processes, including industrial reactions, equilibrium systems, and enzymatic reactions. They provide a dynamic perspective on the behavior of chemical reactions, allowing us to understand and control them more effectively.
Reaction rates and reversible reactions are important concepts in chemistry that are closely related.
Reaction rates refer to the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place. It measures how quickly reactants are consumed or how quickly products are formed during a reaction. Reaction rates can be influenced by various factors such as temperature, concentration, pressure, and the presence of catalysts.
On the other hand, reversible reactions are reactions that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions. This means that reactants can form products, and products can also react to form the original reactants. Reversible reactions are denoted by a double-headed arrow (⇌) to indicate their bidirectional nature.
In reversible reactions, the forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously, but the reaction rates may be different. The rate of the forward reaction is determined by the concentrations of the reactants, while the rate of the reverse reaction is determined by the concentrations of the products. At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal, and the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant.
The reaction rate of a reversible reaction can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration. Changing these factors can alter the position of equilibrium, which refers to the relative amounts of reactants and products in a reversible reaction system. For instance, increasing the temperature usually shifts the equilibrium towards the endothermic direction, while increasing the pressure may favor the formation of products with fewer moles.
Understanding the relationship between reaction rates and reversible reactions is important for studying chemical kinetics and thermodynamics. It allows scientists to predict and control the rates and outcomes of chemical reactions. Knowledge of reaction rates and reversible reactions is particularly useful in industrial processes, where optimizing reaction conditions can improve efficiency and yield.
Reaction Rates:
Reaction rate is a measure of how fast a chemical reaction takes place. It is often described as the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit of time. The rate of a chemical reaction is influenced by several factors, including temperature, concentration of reactants, surface area, and the presence of catalysts.
Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally increases the reaction rate. This is because higher temperatures provide more energy to the reactant particles, causing them to move faster and collide with greater force. This leads to a higher frequency of effective collisions, resulting in a faster reaction rate.
Concentration: Increasing the concentration of reactants typically increases the reaction rate. This is because a higher concentration means there are more reactant particles present, leading to a higher frequency of collisions and a greater likelihood of effective collisions.
Surface Area: Increasing the surface area of solid reactants can increase the reaction rate. This is because greater surface area provides more opportunities for reactant particles to come into contact with each other, increasing the frequency of collisions.
Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction with lower activation energy. They do not get consumed in the reaction and can be reused. Catalysts work by reducing the energy barrier required for the reaction to occur, allowing more reactant particles to overcome this barrier and participate in the reaction.
Reversible Reactions:
Reversible reactions are chemical reactions that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions. This means that reactants can form products, and products can also react to form the original reactants. Reversible reactions are often represented by a double-headed arrow, indicating that the reaction can occur in both directions.
An example of a reversible reaction is the formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen:
2H2 + O2 ⇌ 2H2O
In this reaction, hydrogen and oxygen can react to form water, and water can also decompose to form hydrogen and oxygen. The double-headed arrow represents the equilibrium between the forward and reverse reactions.
In a reversible reaction, the reaction rate of the forward and reverse reactions can be different. The extent to which a reversible reaction proceeds in the forward direction depends on the relative concentrations of reactants and products. At equilibrium, the reaction rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal, and there is no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
Factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration can affect the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction. These factors can shift the equilibrium towards the formation of more products or reactants.
In today’s English lesson, I will help you master 31* English phrases that will help you advance your English vocabulary, Fluent English speakers can integrate a variety of phrases into their everyday speaking.
Visit https://englishwithkayla.com/ to upgrade your English conversations with my new six-week conversation course
Download this week’s PDF guide https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/cd3e9td6qe7u53iyd77d4/PDF-Guide_Learn-31-Advanced-English-phrases.pdf?rlkey=4xqzft1iqkrf3vqe7a6xfqvov&dl=0
//ENGLISH READING RECOMMENDATIONS (beginner, intermediate, advanced)
✨ https://amzn.to/3H6fZ97
//THE ENGLISH VOCABULARY HELP PODCAST
✨ Spotify https://open.spotify.com/show/....7was2eefHcQbJQVsV199
✨ Anchor https://anchor.fm/english-with-kayla
//MY WEBSITE
✨ https://englishwithkayla.com/
//COME SAY HI!
✨ @Englishwithkayla https://www.instagram.com/englishwithkayla/
//CONTACT:
✨ For business inquiries: EMAIL: ENGLISHWITHKAYLA@GMAIL.COM
Subscribe to my channel!
__________________________
Subscribe to English with Kayla to learn English with Teacher Kayla from the United States. Learn about different English conversation topics each week, and learn many new natural English phrases. Study the American accent, vocabulary, idioms, and phrasal verbs with Kayla. English with Kayla will help you expand your English vocabulary and feel confident to speak in English conversation. I teach English that you will find native English speakers using in their daily vocabulary, not English from a textbook. Subscribe for New Natural English-speaking lessons every week and visit Englishwithkayla.com for more lessons.
DISCLAIMER: Links included in this description might be affiliate links. If you purchase a product or service with the links that I provide I may receive a small commission. There is no additional charge to you! Thank you for supporting my channel so I can continue to provide you with free content each week!
Namugongo Secondary - Entrepreneurship
To identify the best oxidizing agent using Eo(red.) values, you need to compare the Eo(red.) values of the potential oxidizing agents. The species with the higher Eo(red.) value will be the stronger oxidizing agent.
Here are some general rules for comparing Eo(red.) values:
1. The species with the higher Eo(red.) value will be more likely to undergo reduction and, therefore, act as the oxidizing agent.
2. The species with the lower Eo(red.) value will be more likely to undergo oxidation and, therefore, act as the reducing agent.
3. The larger the difference in Eo(red.) values between two species, the stronger the oxidizing agent and the weaker the reducing agent.
For example, consider the following half-reactions:
Half-reaction 1: A+ + e- --> A (Eo(red.) = 0.8 V)
Half-reaction 2: B2+ + 2e- --> 2B+ (Eo(red.) = 1.5 V)
In this case, half-reaction 2 has the higher Eo(red.) value (1.5 V) compared to half-reaction 1 (0.8 V). Therefore, B2+ is the stronger oxidizing agent.
It is important to note that Eo(red.) values can only be compared within the same system, meaning you cannot directly compare Eo(red.) values from different reference electrodes or different systems. Additionally, other factors such as concentration and temperature can also influence the oxidizing strength of a species, so it is important to consider these variables as well.
Le Chatelier's Principle is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how systems at equilibrium respond to changes in conditions. According to this principle, when a system at equilibrium is subjected to an external influence, it will adjust in such a way as to counteract the change and reestablish equilibrium.
Adding a catalyst to a reaction is one such external influence. However, unlike changes in temperature, pressure, or concentrations, adding a catalyst does not directly affect the position of the equilibrium or alter the concentrations of reactants or products. Instead, a catalyst provides an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, lowering the activation energy barrier. This allows the reaction to proceed at a faster rate without being consumed itself.
In the context of Le Chatelier's Principle, adding a catalyst to a reaction at equilibrium does not cause any immediate response. The equilibrium composition and concentrations of reactants and products remain unaffected. However, the presence of a catalyst can increase the rate at which the reaction reaches equilibrium.
It's important to note that catalysts do not shift the equilibrium position or favor the formation of products or reactants. They only enhance the rate at which the equilibrium is reached by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. Once equilibrium is attained, the catalyst does not affect the equilibrium concentrations.
On Khan Academy, you can find more detailed explanations and examples of Le Chatelier's Principle, as well as related topics in equilibrium chemistry. Their resources, including videos, articles, and practice exercises, can help you fully understand the principles and applications of equilibrium reactions in chemistry.
Enjoy your learning and exploration of this fascinating field!
In this episode , we look at how the body is able to regulate blood glucose.This episode can be good for both ordinary and advanced levels
The regulation of blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, involves complex mechanisms that ensure the body maintains stable glucose levels. Here is an overview of the process:
1. Role of Pancreas: The pancreas plays a central role in blood glucose regulation through the secretion of two important hormones - insulin and glucagon.
2. Insulin:
- When blood glucose levels rise after a meal, cells in the pancreas called beta cells secrete insulin into the bloodstream.
- Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, particularly in the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue.
- Insulin promotes the storage of excess glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles, lowering blood glucose levels.
3. Glucagon:
- In contrast to insulin, when blood glucose levels drop too low, alpha cells in the pancreas release glucagon into the bloodstream.
- Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, releasing it into the bloodstream to increase blood glucose levels.
4. Liver's Role:
- The liver plays a vital role in blood glucose regulation. It stores glucose as glycogen and can release or generate glucose through glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, respectively.
- During periods of fasting or prolonged exercise, glucagon stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen or other molecules (amino acids, lactate) into glucose for energy.
5. Hormonal Regulation:
- Several hormones affect blood glucose levels. Besides insulin and glucagon, other hormones such as cortisol, epinephrine, and growth hormone influence glucose metabolism.
- These hormones can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating glucose production through gluconeogenesis or by reducing glucose uptake in certain tissues.
6. Role of Adipose Tissue:
- Adipose tissue, or fat cells, also contribute to blood glucose regulation.
- They release fatty acids into the bloodstream in response to insulin, which provides an alternative source of fuel for cells instead of glucose.
- Fatty acids spare glucose, allowing it to be available for tissues that primarily rely on glucose for energy.
7. Feedback Loop:
- Blood glucose regulation involves a complex feedback loop system. Specialized cells in the pancreas sense the glucose levels in the blood and release insulin or glucagon accordingly.
- As blood glucose levels rise, insulin is released to facilitate glucose uptake and reduce glucose production.
- Conversely, when blood glucose levels decrease, glucagon is released to stimulate glucose production and maintain glucose homeostasis.
These processes work together to maintain blood glucose levels within a narrow range, as excessive or insufficient glucose can have detrimental effects on various organs and bodily functions. Blood glucose regulation is crucial for energy production, cellular function, and overall metabolic health.
Sodium ions keep the body fluids in normal balance. Sodium ions regulate blood pressure and volume. Sodium ions also play an important role in nervous transmission.Therefore maintaining a constant level enables different metabolic processes to proceed normally.
The regulation of sodium ions in the body involves several processes that ensure a balance between sodium intake and excretion. Here is a step-by-step explanation of these processes:
1. Sodium Intake: Sodium ions enter the body primarily through dietary sources, such as table salt (sodium chloride) and processed foods. The average daily sodium intake is around 3,400 mg.
2. Filtration in the Kidneys: As blood passes through the kidneys, a filtration process occurs in the glomeruli, where sodium ions are filtered out of the blood along with other waste products.
3. Sodium Reabsorption in the Proximal Tubules: In the renal tubules, around 65-70% of the filtered sodium ions are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream in the proximal tubules through passive diffusion.
4. Hormonal Control:
a. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS): When the body senses a decrease in blood volume or low blood pressure, specialized cells in the kidneys release an enzyme called renin. Renin converts angiotensinogen (a protein produced by the liver) into angiotensin I, which is then converted to angiotensin II by an enzyme called ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme). Angiotensin II stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephrons, promoting the reabsorption of sodium ions back into the bloodstream, leading to water retention and increased blood volume and pressure.
b. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): ADH, also known as vasopressin, is released by the pituitary gland in response to increased plasma osmolality (concentration of solutes in the blood) or decreased blood volume. ADH acts on the collecting ducts of the nephrons, increasing the permeability of the ducts to water. This causes increased reabsorption of water back into the bloodstream, indirectly affecting sodium ion concentration and maintaining water balance.
5. Other Factors Influencing Sodium Regulation:
- Blood Pressure: Sodium plays a key role in maintaining blood pressure. Increases in sodium intake lead to an increase in blood volume, which can raise blood pressure. Conversely, decreased sodium intake can lower blood pressure.
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP): Released by the heart's atria in response to increased blood volume and pressure, ANP acts as a natural antagonist to aldosterone. It promotes the excretion of sodium in the urine, leading to decreased blood volume and pressure.
6. Sodium Excretion: The remaining sodium ions that are not reabsorbed in the renal tubules are eliminated from the body through urine. The rate of sodium excretion depends on the balance between sodium intake and the efficacy of sodium reabsorption.
These processes work together to regulate the concentration of sodium ions in the body, maintaining electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and overall homeostasis.
Here are some precise notes on the regulation of sodium ions in the body:
1. Importance of Sodium Ions:
- Sodium ions (Na+) are essential for many physiological processes in the body, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and maintenance of fluid balance.
- Sodium ions also play a crucial role in maintaining blood volume, blood pressure, and pH balance.
2. Kidney Function in Sodium Regulation:
- The kidneys play a key role in regulating sodium concentration in the body by adjusting its reabsorption and excretion.
- Sodium reabsorption primarily occurs in the renal tubules.
3. Sodium Reabsorption:
- In the proximal tubules of the nephrons, around 65-70% of the filtered sodium is reabsorbed passively.
- Active reabsorption occurs in the distal tubules and collecting ducts, under hormonal control.
4. Hormonal Control:
a. Aldosterone:
- Aldosterone, a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, plays a pivotal role in sodium regulation.
- It promotes the reabsorption of sodium ions in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephrons.
- Aldosterone enhances sodium retention while simultaneously increasing potassium and hydrogen ion excretion.
b. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS):
- The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormonal cascade that regulates sodium balance and blood pressure.
- When blood pressure decreases or sodium levels decrease, renin is released from the kidneys, leading to the activation of angiotensin I and angiotensin II, ultimately triggering the release of aldosterone.
c. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH):
- Another hormone involved in sodium regulation is ADH, also known as vasopressin.
- ADH is released by the pituitary gland in response to high plasma osmolality or decreased blood volume.
- ADH acts on the collecting ducts of the kidneys, promoting water reabsorption, which indirectly affects sodium concentration.
5. Osmoregulation and Water Balance:
- Sodium regulation is closely linked to water balance in the body.
- The movement of sodium ions drives osmosis, affecting the movement of water across cell membranes and in and out of the blood vessels.
- Imbalances in sodium levels can lead to improper water distribution and dehydration or overhydration.
These notes provide a concise overview of the regulation of sodium ions in the body.
DID U KNOW THATUp to 60% of the human adult body is water. According to H.H. Mitchell, Journal of Biological Chemistry 158, the brain and heart are composed of 73% water, and the lungs are about 83% water.This video explains to you very well what the body does in order to ensure that water in your body is neither in excess nor inadequate.
Water regulation in the body is essential for maintaining proper cellular function, blood volume, and electrolyte balance. Several organs and hormones work together to regulate water in the body. Here are some key aspects of water regulation:
1. The hypothalamus: The hypothalamus in the brain senses changes in blood osmolality, or the concentration of particles in the blood. When the osmolality increases, the hypothalamus stimulates the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the pituitary gland.
2. ADH: ADH, also known as vasopressin, is a hormone that regulates water reabsorption in the kidneys. ADH acts on the kidneys to increase the reabsorption of water, leading to decreased urine output and increased water retention. When blood osmolality decreases, ADH release is inhibited, and the kidneys excrete more water, leading to increased urine output and decreased water retention.
3. Kidneys: The kidneys play a critical role in regulating water balance in the body. The kidneys filter waste products and excess water from the blood, which is then excreted as urine. The amount of water reabsorbed in the kidneys is regulated by ADH, as described above.
4. Thirst mechanism: The sensation of thirst is an important mechanism for regulating water balance. When dehydration occurs, the body senses a decrease in blood volume, which triggers the release of hormones that stimulate thirst, leading to increased water intake.
5. Electrolyte balance: Regulating water balance also involves maintaining electrolyte balance. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, are essential for proper cellular function, and their concentrations are carefully regulated by the kidneys and several hormones.
Disruptions to the regulation of water balance can lead to various disorders, such as dehydration or overhydration, which can have significant effects on electrolyte balance and cellular function.
Watch, and learnThe parathyroid hormone (PTH), secreted by the parathyroid glands, is responsible for regulating blood calcium levels; it is released whenever blood calcium levels are low. PTH increases blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoclasts, which break down bone to release calcium into the blood stream
Calcium ions play a vital role in numerous physiological processes in the body, including muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and bone health. The regulation of calcium ions in the body is achieved through a complex series of mechanisms involving several organs and hormones. Here are some key aspects of calcium ion regulation:
1. Parathyroid hormone (PTH): When the calcium levels in the blood are low, the parathyroid glands, located in the neck, release PTH. PTH acts on the bones, kidneys, and intestines to increase calcium levels. It stimulates bone resorption, where calcium is released from the bones, and enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and the absorption of calcium from the intestines.
2. Calcitonin: Released by the thyroid gland, calcitonin opposes the actions of PTH. It promotes the deposition of calcium into the bones, inhibits bone resorption, and reduces the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys.
3. Vitamin D: Often known as the "sunshine vitamin" because it can be synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight, vitamin D plays a critical role in calcium regulation. Vitamin D enhances the absorption of calcium from the intestines by stimulating the synthesis of calcium-binding proteins.
4. Kidneys: The kidneys regulate calcium levels by controlling its reabsorption and excretion. PTH stimulates the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium, preventing its loss through urine. Conversely, high blood calcium levels can trigger the kidneys to excrete excess calcium.
5. Bones: Calcium is stored in the bones and can be released or deposited depending on the body's needs. PTH and vitamin D influence bone cells called osteoclasts, which break down bone to release calcium, and osteoblasts, which build bone and incorporate calcium.
Disruptions to the regulation of calcium ions can lead to various disorders such as hypercalcemia (high blood calcium) or hypocalcemia (low blood calcium), which can have significant effects on muscle and nerve function, among other physiological processes.
Proteins are broken down to peptides in stomach and duodenum after which the peptides are broken down finally to amino acids in the ileum.When amino acids are in excess the body, the body does not store them but rather breaks them down in a process called deamination which involves removal of amino group from amino acid to form ammonia.Ammonia is a toxic product especially for mammals which do not have enough water in their bodies ( unlike organisms like bony fish). Therefore mammals turn the toxic ammonia into less toxic product called urea through a series of reactions in the ornithine cycle as discussed aboveOrnithine, arspatate, arginine are all amino acids.
The ornithine cycle, also known as the urea cycle, is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the liver and other tissues. It is responsible for the synthesis of urea and the detoxification of ammonia, which is a byproduct of protein metabolism. The liver plays a crucial role in this cycle by converting ammonia into urea, which can then be excreted by the kidneys.
Deamination is another important process in protein metabolism, which involves the removal of the amine group from an amino acid. This process also generates ammonia, which can be toxic to the body if it accumulates. Once again, the liver plays a critical role in removing ammonia from the body by converting it into urea, which can be safely excreted in urine.
Overall, the liver is essential for maintaining the body's nitrogen balance and preventing accumulation of toxic ammonia. Dysfunction of the liver, such as in liver disease or damage, can result in impaired ornithine cycle and deamination, leading to harmful levels of ammonia buildup in the body.
A step-by-step guide on how to do so.
1. Identify the balanced chemical equation: Begin by identifying the balanced chemical equation that represents the dissolution of the compound. This equation shows how the compound dissociates into its constituent ions in aqueous solution.
2. Write the dissolution equation: Write the dissolution equation using the appropriate state symbols (s for solid and aq for aqueous). Ensure that the equation is balanced in terms of atoms and charges. For example, let's consider the dissolution of calcium carbonate (CaCO3):
CaCO3 (s) → Ca2+ (aq) + CO3^2- (aq)
3. Write the Ksp expression: The Ksp expression represents the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of the compound. It is written by taking the product of the concentrations of the constituent ions, each raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. For the dissolution of calcium carbonate, the Ksp expression would be:
Ksp = [Ca2+]^1 * [CO3^2-]^1
4. Exclude solids from the expression: Only the concentrations of the dissolved ions are included in the Ksp expression. Any solid compounds are excluded. In this case, the solid calcium carbonate (CaCO3) would not be included.
5. Use brackets to denote concentration: The concentrations of the ions in the Ksp expression are typically denoted within square brackets, [ ]. However, if the ion is a polyatomic ion, such as CO3^2-, the brackets are still used, but the charge is outside the brackets.
6. Include units: It is important to include the units of concentration used in the Ksp expression. Typically, molarity (M) or moles per liter (mol/L) are used. Make sure to use consistent units for all concentrations in calculations or comparisons.
7. Don't include coefficients: The Ksp expression does not include any coefficients in front of the ions. Only the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation are used to determine the powers to which the concentrations are raised.
I hope this guide assists you in writing Ksp expressions. If you have any further questions or require additional explanation, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Thank you for your attention.
Best regards,
The relationship between Ksp (solubility product constant) and precipitation is fundamental in understanding how solids dissolve and come out of solution. Here's the key concept:
* **Ksp is a constant value for a specific ionic compound.** It represents the equilibrium point at which the dissolved ions (from the compound) and the undissolved solid are in balance within a solution.
* **Precipitation occurs when the concentration of dissolved ions exceeds the Ksp value.** This means there are more ions floating around in the solution than the system can stably hold at equilibrium. To re-establish equilibrium, the excess ions come together and form a solid precipitate.
Here's a breakdown of the relationship:
* **Ksp > Qsp (ionic product):** Solution is unsaturated. No precipitation occurs.
* **Ksp = Qsp:** Solution is saturated. Ions are at equilibrium and neither dissolving nor precipitating.
* **Ksp < Qsp:** Solution is supersaturated. Precipitation will occur to reduce the ion concentration and reach equilibrium.
In essence, Ksp acts as a threshold. If you push the system past this point (by adding more solute or changing conditions), precipitation will happen to restore equilibrium.
This animation introduces the key concepts of unconscious bias. It forms part of the Royal Society’s efforts to ensure that all those who serve on Royal Society selection and appointment panels are aware of differences in how candidates may present themselves, how to recognise bias in yourself and others, how to recognise inappropriate advocacy or unreasoned judgement. You can find out more about unconscious bias and download a briefing which includes current academic research at www.royalsociety.org/diversity.
Presented by: Dr. Mridusmita Duara
Camera: Rashmi Duwarah
Editing & Graphics: Bitu Das
Produced by: Dr. Sangeeta Kakoty, Deputy Director, Multimedia, KKHSOU
Completely soluble salts are those that dissolve entirely in water to form a homogeneous solution. The solubility of these salts in water depends on various factors such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the salt and solvent.
There are some general rules for predicting the solubility of ionic compounds in water. These rules are based on the principle that “like dissolves like,” where polar substances dissolve in polar solvents, and nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
1. Salts containing group 1 cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+) are completely soluble in water.
2. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are completely soluble in water.
3. Salts containing the nitrate ion (NO3-) are completely soluble in water.
4. Salts containing the chloride ion (Cl-) are mostly soluble in water. However, some chloride salts of less electronegative metals such as AgCl and PbCl2 are insoluble.
5. Salts containing the sulfate ion (SO42-) are mostly soluble in water. However, some sulfate salts of less electronegative metals such as BaSO4 and PbSO4 are insoluble.
6. Salts containing the carbonate ion (CO32-) and the phosphate ion (PO43-) are mostly insoluble in water. However, some of their soluble salts, such as Na2CO3 and Na3PO4, are completely soluble.
These rules are useful in predicting the solubility of completely soluble salts in water and can help in identifying insoluble salts. Keep in mind that these rules are not absolute, and some exceptions to them can occur.
A titration pH curve is a graphical representation of how the pH of a solution changes as a titration progresses. It typically exhibits several distinct features that can provide valuable information about the reaction being studied. The main features of a titration pH curve are:
1. Initial pH: At the start of the titration, before any titrant has been added, the initial pH is determined by the solution being titrated. For example, if an acidic solution is being titrated against a basic titrant, the initial pH will be low (acidic).
2. Slow pH change: Initially, as the titrant is added slowly, the change in pH is relatively slow because the reaction between the titrant and analyte is not yet significant enough to alter the pH dramatically. This region is often referred to as the buffering region, as the solution's pH remains relatively stable.
3. Equivalence point: The equivalence point is the point at which the stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have reacted. At this point, the pH undergoes a rapid change. For the reaction between a strong acid and a strong base, the equivalence point occurs at pH 7, indicating a neutral solution.
4. Midpoint of the buffering region: Before reaching the equivalence point, there is a point where the pH undergoes the steepest slope, known as the midpoint of the buffering region. This point corresponds to approximately halfway between the initial pH and the pH at the equivalence point. It is an important reference point as it helps determine the pH range over which the buffer works effectively.
5. Endpoint: The endpoint is the point at which the indicator used in the titration changes color, indicating that the reaction is approaching completion. Ideally, the endpoint should coincide with the equivalence point, but in practice, slight differences may occur.
6. Post-equivalence region: After passing the equivalence point, the pH continues to change, but at a slower rate compared to the pre-equivalence region. In the case of titrating a strong acid with a strong base or vice versa, the pH in this region approaches the pH of the excess titrant. Thus, if a strong acid is being titrated with a strong base, the pH will increase above 7. The shape and steepness of this region depend on the nature and concentration of the titrant and analyte.
These features collectively provide insight into the behavior of the titration, helping determine the equivalence point, the stoichiometry of the reaction, the strength of the acid or base, and the buffering capacity of the solution. Analyzing the pH curve allows for the proper interpretation of the experimental data obtained during titration.
Steam distillation is a technique used for the purification of substances, particularly volatile or organic compounds, which are highly sensitive to heat. It involves the process of separating a mixture based on the difference in boiling points of the components. The principle of steam distillation lies in the fact that when a substance is mixed with water and heated, the vapor produced will have a higher concentration of the more volatile component.
The procedure of purifying substances by steam distillation involves the following steps:
1. A mixture of the substance to be purified and water is placed in a distillation flask.
2. The mixture is heated, and as the temperature rises, vapor is produced. The vapor consists of the volatile component(s) of the mixture, along with steam.
3. The vapor passes through a condenser, where it is cooled and liquified.
4. The condensed liquid is collected in a separate flask, which contains the purified substance.
The conditions under which steam distillation is performed can vary depending on the specific substance or mixture being purified. However, some general conditions include maintaining a controlled temperature and ensuring a sufficient supply of water to produce steam.
Advantages of steam distillation include:
1. Preservation of the heat-sensitive components: Steam distillation allows for the separation of substances that would be damaged or decomposed by higher temperatures. By using steam as a heat transfer medium, the mixture can be heated more gently, preserving the integrity of the volatile components.
2. Removal of impurities: Steam distillation can effectively remove impurities from the substance being purified. As the volatile components vaporize along with the steam, any impurities left behind in the boiling flask are not carried over into the distilled product.
3. Relatively simple technique: Steam distillation is a straightforward and commonly used technique in the laboratory. It doesn't require sophisticated equipment or complex procedures, making it accessible and cost-effective.
Overall, steam distillation is a valuable method for purifying substances that are sensitive to high temperatures while efficiently separating the desired components from impurities.
http://www.rootmath.org | Linear Algebra
This will be a basic introduction to vectors. Vectors communicate 2 pieces of information, direction and length. Graphically we represent vectors with an arrow, and structurally we represent vectors with their components.
Explains variables, systems of equations, Cartesian coordinates, and many other concepts. Fun and educational for all ages.
This is a continuation of thermochemistry. The greatest component of this video is about enthalpy diagrams.
Solubility is an important concept in chemistry as it helps us understand the behavior of different substances when they interact with solvents. In particular, we will be focusing on the solubility of soluble salts and sparingly soluble salts.
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a given solvent. When a substance is soluble, it means it has the ability to dissolve in a significant amount in a particular solvent, while sparingly soluble substances can only dissolve in a small quantity.
Soluble salts are those that readily dissolve in a solvent, usually water, to form a homogeneous solution. These salts usually dissociate into their constituent ions when dissolved. For example, when table salt (sodium chloride) is dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-). This process is reversible, and the dissociated ions can recombine to form the original salt when the solvent is evaporated.
On the other hand, sparingly soluble salts have a limited ability to dissolve in a solvent. This means that only a small amount of the salt can dissolve, resulting in an unsaturated solution. Some examples of sparingly soluble salts include silver chloride (AgCl) and lead(II) iodide (PbI2). When these salts are added to water, only a small fraction will dissolve, while the rest will remain as solid particles.
There are several factors that affect the solubility of both soluble and sparingly soluble salts. They include temperature, pressure, and the presence of other substances in the solvent. For example, for most salts, their solubility increases with increasing temperature. However, this is not always the case, as some salts exhibit a decrease in solubility with increasing temperature.
Understanding the solubility of soluble and sparingly soluble salts is important for various applications in chemistry. It helps us predict the formation of precipitates when two solutions are mixed, determine the concentrations of ions in a solution, and even design drug formulations that can be readily absorbed by the body.
In conclusion, the solubility of soluble and sparingly soluble salts is a fundamental concept in chemistry. It allows us to understand the behavior of substances when they interact with solvents, and it has important applications in various fields of study. As advanced level chemistry students, it is crucial to grasp the concept of solubility and its implications in order to enhance our understanding of chemical reactions and equilibrium.
Lymph is the blood plasma that oozes out of the holes in the blood capillaries. The lymph vessels clear out this lymph and recirculate it back into the bloodstream. The lymph nodes contain WBCs that help provides immunity.
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Let's explore the central and the peripheral nervous system.
More free lessons & practice -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class9th
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Group VII in chemistry, also known as Group 17 or the halogens, is a group of elements found in the periodic table. This group consists of five elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). These elements are highly reactive and show similar trends in their chemical properties due to having seven valence electrons.
Here are some key characteristics and trends associated with Group VII chemistry:
1. Electron Configuration: All the elements in Group VII have outer electron configurations ending in ns^2np^5, where n represents the principal energy level. This electron arrangement means they require one additional electron to complete their octets and attain a stable electron configuration.
2. Reactivity: The halogens are highly reactive due to their strong desire to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration. They readily react with other elements to form compounds, particularly with alkali metals (Group I metals), such as sodium, to form salts known as halides.
3. Diatomic Molecules: The halogens exist as diatomic molecules in their elemental forms. For example, fluorine is found as F2, chlorine as Cl2, bromine as Br2, and iodine as I2. These diatomic molecules are the most stable forms of halogens at room temperature.
4. Physical Properties: The physical properties of the halogens vary, with fluorine being a pale yellow gas, chlorine a greenish-yellow gas, bromine a reddish-brown liquid, and iodine a shiny purple-black solid. Astatine is a rare and radioactive element that exists in trace amounts.
5. Reactivity Trend: As you move down Group VII, the reactivity of the halogens decreases. Fluorine is the most reactive element, while iodine is less reactive and requires more energy to undergo chemical reactions. Astatine is the least reactive element due to its radioactive nature and limited availability for study.
6. Oxidizing Agents: The halogens are strong oxidizing agents, meaning they readily accept electrons from other substances to undergo reduction themselves. They can oxidize many elements and compounds, forming halide ions (e.g., F-, Cl-, Br-, I-) in the process.
7. Uses: Halogens and their compounds have various applications. For example, chlorine plays a vital role in water treatment, fluorine is used in dental products and non-stick coatings, bromine is utilized in flame retardants, and iodine is used as a disinfectant and in medical applications.
Understanding the properties and reactivity trends of Group VII elements is crucial in many areas of chemistry, including chemical reactions, bonding, and understanding the behavior of halogen-based compounds.
Physical equilibria refer to the state of balance or stability between two or more phases of matter. Systems, phases, and components play a crucial role in understanding and analyzing physical equilibria.
A system can refer to a collection of components that interact with each other, and physical equilibria can occur within these systems. In particular, a one-component system refers to a system containing only one substance in more than one phase. For example, a water system can be composed of water in both liquid and vapor phases. Similarly, a carbon dioxide system can consist of carbon dioxide in both liquid and gaseous phases.
Phases are the different states of matter that can coexist in a system. For example, in a water system, liquid water and water vapor can coexist in a phase equilibrium. The state of equilibrium between these two phases is referred to as the saturation point or the boiling point. Similarly, a carbon dioxide system can exhibit a phase equilibrium between carbon dioxide in a gaseous and a liquid phase.
Components refer to the individual parts that make up a larger system. In a one-component system, the component refers to the substance that exists in multiple phases. For instance, in a carbon dioxide system, the component is carbon dioxide, which can exist in both gaseous and liquid phases.
An example of physical equilibria in a one-component system is the phase transition between water in liquid and vapor states. At a particular temperature, known as the boiling point, the vapor pressure of water equals the atmospheric pressure, resulting in the formation of water vapor. Similarly, in a carbon dioxide system, at a particular temperature and pressure, the vapor pressure of carbon dioxide equals the pressure above the liquid, resulting in the formation of gaseous carbon dioxide.
In conclusion, physical equilibria in one-component systems such as water and carbon dioxide systems are critical concepts in advanced-level students' studies. Understanding the relationships between systems, phases, and components is essential for comprehending physical equilibria and their applications in various fields such as chemistry, engineering, and physics.
One experiment that demonstrates the migration of ions during electrolysis is the electrolysis of water using a solution of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4). This experiment showcases the migration of both positively and negatively charged ions.
Materials:
1. 9-volt battery or a power source
2. Two graphite electrodes (pencil leads or graphite rods)
3. Sodium sulfate solution (Na2SO4)
4. Two wires with alligator clips
5. Beaker
6. Voltmeter (optional)
Procedure:
1. Fill a beaker with the sodium sulfate solution, ensuring that it covers the graphite electrodes completely.
2. Connect one graphite electrode to the positive terminal of the battery using a wire with an alligator clip.
3. Connect the other graphite electrode to the negative terminal of the battery using another wire with an alligator clip.
4. Immerse both graphite electrodes into the sodium sulfate solution, making sure that they do not touch each other.
5. Turn on the power source (battery) and allow the electrolysis process to occur for a few minutes.
Observations:
1. Bubbles start forming around both electrodes, indicating the release of gases.
- Oxygen gas (O2) will be produced at the positive electrode (anode).
- Hydrogen gas (H2) will be produced at the negative electrode (cathode).
Explanation:
During the electrolysis of water using the sodium sulfate solution, the following reactions occur at the electrodes:
At the anode (positive electrode):
2H2O(l) → O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e-
Water molecules break down, producing oxygen gas, positively charged hydrogen ions (H+), and releasing electrons.
At the cathode (negative electrode):
4H+(aq) + 4e- → 2H2(g)
The positively charged hydrogen ions (H+) from the water are reduced, accepting electrons to form hydrogen gas (H2).
This experiment clearly demonstrates the migration of ions in the solution. The positively charged hydrogen ions (H+) migrate towards the cathode, where they are reduced to form hydrogen gas. Conversely, the negatively charged sulfate ions (SO4 2-) remain in the solution as sodium sulfate is a neutral salt.
By observing the gases generated at each electrode, you can visualize and verify the migration of ions during electrolysis. Remember to exercise caution and perform this experiment under adult supervision, as electrolysis involves the use of electricity.
To distinguish between weak, strong, and non-electrolytes, you can perform an experiment known as the light bulb conductivity test. This experiment uses the ability of electrolytes to conduct electricity and complete a circuit, causing a light bulb to light up. Here's how to carry out this experiment:
Materials needed:
1. Light bulb
2. Battery or power source (of appropriate voltage for the light bulb)
3. Wires with alligator clips or connectors
4. Solutions of known weak electrolytes (e.g., acetic acid or vinegar)
5. Solutions of known strong electrolytes (e.g., sodium chloride or table salt)
6. Solutions of known non-electrolytes (e.g., sugar or ethanol)
7. Conductivity tester or conductivity meter (optional)
8. Glass containers or beakers
9. Disposable pipettes or droppers
Procedure:
1. Set up the circuit by connecting the positive terminal of the battery to the bottom terminal of the light bulb using a wire with an alligator clip or connector.
2. Connect the top terminal of the light bulb to one end of another wire.
3. Fill separate glass containers or beakers with solutions of the known weak electrolyte, known strong electrolyte, and known non-electrolyte.
4. Label each container with the corresponding solution.
5. Dip the free end of the wire from step 2 into one of the solutions.
6. Observe if the light bulb lights up or not.
7. Repeat steps 5-6 for each solution, noting whether the light bulb lights up or not.
Results and Interpretation:
- Weak electrolyte solution: If the light bulb glows dimly or flickers, it indicates that the weak electrolyte solution allows some conductivity and completes the circuit, but not as effectively as a strong electrolyte.
- Strong electrolyte solution: If the light bulb lights up brightly and stays consistently lit, it suggests that the strong electrolyte solution conducts electricity well and completes the circuit effectively.
- Non-electrolyte solution: If the light bulb does not light up at all, it suggests that the non-electrolyte solution does not allow any significant conductivity and does not complete the circuit.
By observing the behavior of the light bulb in each solution, you can distinguish weak, strong, and non-electrolytes based on their ability to conduct electricity and complete the circuit.
Electrolytic cells are devices that use an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, known as electrolysis. They consist of an anode, a cathode, an electrolyte, and an external power source.
- Anode: The electrode connected to the positive terminal of the power source. It carries out the oxidation half-reaction by losing electrons.
- Cathode: The electrode connected to the negative terminal of the power source. It carries out the reduction half-reaction by gaining electrons.
- Electrode: Conductive surfaces where the redox reactions occur. The anode and cathode are typically made of inert materials such as platinum or graphite.
- Electrolyte: A solution or molten substance that contains ions and allows the flow of electricity. Common examples include aqueous solutions of salts or acids.
- Electric Current: The flow of charged particles (ions or electrons) through a conductor. In electrolytic cells, the power source provides the necessary electrical energy for the movement of ions.
During electrolysis, the anode attracts negatively charged ions from the electrolyte and oxidizes them. This generates electrons that flow through the external circuit to the cathode. At the cathode, positively charged ions from the electrolyte are attracted, and reduction occurs as they gain electrons.
The overall process of electrolysis involves the decomposition of the electrolyte into its constituent ions. For example, in the electrolysis of water, water molecules (H2O) are split into hydrogen ions (H+) at the cathode and oxygen gas (O2) at the anode.
Electrolytic cells have various applications, including electroplating, metal refining, electrorefining, production of chemicals, and water splitting for hydrogen production.
Electrolysis is a process that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. It involves the splitting of a compound into its individual elements or ions using electricity.
The process of electrolysis takes place in an electrolytic cell, which consists of two electrodes - an anode and a cathode - immersed in an electrolyte solution. The anode is positively charged and the cathode is negatively charged. When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, positive ions migrate towards the cathode, while negative ions migrate towards the anode.
At the anode, oxidation occurs, causing the anode to lose electrons and become positively charged. This creates a flow of electrons through the external circuit, allowing the current to continue flowing. At the cathode, reduction occurs, causing the cathode to gain electrons and become negatively charged.
The electrolysis process can be used for various purposes, including extraction of metals from their ores, electroplating, and electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas.
Electrolysis is governed by Faraday's laws, which state that the amount of substance produced or consumed during electrolysis is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the cell. This allows for precise control and measurement of the products formed during electrolysis.
Overall, electrolysis is an important process in various industries, providing a means for generating new chemical substances and extracting valuable materials from compounds. It plays a crucial role in areas such as metallurgy, chemistry, and energy production.
Electrolysis is a process that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. It involves the splitting of a compound into its individual elements or ions using electricity.
The process of electrolysis takes place in an electrolytic cell, which consists of two electrodes - an anode and a cathode - immersed in an electrolyte solution. The anode is positively charged and the cathode is negatively charged. When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, positive ions migrate towards the cathode, while negative ions migrate towards the anode.
At the anode, oxidation occurs, causing the anode to lose electrons and become positively charged. This creates a flow of electrons through the external circuit, allowing the current to continue flowing. At the cathode, reduction occurs, causing the cathode to gain electrons and become negatively charged.
The electrolysis process can be used for various purposes, including extraction of metals from their ores, electroplating, and electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas.
Electrolysis is governed by Faraday's laws, which state that the amount of substance produced or consumed during electrolysis is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the cell. This allows for precise control and measurement of the products formed during electrolysis.
Overall, electrolysis is an important process in various industries, providing a means for generating new chemical substances and extracting valuable materials from compounds. It plays a crucial role in areas such as metallurgy, chemistry, and energy production.
Certainly! Here are a few more calculations involving Faraday's laws of electrolysis:
1. Calculation of Theoretical Yield:
Faraday's Second Law states that the ratio of the quantities of different substances formed or reacted at the electrodes is given by their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. Therefore, to calculate the theoretical yield of a product, you can use the formula:
Theoretical Yield = (Amount of Substance Formed at the Desired Electrode / Stoichiometric Coefficient)
Here, Amount of Substance Formed at the Desired Electrode refers to the quantity of the desired substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles), and Stoichiometric Coefficient is the coefficient of the desired substance in the balanced chemical equation.
2. Calculation of Charge Passed:
The total electric charge passed through the cell during electrolysis can be determined using Faraday's First Law. The formula is:
Charge Passed = Current × Time
Here, Current is the electric current passing through the cell (in Amperes), and Time is the duration of electrolysis (in seconds).
3. Calculation of Mass of a Substance:
To calculate the mass of a substance deposited or consumed during electrolysis, you can use the formula:
Mass of Substance = Amount of Substance × Molar Mass
Here, Amount of Substance is the quantity of the substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles), and Molar Mass is the molar mass of the substance (in g/mol).
4. Calculation of Faraday's Constant:
Faraday's Constant represents the amount of electric charge (in Coulombs) required to deposit or produce one mole of a substance during electrolysis. It can be calculated using the formula:
Faraday's Constant = (Current × Time) / Amount of Substance
Here, Current is the electric current passing through the cell (in Amperes), Time is the duration of electrolysis (in seconds), and Amount of Substance is the quantity of the substance formed or reacted at the electrode (in moles).
These calculations illustrate some applications of Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Make sure to use the appropriate units and values for accurate results.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis describe the fundamental relationship between the mass of a substance produced or consumed during electrolysis, the amount of electrical charge passed through the electrolyte, and the chemical properties of the substances involved. These laws are named after the British physicist and chemist Michael Faraday, who first described them in the early 19th century. There are two laws:
1. Faraday's First Law: The amount of a substance produced or consumed during electrolysis is directly proportional to the amount of electrical charge passed through the electrolyte.
Mathematically, this law can be expressed as:
Mass of substance produced / consumed ∝ Electrical charge passed
or,
m = zQ
where m is the mass of the substance produced or consumed, Q is the electrical charge passed, and z is a constant known as the electrochemical equivalent of the substance.
2. Faraday's Second Law: The amounts of different substances produced or consumed during electrolysis are directly proportional to their equivalent weights.
Mathematically, this law can be expressed as:
Mass of substance A / Mass of substance B = Equivalent weight of substance A / Equivalent weight of substance B
or,
m_A / m_B = EWE_A / EWE_B
where m_A and m_B are the masses of substances A and B produced or consumed, respectively, and EWE_A and EWE_B are the equivalent weights of A and B, respectively.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis are important because they explain the behavior of many electrochemical systems, and are used in a variety of applications, including electroplating, battery technology, and corrosion prevention.
Factors affecting the electrolytic conductivity of electrolytes include:
1. Concentration: The concentration of the electrolyte affects conductivity. Higher concentrations result in more ions available for conduction, thus increasing conductivity.
2. Nature of Electrolyte: Different electrolytes have varying conductivities. Strong electrolytes, such as strong acids or bases, dissociate fully into ions and tend to have higher conductivity compared to weak electrolytes.
3. Temperature: Temperature impacts the mobility of ions in solution. Generally, higher temperatures increase ionic mobility and, therefore, conductivity.
4. Solvent: The nature of the solvent also influences conductivity. Polar solvents, like water, enhance ion dissociation and promote conductivity compared to nonpolar solvents.
5. Presence of Impurities: Impurities, such as dissolved gases or other substances, can affect conductivity either positively or negatively. They can alter the movement of ions and thus impact conductivity.
6. Pressure: Pressure can influence the solubility and mobility of ions, impacting electrolyte conductivity. Higher pressure often leads to higher conductivity.
7. Electrolyte Purity: The purity of the electrolyte is vital. Impurities introduced during production or storage can interfere with conductivity.
8. Presence of Additives: Some additives can enhance or hinder conductivity. They may increase ion dissociation or introduce additional ions that influence conductivity.
It's essential to consider these factors when studying or using electrolytes for various applications, including electrochemistry, batteries, and electrolysis processes.
1. Electroplating: Electrolysis is used in the electroplating industry to coat objects with a thin layer of metal. For example, silver plating is used to enhance the appearance and durability of jewelry, while chrome plating is used to give a shiny finish to car parts.
2. Production of chlorine and hydrogen: Electrolysis of brine (a solution of sodium chloride) is used to produce chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. Chlorine is used in the production of PVC, bleach, and various plastics, while hydrogen gas is used in various industrial processes, such as the production of ammonia and in fuel cells.
3. Electrorefining: Electrolysis is used to purify crude metals obtained from mining operations. For example, electrolysis is used to purify copper, zinc, and nickel to remove impurities, resulting in high-quality metals that can be used in various industrial applications.
4. Water splitting: Electrolysis of water can separate it into hydrogen and oxygen gases. These gases can then be used as a fuel source, for example, in fuel cells which produce electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen.
5. Electroforming: Electrolysis is used in the process of electroforming, where a metal object is produced by depositing metal ions onto a substrate through electrolysis. This process is used to create complex and detailed metal objects, such as jewelry, statues, and precision mechanical components.
6. Electrochemical machining: Electrolysis is used in electrochemical machining processes where a metal workpiece is shaped or machined by controlled removal of material through electrolysis. This can be used to achieve precise and intricate machining on difficult-to-machine materials like superalloys.
7. Electrolytic cells for industrial processes: Electrolytic cells are used in various industrial processes, such as electrowinning and electrorefining, where metals are extracted or purified from their ores. This includes processes like the extraction of aluminum from bauxite ore through the Hall–Héroult process.
Overall, electrolysis has extensive applications in industries ranging from metal refining and plating to chemical production and energy generation.
Faraday's laws of electrolysis provide a framework for quantitative calculations involving the amount of electricity and the mass of substances deposited or liberated during electrolysis.
Here are the two main laws and some examples of calculations you can perform:
**Faraday's First Law:**
This law states that the **mass (m)** of a substance deposited or liberated at an electrode is **directly proportional** to the **amount of charge (Q)** passed through the electrolyte. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
```
m ∝ Q
```
where the symbol "∝" represents proportionality.
**Example 1:**
* You electrolyze copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution for 30 minutes with a current of 2 amps.
* You need to calculate the mass of copper deposited at the cathode.
**Steps:**
1. **Convert time to seconds:** 30 minutes * 60 seconds/minute = 1800 seconds.
2. **Calculate the total charge:** Q = I * t = 2 A * 1800 s = 3600 C.
3. **Look up the electrochemical equivalent (ECE) of copper:** This value is typically found in chemistry handbooks or online resources. Let's assume the ECE of copper is 0.0329 mg/C.
4. **Calculate the mass of copper deposited:** m = Q * ECE = 3600 C * 0.0329 mg/C = 118.44 mg.
**Faraday's Second Law:**
This law states that the **masses of different ions liberated at the electrodes** when the **same amount of electricity (Q)** is passed through **different electrolytes** are **directly proportional to their chemical equivalents (CE)**. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
```
m1 / m2 = CE1 / CE2
```
where:
* m1 and m2 are the masses of the deposited/liberated substances
* CE1 and CE2 are their respective chemical equivalents
**Example 2:**
* You electrolyze silver nitrate (AgNO3) and copper sulfate (CuSO4) solutions simultaneously with the same amount of charge (Q).
* You need to determine the ratio of the masses of silver and copper deposited.
**Steps:**
1. **Look up the chemical equivalents of silver and copper:** Let's assume the CE of silver (Ag) is 107.87 g/eq and the CE of copper (Cu) is 31.78 g/eq.
2. **Apply the second law equation:** m_Ag / m_Cu = CE_Ag / CE_Cu = 107.87 g/eq / 31.78 g/eq ≈ 3.4.
Therefore, the mass of silver deposited will be approximately 3.4 times the mass of copper deposited under the same conditions.
These are just two examples of calculations involving Faraday's laws. Remember, you'll need additional information like current, time, electrochemical equivalents, and chemical equivalents to perform these calculations effectively.
Molar conductivity, denoted by the symbol Λm, is a measure of a solution's ability to conduct electricity, specifically, the conductance of a solution containing one mole of the electrolyte placed between electrodes with a unit area and a distance of one unit length. It is influenced by several key factors:
**1. Concentration of the electrolyte:**
* Molar conductivity generally **increases with dilution** (decreasing concentration). This is because as the solution is diluted, the distance between ions increases, reducing the frequency of collisions and allowing them to move more freely under the influence of an electric field, thus, enhancing conductivity.
[Image of Molar conductivity vs concentration graph]
**2. Nature of the electrolyte:**
* The **degree of dissociation** of the electrolyte plays a crucial role. Strong electrolytes, which dissociate completely in solution, have a higher number of ions per unit volume, leading to higher molar conductivity compared to weak electrolytes, which dissociate only partially.
* The **size and charge of the ions** also influence conductivity. Smaller and highly charged ions have greater mobility and contribute more significantly to conductivity than larger or less charged ions.
**3. Temperature:**
* Molar conductivity generally **increases with temperature**. This is because as the temperature rises, the solvent molecules move faster and collide with the ions more frequently, imparting kinetic energy to the ions and increasing their average velocity. This, in turn, enhances their ability to carry current, leading to higher conductivity.
It's important to note that the relationship between molar conductivity and concentration is not linear. As the concentration approaches zero (infinite dilution), the molar conductivity reaches a limiting value, known as **limiting molar conductivity (Λ⁰m)**. This value represents the maximum conductivity achievable for the electrolyte and is independent of concentration.
Kohlrausch's law of independent migration of ions states that in a solution containing electrolytes, each ion contributes individually to the total conductivity of the solution and moves independently of the others present, unaffected by the presence of other ions. This law can be applied in various ways, including:
1. Determination of Molar Conductivity: The law allows for the calculation of the molar conductivity of an electrolyte solution by summing the ion contributions together. This helps to understand the electrical conductivity of the solution, which is essential in various chemical and biological applications.
2. Study of Electrolytes Behaviour: The law provides insights into the behavior of ions in the solution. It helps to understand how these ions interact with each other and with the solvent. This information is necessary in various fields such as industrial processes, environmental studies and health sciences.
3. Determining the Degree of Dissociation: The law can be used to determine the degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes by measuring their molar conductivity at different concentrations. The dissociation constant can then be calculated for different solvent conditions. This information is useful in chemical equilibrium studies.
4. Calculation of Ion Concentrations: Kohlrausch's law can be used in the determination of ion concentrations in solutions. By measuring the molar conductivity and knowing the molar conductivity values of individual ions, it is possible to calculate their concentrations using the law. This information is necessary in fields such as pharmacology and environmental studies.
Overall, Kohlrausch's law has significant applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, environmental, and health sciences.
The molar conductivity of electrolytes is influenced by the concentration of the solution. Here are some key points to understand the effect of concentration on molar conductivity:
1. Generally, the molar conductivity of an electrolyte decreases as the concentration increases.
2. This behavior is explained by the phenomenon of ion-ion interactions or the association of ions when the concentration increases.
3. Initially, at low concentrations, the ions are far apart from each other, resulting in minimal ion-ion interactions. This allows for higher mobility of the ions and a higher molar conductivity.
4. As the concentration increases, the ions come closer to each other, leading to a greater likelihood of ion-ion interactions or association. This hinders the mobility of the ions, reducing the molar conductivity.
5. At higher concentrations, the molar conductivity approaches a limiting value called the limiting molar conductivity (Λ°). This value represents the maximum molar conductivity attainable for the electrolyte under the given conditions.
6. The decrease in molar conductivity with increasing concentration can be described by Kohlrausch's law, which states that the molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the contributions of the individual ions in the solution.
7. In dilute solutions, where ion-ion interactions are minimal, the molar conductivity is mainly determined by the individual ion mobilities. As the concentration increases, the contributions from individual ion mobilities decrease due to increased ion-ion interactions.
8. Strong electrolytes, which undergo complete ionization in solution, show a more pronounced decrease in molar conductivity with increasing concentration compared to weak electrolytes.
In summary, as the concentration of an electrolyte increases, the molar conductivity tends to decrease due to increased ion-ion interactions or association. However, at very low concentrations, the molar conductivity is higher, indicating greater ion mobility.
Video Two on organic synthesis was a live TV show highlighting key concepts in organic synthesis
- Electrode potential refers to the potential difference or voltage between an electrode and its surrounding solution/electrolyte.
- It is a measure of the tendency of an electrode to gain or lose electrons, which determines its ability to undergo oxidation or reduction reactions.
- The electrode potential is influenced by various factors, including the nature of the electrode material, concentration of ions in the solution, temperature, and pressure.
- The standard electrode potential (E°) is the electrode potential measured under standard conditions, which include a concentration of 1 mole per liter, temperature of 298 Kelvin, and atmospheric pressure of 1 bar.
- Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is often used as a reference electrode for measuring electrode potentials. Its electrode potential is defined as zero.
- Electrons flow from the electrode with a lower potential to the electrode with a higher potential, following the direction of the electrochemical reaction.
- The difference in electrode potentials of two electrodes is related to the cell potential (Ecell) of an electrochemical cell, which can be used to determine the spontaneity and feasibility of a redox reaction.
- A positive electrode potential indicates a tendency for reduction, while a negative electrode potential indicates a tendency for oxidation.
- Electrode potential can be measured using various techniques, such as potentiometry, voltammetry, and electrochemical cells.
Please note that these are just summarized notes. If you require more in-depth information on any specific aspect, please let me know!
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is an important reference electrode used in electrochemistry. It serves as a baseline for comparing the electrode potentials of other half-reactions. The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in a solution with a hydrogen gas atmosphere at a fixed pressure.
The standard reduction potential of the SHE is defined as 0.00 V at all temperatures. This means that other reduction potentials can be measured relative to the SHE. By convention, the reduction potential of the SHE is considered positive when a half-reaction has a higher potential to be reduced compared to the SHE, and negative when it has a lower potential.
The half-reaction for the SHE is the reduction of protons (H+) to hydrogen gas (H2). This reaction takes place as follows:
2H+ + 2e- -> H2
The SHE is often used in electrochemical cells as a reference electrode, with another half-reaction occurring at a different electrode. The potential difference between the SHE and the other electrode is measured to determine the half-cell potential of the other electrode.
In practical situations, it is difficult to have a true SHE. Therefore, other reference electrodes such as the silver/silver chloride electrode are commonly used instead. However, these reference electrodes are calibrated using the SHE and have their own set standard reduction potentials.
The SHE is a crucial reference in electrochemistry as it allows for the determination of the standard reduction potentials of other half-reactions and the prediction of the feasibility of redox reactions. It provides a consistent reference point for measuring and comparing electrode potentials, which helps in understanding the principles and behaviors of electrochemical processes.
This is a zoom recorded video that will introduce A level students to THERMOCHEMISTRY. It was created to enhance learning during the Covid-19 Lockdown. Please like and share and subscribe to our you tube channel for more such videos.
This video looks to seek where Sin (Sine), Cos and Tan actually come from. Looking at the ratios of the sides of right angle triangles, we can notice certain patterns if we measure different right angle triangles with the same angles. Very similar to how ratios exist in circles with circumference and diameter to discover Pi.We can then make trig (trigonometry) tables for all the angles and then draw the graph of sin(x) which forms the sine wave.These trig ratios help us finding missing angles or sides in triangles by using SOHCAHTOA (SOH CAH TOA). The sine function can be obtained by taking ratios of triangle sides at different angles.Media, business and educational enquiries can be made to info@syedinstitute.comThank you for watching.
Common terms used in electrolysis and explanation of the changes that take place during electrolysis
Common Terms Used in Electrolysis:
Electrolyte: A substance that conducts electricity due to the presence of free ions. These ions can be dissolved in a solvent (like aqueous solutions) or molten.
Electrode: An electrical conductor in contact with an electrolyte. There are two types:
Anode: The positive electrode where oxidation occurs. Electrons flow out of the anode.
Cathode: The negative electrode where reduction occurs. Electrons flow into the cathode.
Electrolysis: The process of using electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. An external power source provides the energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction.
Electrolysis products: The substances formed at the electrodes during electrolysis. These products depend on the specific reaction occurring.
Electrolytic cell: A device used to carry out electrolysis, consisting of electrodes, an electrolyte, and a power source.
Changes During Electrolysis:
Electrolysis involves several key changes:
Electrical energy to chemical energy: The external power source provides electrical energy, which is converted into chemical energy to drive the non-spontaneous reaction.
Oxidation at the anode: Anions from the electrolyte lose electrons at the anode, undergoing oxidation. This can involve the electrode itself being oxidized or the oxidation of ions in the electrolyte.
Reduction at the cathode: Cations from the electrolyte gain electrons at the cathode, undergoing reduction.
Movement of ions: Ions in the electrolyte migrate towards the oppositely charged electrode to maintain electrical neutrality.
Formation of electrolysis products: The products of the oxidation and reduction reactions at the electrodes form the final electrolysis products.
Example: Electrolysis of water (H₂O):
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl)
Anode: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻ (Chlorine gas is produced at the anode)
Cathode: 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻ (Hydrogen gas is produced at the cathode)
Overall reaction: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (decomposition of water)
Note: This is a simplified example. The specific reactions and products depend on the nature of the electrolyte and the applied voltage.
Modes of conduction of substances, common terms used in electrolysis
## Modes of Conduction in Substances:
There are three main modes of conduction observed in different substances:
**1. Metallic Conduction:**
* **Description:** Involves the movement of **free electrons** within a metallic lattice. These electrons are not bound to any specific atom and can move freely throughout the metal.
* **Examples:** Metals like copper, aluminum, and silver are good conductors of electricity due to the presence of a large number of free electrons.
**2. Ionic Conduction:**
* **Description:** Occurs in **electrolytes** (molten salts or ionic solutions) where **ions** move through the solution carrying the charge.
* **Examples:** Aqueous solutions of salts like NaCl or molten salts like NaCl (liquid) conduct electricity through the movement of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
**3. Electronic Conduction in Semiconductors:**
* **Description:** Involves the movement of both **electrons** and **holes** (the absence of an electron in the valence band) in semiconductors. The conductivity can be controlled by applying external factors like doping or electric fields.
* **Examples:** Materials like silicon and germanium exhibit semiconducting behavior, where their conductivity can be tailored for various applications in electronics.
## Common Terms Used in Electrolysis:
* **Electrolyte:** A substance that conducts electricity due to the presence of free ions.
* **Electrode:** An electrical conductor that is in contact with an electrolyte.
* **Anode:** The positive electrode where oxidation occurs.
* **Cathode:** The negative electrode where reduction occurs.
* **Electrolysis:** The process of using electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
* **Electrolysis products:** The substances formed at the electrodes during electrolysis.
* **Electrolytic cell:** A device used to carry out electrolysis, consisting of electrodes, an electrolyte, and a power source.
* **Aqueous electrolysis:** Electrolysis involving water as the electrolyte.
* **Electroplating:** The deposition of a metal onto the cathode from a metal-containing solution.
* **Electrorefining:** The purification of a metal by removing impurities that go into the solution during electrolysis.
Understanding these terms and the different modes of conduction is crucial for comprehending the principles and applications of electrolysis in various fields like electroplating, battery technology, and chemical production.
This video was a live show on UBC-Star Tv in which students were introduced to the dos and donts of organic synthesis
describes distribution law of a solute between immiscible solvents and calculated examples . For A-level UACE Exams.
## Distribution Law: Understanding Solute Partitioning Between Immiscible Solvents
The **distribution law**, also known as **Nernst's partition law**, describes the **equilibrium distribution of a solute between two immiscible solvents**. In simpler terms, it explains how a solute will distribute itself between two non-mixing liquids at a constant temperature.
**Key Points:**
* **Immiscible solvents:** These are liquids that don't dissolve in each other, like oil and water.
* **Solute:** The substance that dissolves in both solvents.
* **Equilibrium:** A state where the concentration of the solute in each solvent remains constant over time, even though the molecules continue to move between the layers.
**The Law:**
The distribution law states that the **ratio of the equilibrium concentrations of a solute in two immiscible solvents is constant at a constant temperature**. This constant ratio is called the **distribution coefficient** or **partition coefficient**, denoted by **K<sub>d</sub>**.
**Mathematically:**
```
K_d = C₁ / C₂
```
where:
* C₁ is the concentration of the solute in solvent 1
* C₂ is the concentration of the solute in solvent 2
**Factors Affecting Kd:**
* **Nature of the solute:** Solutes with more affinity for one solvent will have a higher concentration in that solvent, leading to a larger Kd value.
* **Nature of the solvents:** The polarity and ability of solvents to interact with the solute influence the distribution.
* **Temperature:** Kd can change slightly with temperature, although the change is often negligible for most A-Level applications.
**Applications:**
* **Extraction:** Separating a desired compound from a mixture by selectively dissolving it in one solvent and separating the layers.
* **Chromatography:** Utilizing the differing distribution behavior of components to separate them in a mixture.
* **Understanding drug action:** Predicting how drugs distribute between different compartments in the body based on their lipophilicity (affinity for fats).
**Calculated Examples:**
**Example 1:**
A solution of benzoic acid is shaken with water and benzene. After reaching equilibrium, the concentration of benzoic acid in the benzene layer (0.1 M) is found to be ten times higher than its concentration in the water layer (0.01 M). Calculate the distribution coefficient (Kd) for benzoic acid between benzene and water.
```
K_d = C_benzene / C_water = 0.1 M / 0.01 M = 10
```
**Example 2:**
A dye has a Kd value of 5 between chloroform and water. If 10 mg of the dye is dissolved in 10 mL of chloroform, how much dye will be present in 100 mL of water after reaching equilibrium?
* We can assume the initial concentration of the dye in chloroform (C_chloroform) is 1 mg/mL (10 mg / 10 mL).
* We need to find the equilibrium concentration in water (C_water).
```
K_d = C_chloroform / C_water
5 = 1 mg/mL / C_water
C_water = 0.2 mg/mL
```
Therefore, at equilibrium, 0.2 mg/mL x 100 mL = 20 mg of the dye will be present in the water layer.
**Remember:** These are just basic examples. A-Level UACE Exams might involve more complex scenarios and calculations related to distribution law, requiring a deeper understanding of the concepts and their applications.
Describes the chemistry of transition elements; vanadium, chromium and cobaltVanadium and its compound- characteristics of vanadium as transition element- important compound of vanadium such as vanadium pentoxide in contact process.Chromium and its compounds-properties of chromium as transition element- reaction of chromium with air, water, acids, and sodium hydroxide- half reduction equations for chromates and dichromate- inter-conversion of chromates and dichromates- isomerism in chromium (III) chloride hexahydrate, CrCl3.6H2O -hydrolysis of chromium (III) compounds- qualitative analysis of chromium (III) ionsCobalt and its compounds-properties of cobalt as a transition elementqualitative analysis of cobalt (II) ions
## Chemistry of Vanadium, Chromium, and Cobalt (A-Level Chemistry)
These three elements are all **transition metals** located in Group 5, 6, and 7 of the periodic table, respectively. They share some general properties of transition metals, including:
* **Variable oxidation states:** They can exhibit multiple oxidation states due to the availability of electrons in their d-orbitals.
* **Formation of colored compounds:** Their d-orbitals can participate in bonding, leading to various colors in their compounds.
* **Ability to form complexes:** They can form complex ions with various ligands, influencing their properties and reactivity.
Here's a detailed look at the individual chemistry of each element:
**Vanadium (V):**
* **Oxidation states:** +5, +4, +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Vanadium pentoxide (V₂O₅): Used as a catalyst in the Contact process for sulfuric acid production.
* Vanadyl sulfate (VO(SO₄)): Used in photography and as a mordant in dyeing.
* **Properties:**
* Exhibits various colors depending on the oxidation state.
* Vanadium(V) compounds are strong oxidizing agents.
* Forms oxoacids like vanadic acid (HVO₃).
**Chromium (Cr):**
* **Oxidation states:** +6, +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Sodium dichromate (Na₂Cr₂O₇): Used as an oxidizing agent in various reactions.
* Potassium chromate (K₂CrO₄): Used as a pigment and corrosion inhibitor.
* Chromium(III) chloride hexahydrate (CrCl₃•6H₂O): Used as a mordant in dyeing and tanning leather.
* **Properties:**
* Chromium(VI) compounds are strong oxidizing agents and can be carcinogenic.
* Chromium(III) is the most stable oxidation state and forms many stable complexes.
* Exhibits various colors depending on the oxidation state and ligand environment.
**Cobalt (Co):**
* **Oxidation states:** +3, +2
* **Important compounds:**
* Cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl₂): Used as a desiccant and catalyst.
* Cobalt(II) sulfate (CoSO₄): Used in electroplating and pigments.
* Vitamin B₁₂: Contains cobalt(III) and is essential for human health.
* **Properties:**
* Forms many stable complexes with various ligands.
* Exhibits different colors depending on the oxidation state and ligand environment.
* Cobalt(II) compounds are often used as catalysts.
**Additional points to consider:**
* **Redox reactions:** All three elements can undergo redox reactions, involving changes in their oxidation states.
* **Complex formation:** Vanadium, chromium, and cobalt can form complexes with various ligands, influencing their properties like color, stability, and reactivity.
* **Industrial applications:** These elements and their compounds have numerous applications in various industries, including catalysis, pigments, dyes, and electroplating.
**Remember:** This is a general overview, and A-Level chemistry might delve deeper into specific aspects like reaction mechanisms, spectroscopic analysis, and industrial processes related to these elements. It's recommended to consult your textbook or other resources for more detailed information.
Reaction of alkyl halide with hot potasium hydroxide in ethanol to form alkenesAlkyl halides react with alkalis to form alcoholsPotassium cyanides react and increase the carbon chains with alkyl halidesAlkyl halides couples in presence of sodium and ethyl ether to form alkanes with twice the carbon atoms as the parent chainAlkyl halides Form Gridnard’s reagents when reacted with magnesium and dry ether
Classification of aminesboiling and melting points of aminesolubility of aminesbasicity of aminespreparation of amines from alkyl halides, cyanides, nitroalkanesHofmann's degredation
## Amines: Comprehensive Notes
**1. Classification:**
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH₃) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified into four primary types based on the number of alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom:
* **Primary (1°):** One alkyl/aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., CH₃NH₂ - Methylamine)
* **Secondary (2°):** Two alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., (CH₃)₂NH - Dimethylamine)
* **Tertiary (3°):** Three alkyl/aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom (e.g., (CH₃)₃N - Trimethylamine)
* **Quaternary (4°):** All four positions around the nitrogen atom are occupied by alkyl/aryl groups, resulting in a positively charged cation (e.g., [(CH₃)₄N⁺]Cl⁻ - Tetramethylammonium chloride)
**2. Physical Properties:**
* **Boiling and Melting Points:**
* Generally increase with increasing chain length of the alkyl/aryl groups due to stronger London dispersion forces.
* Branching in the chain can decrease boiling and melting points due to a decrease in surface area and weaker intermolecular interactions.
* Amines generally have lower boiling and melting points compared to similarly sized alcohols due to the absence of hydrogen bonding in amines.
* **Solubility:**
* Lower amines (primary and secondary) exhibit good water solubility due to the ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
* Solubility in water decreases with increasing size and branching of the alkyl/aryl groups due to the dominance of hydrophobic interactions over hydrogen bonding.
* Tertiary and quaternary amines with no N-H bonds are typically less soluble in water but may show solubility in organic solvents.
**3. Basicity:**
Amines exhibit basic character due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. This lone pair can accept a proton from acids, forming a positively charged ammonium ion. The basicity of amines follows the trend:
**Tertiary > Secondary > Primary > Ammonia**
Several factors influence the basicity of amines:
* **Inductive effect:** Electron-donating groups (e.g., alkyl groups) attached to the nitrogen atom increase basicity by pushing electron density towards the nitrogen, making it more willing to accept a proton.
* **Steric hindrance:** Bulky groups around the nitrogen atom hinder the approach of a proton, decreasing basicity.
**4. Preparation:**
Amines can be synthesized through various methods, some of the most common being:
* **Alkylation of ammonia or amines:** Reaction of ammonia or amines with alkyl halides under suitable conditions (e.g., heating with KOH).
* **Reduction of nitriles:** Conversion of nitriles (R-CN) to primary amines (R-CH₂NH₂) using reducing agents like LiAlH₄ or catalytic hydrogenation.
* **Reduction of nitroalkanes:** Conversion of nitroalkanes (R-NO₂) to primary, secondary, or tertiary amines depending on the reaction conditions and reducing agent used.
* **Gabriel synthesis:** Synthesis of primary amines from phthalimide using strong bases and alkyl halides.
**5. Hofmann Degradation:**
This reaction allows the conversion of a primary amide to a primary amine with one fewer carbon atom. The process involves treating the amide with bromine (Br₂) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), leading to rearrangement and cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond.
**6. Applications of Amines:**
Amines have diverse applications in various fields, including:
* **Pharmaceuticals:** Many drugs, such as antidepressants, decongestants, and antihistamines, contain amine groups.
* **Dyes and pigments:** Amines are used in the production of various dyes and pigments used in textiles, paints, and plastics.
* **Polymers and resins:** Amines are essential components in the synthesis of various polymers like nylon and resins used in adhesives and coatings.
* **Agrochemicals:** Some herbicides and insecticides contain amine functionalities.
* **Surfactants:** Quaternary ammonium salts are used as cationic surfactants in detergents and fabric softeners.
**7. Safety Considerations:**
Amines can exhibit various toxicities depending on their structure and properties. It is crucial to handle them with appropriate safety precautions, including wearing gloves, eye protection, and working in well-ventilated areas. Some amines may be flammable or corrosive, and proper handling procedures should be followed.
reaction of amines with acidsreaction of amines with alkanoyl halidesreaction of primary amines with carbonyl compoundsmeans of distinguishing between classes of amines
1. Reaction of Amines with Acids:
When amines react with acids, they undergo acid-base reactions to form salts. The amine acts as a base and accepts a proton (H+) from the acid. The resulting salt is formed by the ammonium cation (RNH3+) and the anion of the acid.
Example: RNH2 + HCl → RNH3+Cl-
2. Reaction of Amines with Alkanoyl Halides:
Amines can also react with alkanoyl halides (acyl halides) to form amides. The halogen atom attached to the alkanoyl halide is replaced by the amine group, resulting in the formation of an amide bond.
Example: RNH2 + RCOX → RCONHR + HX (where X = halogen atom)
3. Reaction of Primary Amines with Carbonyl Compounds:
Primary amines can react with carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes or ketones, to form imines or Schiff bases. In this reaction, the nitrogen of the primary amine forms a double bond with the carbon of the carbonyl group.
Example: RCH=O + RNH2 → RCH=NHR + H2O
Means of distinguishing between classes of amines:
There are several methods to distinguish between different classes of amines, including:
1. Solubility: Primary amines are generally more soluble in water compared to secondary and tertiary amines due to the presence of a hydrogen atom on the nitrogen, which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
2. N-Methylation: Primary amines can be methylated by treatment with methyl iodide and a base to form a tertiary amine. Secondary amines can also be methylated to form quaternary ammonium salts.
3. Reaction with Nitrous Acid: Primary amines react with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form a diazonium salt, which is an unstable compound. Secondary and tertiary amines do not react with nitrous acid. This reaction can be used as a distinguishing test.
4. Boiling Point: Tertiary amines generally have higher boiling points compared to primary and secondary amines due to the presence of more alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, which increase intermolecular forces.
5. Chromatographic Methods: Techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or gas chromatography (GC) can be used to separate and analyze different classes of amines based on their different retention times or chromatographic behavior.
Follow Us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ic3movement1/
Follow Us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ic3movement
Presented as part of the 2017 Annual IC3 Conference inauguration program: a tribute to Teacher Molly Abraham.
IC3 Movement: https://www.ic3movement.com/
IC3 Live: https://ic3live.com/
chemistry of period 2 elements and diagonal relationships for Advanced Level students
The period 2 elements in the periodic table include lithium (Li), beryllium (Be), boron (B), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), fluorine (F), and neon (Ne). These elements display a wide range of chemical properties and behaviors due to variations in their atomic structure and electron configurations.
1. Lithium (Li): Lithium is the lightest metal in the periodic table and is highly reactive. It readily loses its outermost electron to form a Li+ cation, making it a strong reducing agent. Lithium compounds are used in batteries, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Beryllium (Be): Beryllium is a lightweight alkaline earth metal. It is strong, lightweight, and resistant to high temperatures, making it valuable in industries such as aerospace and nuclear power. Beryllium oxide is used as a ceramic material and a thermal conductor.
3. Boron (B): Boron is a metalloid with both nonmetallic and metallic properties. It forms covalent bonds and exhibits variations in hybridization, resulting in a diverse range of compounds. Boron compounds have numerous applications, including as fertilizers, flame retardants, and as a component in borosilicate glass.
4. Carbon (C): Carbon is a nonmetal that forms the basis of organic chemistry. It has four valence electrons, allowing it to form a large variety of compounds with other elements. Carbon compounds include hydrocarbons, such as methane and ethane, as well as complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and DNA.
5. Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is a diatomic nonmetal that makes up about 78% of Earth's atmosphere. It is relatively inert and forms strong triple bonds between nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen compounds are important in fertilizers, explosives, and as a coolant in various applications.
6. Oxygen (O): Oxygen is a highly reactive nonmetal that readily forms compounds, including oxides. It is essential for respiration and combustion processes. Oxygen also plays a crucial role in the ozone layer of the Earth's atmosphere.
7. Fluorine (F): Fluorine is the most electronegative element and is highly reactive. It is a diatomic nonmetal that reacts with almost all other elements, often resulting in the release of energy. Fluorine compounds are used in toothpaste, refrigerants, and in the production of plastics.
8. Neon (Ne): Neon is a noble gas and has a completely filled valence electron shell. It is chemically inert and does not readily form compounds. Neon is commonly used in neon signs due to its bright orange-red glow when an electric current passes through it.
These period 2 elements demonstrate a wide range of chemical behaviors and applications, from highly reactive metals (such as lithium) to non-reactive noble gases (such as neon). Their properties and reactivities are a result of their electronic configurations and atomic structures.
Here are some examples of reactions involving period 2 elements:
1. Lithium and water: Lithium reacts vigorously with water to produce lithium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The reaction is highly exothermic and liberates a large amount of heat.
2. Beryllium and oxygen: Beryllium reacts with oxygen to form beryllium oxide. This reaction is highly exothermic and releases a large amount of heat.
3. Carbon and oxygen: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. This reaction occurs during combustion processes and is responsible for the production of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
4. Nitrogen and hydrogen: Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia in the Haber process. The reaction is catalyzed by an iron catalyst and occurs at high temperature and pressure.
5. Oxygen and hydrogen: Oxygen reacts with hydrogen to form water. This reaction occurs during combustion processes, and it is also an important component of the water cycle.
6. Fluorine and metals: Fluorine reacts vigorously with metals to form metal fluorides. This reaction is highly exothermic and can result in the release of toxic fluorine gas.
7. Beryllium and acids: Beryllium reacts readily with acids to form beryllium salts and hydrogen gas. This reaction can release hydrogen gas, which may pose a hazard.
8. Boron and halogens: Boron reacts with halogens, such as chlorine and fluorine, to form boron halides. These compounds are often used as reagents in organic chemistry reactions.
9. Carbon and water: Carbon can react with water to produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of chemical reactions that period 2 elements can participate in. The reactivity and behavior of each element are related to its electronic structure and valence electron configuration.
Physical chemistry for A level students especially for those for UACE exams in Uganda
Acid-base indicators are substances that undergo a color change in response to changes in the pH of a solution. They are often used in chemical experiments and titration procedures to determine the endpoint of an acid-base reaction. Different indicators have different pH transition ranges and colors, allowing for the identification of the pH range during a titration.
pH titration curves, on the other hand, are graphical representations of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of a titrant added during a titration. In an acid-base titration, a solution of known concentration (titrant) is slowly added to a solution of unknown concentration (analyte) until the reaction between the two is complete. The pH titration curve plots the pH of the solution being titrated against the volume of titrant added.
The shape of a pH titration curve depends on the nature of the acid and base involved in the reaction, as well as their relative concentrations. The curve typically starts at a low pH when only the acid is present, rises gradually as the titrant is added, and eventually undergoes a rapid change near the equivalence point, where stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have reacted. After the equivalence point, the curve levels off and remains at a high pH when only excess base is present.
The behavior of the pH titration curve depends on the strength of the acid and base being titrated. For strong acids and strong bases, the curve is relatively steep around the equivalence point, resulting in a sharp endpoint and a well-defined titration. For weak acids and weak bases, the curve will be smoother and have a more gradual change around the equivalence point, making it more difficult to determine the exact endpoint of the titration.
By using acid-base indicators in titrations, the color change of the indicator can be used to visually identify the endpoint of the titration. The indicator is chosen based on its pH transition range, which is the pH range over which the indicator changes color. For example, phenolphthalein is often used as an indicator in acid-base titrations, as it changes from colorless to pink in a pH range of 8.2 to 10.0. By observing the color change of the indicator, the endpoint of the titration can be determined, indicating that the reaction is complete.
In summary, acid-base indicators are substances that change color in response to changes in pH, allowing for the observation of endpoint during titrations. pH titration curves, on the other hand, are graphical representations of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of titrant added during a titration. They depict the behavior of pH during a titration and can be used to determine the equivalence point and the strength of the acid and base involved.
physical chemistry; hydrolysis of salts for A-level students
In chemistry, hydrolysis of salts refers to the reaction of a salt with water, resulting in the formation of an acidic or basic solution. Salts are ionic compounds formed from the neutralization of an acid and a base. When a salt dissolves in water, it dissociates into its component ions, which can either be acidic, basic, or neutral.
The hydrolysis of salts can be classified into two categories: acidic hydrolysis and basic hydrolysis, depending on the nature of the salt and the pH of the resulting solution.
1. Acidic hydrolysis: This type of hydrolysis occurs when the salt formed from a weak acid and a strong base is dissolved in water. The anion of the salt acts as a base and reacts with water to produce hydroxide ions and the corresponding acid. For example, when ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis according to the equation:
NH4Cl + H2O ⇌ NH3 + HCl
The ammonium ion (NH4+) acts as an acid and donates a proton to the water, forming ammonium hydroxide (NH3) and hydronium ion (H3O+). The chloride ion (Cl-) acts as a base and accepts a proton from water, forming hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hydroxide ion (OH-).
2. Basic hydrolysis: This type of hydrolysis occurs when the salt formed from a strong acid and a weak base is dissolved in water. The cation of the salt acts as an acid and reacts with water to produce hydronium ions and the corresponding base. For example, when sodium acetate, NaC2H3O2, is dissolved in water, it undergoes hydrolysis according to the equation:
NaC2H3O2 + H2O ⇌ Na+ + C2H3O2- + H3O+ + OH-
The sodium ion (Na+) and acetate ion (C2H3O2-) remain unchanged, while water reacts with a small fraction of acetate ions to form acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and hydroxide ion (OH-). At the same time, water reacts with a small fraction of hydronium ions to form hydronium ion (H3O+) and hydroxide ion (OH-).
In summary, hydrolysis of salts can either produce acidic or basic solutions, depending on the nature of the salt and the pH of the resulting solution. Understanding the hydrolysis of salts is important in various chemical and biochemical processes, including the buffering capacity of biological fluids and the maintenance of pH in water treatment processes.
worked examples to thermodynamics question
this academic video for Advanced level students taking chemistry for UACE exams; it describes equilibrium constant Kc and its application with several worked examples.
In chemistry, equilibrium refers to a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction are equal. This means that the concentration of reactants and products remain constant over time, even though the reactions continue to occur. At equilibrium, the system is said to be in a dynamic balance.
The equilibrium constant, denoted by Kc, is a numerical value that represents the ratio of the concentrations of products to the concentrations of reactants, with each concentration raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation. The equilibrium constant expression is written as:
Kc = [C]^c [D]^d / [A]^a [B]^b
Where A, B, C, and D represent the reactants and products, and a, b, c, and d represent their stoichiometric coefficients.
The equilibrium constant is a measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds toward the formation of products. It is a constant at a given temperature and is independent of the initial concentrations of the reactants. The value of Kc reflects the relative concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant provides information about the position of equilibrium.
- If Kc > 1, it indicates that the equilibrium favors the products. This means that at equilibrium, the concentration of the products is higher compared to the concentrations of the reactants.
- If Kc < 1, it suggests that the equilibrium favors the reactants. At equilibrium, the concentration of the reactants is higher compared to the concentrations of the products.
- If Kc = 1, it signifies that the reactants and products are present in roughly equal concentrations at equilibrium.
The equilibrium constant provides insights into the direction in which a reaction will proceed or which species will be present in greater abundance at equilibrium. It also allows for predictions about the effect of changes in concentration, temperature, or pressure on the position of equilibrium.
reactions of amines in A-level organic chemistry
Certainly! Amine chemistry refers to the branch of organic chemistry that focuses on the study of compounds containing amine functional groups (-NH2). Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups.
Amines can be classified into three main types based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom:
1. Primary Amines: These are amines where one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. They have the general formula R-NH2.
2. Secondary Amines: In secondary amines, two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. They are represented by the general formula R2-NH.
3. Tertiary Amines: Tertiary amines have three alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Their general formula is R3-N.
Amine chemistry plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, materials science, and biochemistry. Amines can participate in various reactions, such as substitution, oxidation, reduction, condensation, alkylation, and acylation.
Some notable reactions involving amines include:
1. Amine substitution: Amines can undergo substitution reactions with various electrophiles, wherein the amino group is replaced by another atom or group. This allows for the introduction of different functional groups onto the amine molecule.
2. Amine oxidation: Amines can be oxidized to form amine oxides or further oxidized to form nitro compounds. This reaction is commonly achieved using oxidizing agents such as peroxides or metal oxides.
3. Amine reduction: Amines can be reduced to form secondary or tertiary amines, or even to primary amines from nitro compounds. Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation can be used for these reactions.
4. Amine condensation: Amines can undergo condensation reactions, combining with other compounds to form imines, enamines, or Schiff bases. These reactions are often used in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and pharmaceuticals.
5. Amine alkylation and acylation: Amines can be alkylated or acylated to form N-alkyl or N-acyl amines, respectively. These reactions involve the addition of an alkyl or acyl group to the nitrogen atom of the amine.
Understanding amine chemistry is crucial for designing and synthesizing new molecules with specific properties and functions. It allows chemists to modify amine-containing compounds for various applications, including drug design, organic synthesis, and materials science.
Rate, rate law, rate equation, the rate constant, the order of reaction with worked examples
Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence those rates. It involves the measurement and analysis of reaction rates, the determination of reaction mechanisms, and the understanding of how reaction rates can be altered.
Here are some important concepts and topics in chemical kinetics at an advanced level:
1. Reaction Rate: The reaction rate represents how fast a reactant is consumed or how fast a product is formed in a chemical reaction. It is typically expressed as the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time.
2. Rate Law: The rate law for a chemical reaction relates the rate of the reaction to the concentrations of the reactants. It is determined experimentally and is expressed as a mathematical equation. The rate law shows the order of reaction with respect to each reactant and the overall order of the reaction.
3. Rate Constant: The rate constant (k) is a proportionality constant in the rate equation that quantifies the relationship between the rate of the reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. It is specific to a given reaction at a given temperature and is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and catalysts.
4. Activation Energy: Activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that must be overcome for reactant molecules to transform into products. The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant to the activation energy and temperature.
5. Reaction Mechanisms: Reaction mechanisms describe the step-by-step sequence of elementary reactions that lead to the overall reaction. Elementary reactions involve the collision or interaction of individual molecules or atoms. Determining the reaction mechanism provides insight into the detailed pathway of the reaction.
6. Reaction Order: The reaction order of a reactant determines how changes in its concentration affect the reaction rate. The reaction order can be zero, first, second, or a combination of these orders. The overall reaction order is the sum of the individual reaction orders.
7. Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. They provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts can significantly influence reaction rates and are extensively used in industrial processes.
8. Temperature and Reaction Rate: Temperature plays a crucial role in determining reaction rates. Increasing temperature generally increases the rate of a reaction by increasing the number of collisions and providing greater kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier.
9. Reaction Rate Laws and Integrated Rate Laws: Reaction rate laws and integrated rate laws describe the relationship between reactant concentrations and time during a chemical reaction. They can be used to determine reaction orders, rate constants, and monitor the progress of a reaction.
10. Reaction Kinetics and Equilibrium: The study of reaction kinetics provides insights into the time-dependent behavior of chemical reactions. It helps in understanding how reaction rates change as a system approaches equilibrium and how reaction conditions can be manipulated to shift the equilibrium position.
These concepts represent a deeper level of understanding in chemical kinetics, and they are often explored in advanced level chemistry courses and research. The study of chemical kinetics is essential for understanding reaction mechanisms, designing efficient chemical processes, and predicting the behavior of chemical systems.
Carbon and its compounds (hydrides, halides, oxides, Carbonic acids);
Silicon and its compounds (reaction of silicon dioxide with sodium hydroxide and hydrogen fluoric acid)
compounds of germanium, tin and lead (oxides, chlorides, nitrates)
mechanism of electrolysis, factors affecting selective discharge, application of electrolysis, extraction of sodium, preparation of sodium hydroxide, Faraday's laws of electrolysis
Here are some examples of applications of electrolysis:
1. Electroplating: Electroplating is a process that uses electrolysis to deposit a layer of metal onto the surface of an object. It is commonly used to enhance the appearance, protect against corrosion, or improve conductivity of objects. For example, jewelry, automotive parts, and electronic components undergo electroplating.
2. Electrorefining of Metals: Electrorefining is the process of purifying impure metals using electrolysis. Impure metal is used as the anode, and a pure metal or graphite rod is used as the cathode. Through electrolysis, the impurities are dissolved into the electrolyte or settle as a sludge, leaving a pure metal at the cathode. This process is used in the refining of copper, lead, and other metals.
3. Electrolytic Cells for Energy Storage: Electrolytic cells, such as electrolyzers, are used to store energy in the form of chemical compounds. For example, during periods of excess renewable energy production, electrolyzers can use the electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. The hydrogen gas can be stored for later use as a fuel source in fuel cells or for powering vehicles.
4. Chlor-Alkali Industry: The chlor-alkali industry relies heavily on electrolysis. In this industry, electrolysis is used to produce chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and alkali metal hydroxides (such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) simultaneously. These compounds have various industrial applications, including the production of bleach, detergents, paper, and textiles.
5. Electrolysis in Water Treatment: Electrolysis can be used for water treatment and disinfection. By applying an electrical current through water, electrolysis can produce disinfecting agents such as chlorine or ozone. These agents can effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens present in water.
6. Electrolysis in Electrochemical Cells: Electrochemical cells, such as batteries and fuel cells, rely on electrochemical reactions driven by electrolysis. For example, rechargeable batteries like lithium-ion batteries use electrolysis during the charging process, allowing the flow of ions between electrodes.
7. Electrolysis in Electrolytic Capacitors: Electrolytic capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for energy storage. These capacitors are constructed using an electrolyte, which undergoes electrolysis during operation. The electrolysis maintains the capacitance and enables energy storage in the capacitor.
These are just a few examples of the numerous applications of electrolysis in various industries and technological advancements. Electrolytic processes involving electrolysis have a significant impact on our daily lives, from manufacturing processes to energy storage and environmental solutions.
the resistance of the electrolyte, the resistivity of electrolyte, the conductivity of electrolytes, molar conductivity, molar conductivity at infinite dilution, conductometric curves
Electroconductivity, in the context of A-Level studies, refers to the ability of a substance or solution to conduct electricity. Here are some key points about electroconductivity at the A-Level:
1. Electrical Conductivity: Electrical conductivity is a measure of how well a substance allows the flow of electric current through it. Materials or solutions that are good conductors have high electrical conductivity, while those that impede the flow of current have low electrical conductivity.
2. Conductivity and Ions: The ability of a substance to conduct electricity is directly related to the presence of mobile charge carriers. In the case of solutions, the presence of ions in solution allows the solution to conduct electricity. In solid conductors, delocalized electrons enable the flow of current.
3. Electrolytes: Substances that readily form ions in solution are called electrolytes. Electrolytes can be strong or weak depending on their ability to ionize completely or partially. Strong electrolytes, such as strong acids or salts, produce a high concentration of ions and thus have high electrical conductivity. Weak electrolytes, on the other hand, produce a lower concentration of ions and have lower electrical conductivity.
4. Ionic Solutions: Ionic solutions, which contain ions in solution, exhibit higher electrical conductivity compared to non-ionic solutions. This is because ions act as charge carriers and facilitate the flow of current.
5. Ionic Compound Dissociation: When an ionic compound dissolves in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions. The dissociation of the compound into ions increases electrical conductivity, as the resulting solution contains mobile ions.
6. Conductivity Measurements: The electrical conductivity of a solution is typically measured using a conductivity meter. This device measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electric current and provides a numerical value for the conductivity.
7. Factors Affecting Conductivity: The electrical conductivity of a solution is influenced by several factors. Temperature, concentration of ions, and the presence of impurities can all affect the conductivity of a solution.
8. Applications: Understanding electroconductivity is important in various applications, such as in the design and operation of electrochemical cells, batteries, circuitry, and conductivity-based sensors. It is also relevant in fields like environmental science, where water quality is assessed based on its electrical conductivity.
These points provide a basic overview of electroconductivity at the A-Level. Further exploration of the topic can involve studying conductivity measurements, conductivity trends across the periodic table, and the relationship between conductivity and electrolysis or galvanic cells.u
Phases and factors affecting the phase of a substance, physical chemistry A-level.
Physical Equilibria, also known as physical phase equilibria, refers to the equilibrium between different physical states of matter such as solid, liquid, and gas. Here are some key points about physical equilibria:
1. Phase Transitions: Physical equilibria involve phase transitions, which are the changes of a substance from one phase to another. Common phase transitions include solidification (from liquid to solid), melting (from solid to liquid), vaporization (from liquid to gas), condensation (from gas to liquid), sublimation (from solid to gas), and deposition (from gas to solid).
2. Equilibrium Conditions: For a physical equilibrium to be established, the rates of the forward and backward phase transitions must be equal. This means that the amount and concentration of each phase remain constant over time.
3. Equilibrium Temperature: Each phase transition occurs at a specific temperature, known as the equilibrium temperature. This temperature depends on the pressure and composition of the system.
4. Phase Equilibrium Diagrams: Phase equilibrium diagrams, such as the water phase diagram or the phase diagram of a substance, provide a graphical representation of the conditions at which different phases coexist in equilibrium. These diagrams show the temperature and pressure ranges for each phase and the boundaries between them.
5. Triple Point: The triple point on a phase equilibrium diagram represents the unique set of conditions (temperature and pressure) at which all three phases (solid, liquid, and gas) of a substance can coexist in equilibrium.
6. Critical Point: The critical point is the temperature and pressure above which a substance can no longer exist as a distinct liquid phase, regardless of pressure. At the critical point, the liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable and merge into a supercritical fluid.
7. Phase Equilibrium Calculations: Thermodynamic models and equations, such as the Clapeyron equation or the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, are used to calculate and predict phase equilibrium conditions. These calculations require knowledge of properties such as enthalpy, entropy, and temperature.
8. Applications: Understanding physical equilibria is important in various fields, including material science, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and atmospheric science. It helps in designing processes, predicting phase behavior, and optimizing the production and use of substances.
Physical equilibria play a crucial role in various natural and technological processes, and studying their behavior is fundamental to understanding the physical properties and transformations of matter.
Describes ionic, covalent, dative bonds, bond polarity and polarization of bonds suitable students taking chemistry at advanced level of education
Ionic bonds:
Ionic bonds are formed between two atoms when one atom donates one or more electrons to another atom. This transfer of electrons leads to the formation of ions - positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. Ionic bonds typically occur between a metal and a non-metal.
Covalent bonds:
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases. Covalent bonds typically occur between non-metals.
Dative bonds (also known as coordinate covalent bonds):
Dative bonds occur when both electrons in a shared pair come from the same atom. In other words, one atom donates both electrons to the bond, while the other atom does not contribute any electrons. Dative bonds can be thought of as a special case of covalent bonds, where one atom supplies both electrons. This type of bonding is commonly found in Lewis acid-base reactions.
Bond polarity:
Bond polarity refers to the unequal sharing of electrons between two atoms in a covalent bond. This unequal sharing occurs when one atom has a higher electronegativity (tendency to attract electrons) than the other atom. The difference in electronegativity leads to a separation of charges, creating a polar bond. The atom with higher electronegativity will have a partial negative charge (δ-) while the other atom will have a partial positive charge (δ+).
Polarization of bonds:
Polarization of bonds refers to the distortion of the electron cloud in a chemical bond due to the influence of external or internal forces. This can occur when a more electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud towards itself, causing an uneven distribution of electron density along the bond. Bond polarization can lead to the formation of partial charges or dipoles within a molecule.
Students taking chemistry at an advanced level of education will study these concepts in greater detail and explore their applications in various chemical reactions, organic chemistry, molecular geometry, and spectroscopy.
Suitable for Advance level students tacking physical chemistry: the video describe how to use Raoult's laws to calculate the composition and vapour pressures of components in the ideal mixtures
An exponential equation is an equation in the form of y = ab^x, where a and b are constants and x is the variable.
The variable x is typically the exponent, and the base b is usually a constant greater than 1. The constant a is the initial value or y-intercept of the exponential function.
Exponential equations are used to model relationships where the value of y grows or decays exponentially with respect to x. They are commonly used in finance, population growth, radioactive decay, and other natural phenomena.
The general form of an exponential equation is:
y = ab^x
where:
- y is the dependent variable or output
- x is the independent variable or input
- a is the initial value or y-intercept
- b is the base or growth/decay factor
Examples of exponential equations:
1. Population Growth:
y = 1000 * 1.03^x
where the initial population is 1000 and it grows at a rate of 3% per year.
2. Radioactive Decay:
y = 500 * 0.9^x
where an initial amount of 500 radioactive particles decays at a rate of 10% per hour.
3. Compound Interest:
y = 1000 * (1 + 0.05)^x
where an initial investment of $1000 grows at an annual interest rate of 5%.
General CHS 102 - History and Development of Organic Chemistry....For Private Tutoring:Contact Me: +256787503215
This lecture is about inductive effect in organic chemistry. I will teach you the super concept of inductive effect in chemistry. Also, I will teach the factors effecting inductive effect. At the end of this lecture, I will teach you how to solve questions of inductive effect.
To learn more, watch this lecture till the end.
#inductiveeffect
#trick
#najamacademy
#chemistry
Inductive effect: https://youtu.be/-JrFIB3DYzk
Mesomeric effect: https://youtu.be/Xdp48E7C_Xo
Hyperconjugation: https://youtu.be/x21FhoKh7bE
Electromeric effect: https://youtu.be/unCd-qIxH_o
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC_ltCdLVMRZ7r3IPz
Facebook link: https://www.facebook.com/Najamacademy/
Stoichiometry Calculations involving Equation of Reactions" Pt 1
chemistry of period 3 for Advanced level students
molecular, ionic, atomic and metallic solids
electrode potential, standard electrode potential, factors affecting electrode potential, factors affecting standard electrode potential, standard hydrogen electrode, measurent of electrode potentials, emf cells and calculations.
Nucleic Acids such as DNA and RNA are very important molecules in the bodies of living organisms.
This video gives an introduction looking at the monomers of nucleic Acids which are nucleotides ie the components of nucleotides, how the components combine to form nucleotides, and finally how the nucleotides combine to form nucleic Acids.
The next episodes will be about specific nucleic Acids ie RNA and DNA. So please subscribe so that you are notified whenever I post.
Always leave a comment
Thanks and may God bless you.
Bone tissue is a type of connective tissue that forms the skeletal system of the body. It is a hard and dense tissue that provides support, protection, and movement to the body, as well as housing and protecting vital organs.
Bone tissue is made up of specialized cells, called osteocytes, embedded within a matrix composed of collagen fibers and mineral salts, predominantly calcium and phosphate. This combination of organic and inorganic materials gives bone its unique properties of strength and hardness.
Bones are classified into two types: compact bone and spongy bone. Compact bone makes up the outer layer of bones and provides strength and protection, while spongy bone is found in the interior of bones and provides structural support. Both types of bone tissue contain osteons, which are cylindrical structures composed of concentric layers called lamellae that surround a central canal containing blood vessels and nerves.
Bone tissue undergoes continuous remodeling throughout life in a process called bone remodeling. This involves the removal of old or damaged bone tissue by cells called osteoclasts and the formation of new bone tissue by cells called osteoblasts. This constant remodeling allows bones to adapt to mechanical stress, repair damage, and maintain optimal strength and structure.
In addition to its mechanical functions, bone tissue also serves as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate, which are essential for various physiological processes in the body. When blood calcium levels are low, bone tissue releases calcium into the bloodstream to maintain homeostasis.
Overall, bone tissue plays a crucial role in providing support and protection to the body, facilitating movement, and contributing to mineral homeostasis.
English language lesson centered around the topic of modern communication technology:
Lesson Objective: By the end of this lesson, you will be able to discuss various aspects of modern communication technology and express your opinions on its impact.
1. Vocabulary:
a. Communication: The imparting or exchanging of information or news.
b. Technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes.
c. Digitalization: The process of converting information into a digital format.
d. Social media: Platforms or websites that enable users to create and share content.
e. Connectivity: The state of being connected or interconnected.
f. Cybersecurity: Measures taken to protect computer systems from theft or damage.
2. Discussion:
Begin the lesson by initiating a conversation with your students about modern communication technology. Ask them questions such as:
a. What are some examples of modern communication technology?
b. How do these technologies impact our daily lives?
c. What advantages and disadvantages do you see in using these technologies?
d. How has communication technology evolved over the years?
3. Reading Activity:
Provide the students with a short article or passage related to modern communication technology. Ask them to read it and identify any new vocabulary words they encounter. After reading, discuss the main points and ask for their opinions on the topic.
4. Speaking Activity:
Divide the students into pairs or small groups. Assign each group a specific aspect of modern communication technology, such as social media, smartphones, or online messaging apps. Ask them to discuss the pros and cons of their assigned topic and present their findings to the class.
5. Writing Task:
Ask the students to write a short essay or opinion piece on the topic of modern communication technology. Encourage them to express their thoughts on its impact on society, relationships, and personal wellbeing. Remind them to use vocabulary and phrases related to the topic.
6. Extension Activity:
To further engage the students, you can assign them a project to create a presentation or poster on a specific modern communication technology. They can use visuals, statistics, and facts to support their findings.
Remember to encourage participation, provide support, and create a positive learning environment throughout the lesson.
Reaction of alkynes with water
Reaction of alkynes with ammoniacal silver nitrate or ammoniacal copper I chloride
distinguishing between terminal alkynes and those with the tripple bond in the middle of the chain
In this introductory lesson we will examine the 14 different things and events whose origins are found in the book of Genesis.
Subscribe to BibleTalk.tv:
https://bibletalk.tv/subscribe
Student Workbook:
Buy - https://www.amazon.com/dp/B09HFXVLL1
PDF - https://bibletalk.tv/genesis.workbook.pdf
Next lesson in this series:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=CDZju76JhVQ
Download:
https://bibletalk.tv/introduction-to-genesis
About Mike Mazzalongo:
https://bibletalk.tv/teachers/mike-mazzalongo
#MikeMazzalongo
Genesis:
https://bibletalk.tv/genesis
Support this Ministry:
https://bibletalk.tv/support
Available on Amazon Prime:
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07756BK34
Available on iTunes:
https://itunes.apple.com/us/podcast/id804928307
Available on Spotify:
https://open.spotify.com/show/....6hZIobsTOJ7mB5bvHVY3
#Genesis #BibleTalk #BibleTalkTV
Parts of flowers, pollen grain and ova formation, structures of mature pollen grain and ovum, pollination and fertilization, agents of pollination, advantages of sexual reproduction, means employed by plants to limit self-fertilization, dispersal and agents of dispersal, seed dormancy, causes of seed dormancy, how to break seed dormancy.
Male and female reproductive systems, spermatogenesis, oogenesis, fertilization, advantages of internal fertilization, menstrual cycle, events in pregnancy, the function, structure, and adaptations of placenta, hormonal control of birth, causes of infertility in male and female
Reproduction in animals refers to the biological process through which animals produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of their species. There are various modes of reproduction in animals, including sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
1. ****ual Reproduction:
****ual reproduction involves the fusion of genetic material from two parents, typically a male and a female, to produce offspring. This process includes several steps:
- Mating: The male and female individuals come together for copulation, either through direct contact or via specialized reproductive organs.
- Fertilization: The fusion of sperm and egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote.
- Development: The zygote undergoes embryonic development and eventually matures into a new individual.
- Gestation: In many species, particularly mammals, the female carries and nourishes the developing embryo/fetus internally before giving birth.
****ual reproduction contributes to genetic diversity as offspring inherit a combination of traits from both parents.
2. Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction involves the production of offspring without the involvement of gametes (sperm and egg) or the fusion of genetic material from two parents. Types of asexual reproduction include:
- Binary Fission: The parent organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells. This is commonly observed in microorganisms such as bacteria.
- Budding: A small outgrowth or bud forms on the parent organism and eventually detaches to become a new, genetically identical individual. It is seen in organisms like hydra and yeast.
- Fragmentation: The parent organism breaks into fragments, with each piece regenerating into a complete new individual. This is observed in some invertebrates such as starfish and planarians.
- Parthenogenesis: Offspring are produced from unfertilized eggs, where the female gamete develops into an embryo without fertilization. It is seen in some reptiles, insects, and fish.
Asexual reproduction typically leads to offspring that are genetically identical or very similar to the parent.
The mode of reproduction in animals varies across different species and is influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, availability of mates, and evolutionary adaptations. ****ual reproduction is more common among animals as it promotes genetic diversity, increasing the chances of survival in changing environments.
Temperature regulation in animals is the process by which animals maintain their internal body temperature within a narrow range to match the external environment. This is crucial for survival and maintaining proper bodily functions. There are two main types of animals in terms of temperature regulation, endotherms and ectotherms.
1. Endotherms:
Endotherms, also known as warm-blooded animals, are those that maintain a constant internal body temperature by generating heat through metabolic processes. Examples of endotherms are mammals and birds. These animals have a complex system of thermoregulation that enables them to maintain their body temperature within a narrow range, regardless of the external temperature.
Endotherms have several mechanisms for temperature regulation, such as:
- Shivering: Muscular contractions generate heat and raise body temperature.
- Sweating: Evaporation of sweat cools the body down.
- Vasodilation and vasoconstriction: The dilation and constriction of blood vessels regulate heat loss or gain.
- Behavioral regulation: Seeking shade or exposure to the sun to regulate body temperature.
2. Ectotherms:
Ectotherms, also known as cold-blooded animals, are those that rely on the external temperature to regulate their body temperature. Examples of ectotherms are reptiles, amphibians, and fish. These animals do not generate heat internally but instead rely on the environment to provide heat or to facilitate heat loss.
Ectotherms have different ways of regulating their body temperature, such as:
- Basking: Exposure to the sun to increase body temperature.
- Burrowing: Going underground to avoid high temperatures.
- Constriction and dilation: Constricting or dilating blood vessels to regulate blood flow and heat loss.
In summary, animals use different mechanisms to regulate their body temperature depending on whether they are endothermic or ectothermic. Both types of animals have adaptations to maintain their internal body temperature within a narrow range to ensure proper bodily functions and survival in their respective environments.
Significance of temperature regulation, types of temperature regulation, endotherms, warm blooded, ectoderms,, cold blooded, skin, responses of humans to cold and hot environment, behavioral responses, temperature regulation in plants, lower and upper critical temperatures, lower and upper lethal temperatures
Temperature regulation in animals is the process by which animals maintain their internal body temperature within a narrow range to match the external environment. This is crucial for survival and maintaining proper bodily functions. There are two main types of animals in terms of temperature regulation, endotherms and ectotherms.
1. Endotherms:
Endotherms, also known as warm-blooded animals, are those that maintain a constant internal body temperature by generating heat through metabolic processes. Examples of endotherms are mammals and birds. These animals have a complex system of thermoregulation that enables them to maintain their body temperature within a narrow range, regardless of the external temperature.
Endotherms have several mechanisms for temperature regulation, such as:
- Shivering: Muscular contractions generate heat and raise body temperature.
- Sweating: Evaporation of sweat cools the body down.
- Vasodilation and vasoconstriction: The dilation and constriction of blood vessels regulate heat loss or gain.
- Behavioral regulation: Seeking shade or exposure to the sun to regulate body temperature.
2. Ectotherms:
Ectotherms, also known as cold-blooded animals, are those that rely on the external temperature to regulate their body temperature. Examples of ectotherms are reptiles, amphibians, and fish. These animals do not generate heat internally but instead rely on the environment to provide heat or to facilitate heat loss.
Ectotherms have different ways of regulating their body temperature, such as:
- Basking: Exposure to the sun to increase body temperature.
- Burrowing: Going underground to avoid high temperatures.
- Constriction and dilation: Constricting or dilating blood vessels to regulate blood flow and heat loss.
In summary, animals use different mechanisms to regulate their body temperature depending on whether they are endothermic or ectothermic. Both types of animals have adaptations to maintain their internal body temperature within a narrow range to ensure proper bodily functions and survival in their respective environments.
Excretion is the process by which organisms remove waste products from their bodies to maintain homeostasis. It is an essential function that helps regulate the internal environment of living organisms.
1. Purpose of Excretion:
- Elimination of metabolic waste: Cells produce waste products as a result of their normal metabolic processes. Excretion removes these waste substances, such as carbon dioxide, urea, and excess ions like ammonia, to prevent their accumulation and toxicity.
- Maintenance of osmotic balance: Many organisms excrete excess water and salts to maintain proper osmotic balance within their bodies. This helps prevent dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
2. Organs and Systems involved in Excretion:
- Kidneys: In most vertebrates, including humans, kidneys play a key role in excretion. They filter blood, remove waste products, regulate water and electrolyte balance, and produce urine.
- Lungs: In humans and many other organisms, the lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor during the process of breathing.
- Skin: Sweating helps remove water, salts, and some nitrogenous wastes like urea from the body.
- Liver: The liver is involved in the excretion of certain waste products, like bilirubin and some drugs, as part of its detoxification functions.
3. Excretion in Plants:
- Plants excrete waste products through various mechanisms, including the shedding of leaves, bark, and fruit.
- Some plants also excrete excess salts through salt glands in leaves.
4. Excretion in Single-celled Organisms:
- Single-celled organisms, like bacteria and protists, excrete waste products directly into their environment.
- Amoebas, for example, excrete metabolic wastes through the cell membrane.
5. Importance of Excretion:
- Eliminating waste products helps maintain proper internal balance and prevent toxic buildup.
- Rebalancing water and ion levels is crucial for cellular functioning and overall homeostasis.
In summary, excretion is the process by which organisms eliminate waste products. It involves various organs and systems, including kidneys, lungs, skin, and liver. Excretion is important for maintaining internal balance and preventing toxin buildup in organisms.
Fully discussed revision questions
Fully discussed revision questions
Excretion and osmoregulation in marine invertebrates and vertebrates, excretion and osmoregulation fresh water animals and fish, excretion and osmoregulation in insects, excretion in plants, adaptations of xerophytes and halophytes
Excretion and osmoregulation are closely related processes that work together to maintain the balance of water and dissolved substances, such as salts, inside an organism's body.
1. Excretion:
Excretion is the process of removing metabolic waste products from an organism's body. These waste products include substances like carbon dioxide, urea, ammonia, and excess ions. Excretion helps prevent the accumulation of toxic substances and maintains the proper functioning of an organism. Examples of organs involved in excretion are the kidneys, lungs, skin, and liver.
2. Osmoregulation:
Osmoregulation is the process by which an organism regulates the balance of water and dissolved substances in its body fluids. It ensures that the concentration of solutes inside the body remains within a certain range, maintaining homeostasis. Osmoregulation involves mechanisms for retaining or excreting water and salts to maintain the proper balance.
3. Relationship between Excretion and Osmoregulation:
Excretion and osmoregulation are interconnected processes that work together to maintain the internal balance of an organism.
- Waste products, such as urea and ammonia, are excreted by the kidneys, which also play a significant role in regulating the concentration of water and ions in the body.
- The lungs, through respiration, eliminate carbon dioxide and also help regulate the body's acid-base balance.
- The skin excretes water and salts through sweating, which helps cool the body and maintain proper levels of hydration.
- The liver is involved in excreting waste products, such as bilirubin and drugs, and plays a role in maintaining the balance of various nutrients and metabolites.
Osmoregulation ensures that the concentration of water and dissolved substances in the body is maintained within a narrow range. This is achieved through various mechanisms, including the control of water intake and output, ion regulation, and adjustment of excretory processes. Excretory organs, such as the kidneys, play a vital role in osmoregulation by filtering and selectively reabsorbing substances to maintain water and salt balance.
In summary, excretion and osmoregulation are interconnected processes that work together to maintain the balance of water and dissolved substances in an organism's body. Excretion removes waste products, while osmoregulation regulates the water and solute content to maintain proper internal balance, ensuring the overall health and well-being of the organism.
definition of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two types of cells that make up all living organisms. They differ in their structural complexity and organization.
1. Structure:
- Prokaryotic cells: Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their DNA is present in a region called the nucleoid, and they have few internal structures called ribosomes.
- Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex. They contain a well-defined nucleus that houses the DNA. In addition, eukaryotic cells possess various membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and others.
2. DNA Organization:
- Prokaryotic cells: Prokaryotes have a single, circular DNA molecule floating freely in the cytoplasm. It lacks the organization into chromosomes seen in eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotes have linear DNA molecules that are organized into multiple chromosomes, typically found within the nucleus.
3. Membrane-bound Organelles:
- Prokaryotic cells: Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles. They have some specialized regions within their cytoplasm, such as ribosomes for protein synthesis, but these structures are not surrounded by membranes.
- Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotes possess membrane-bound organelles that perform specific functions. These include the nucleus (DNA storage and transcription), mitochondria (energy production via cellular respiration), endoplasmic reticulum (protein synthesis and lipid metabolism), and golgi apparatus (modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins).
4. Complexity:
- Prokaryotic cells: Prokaryotes are simpler in structure and organization, lacking compartmentalization. They can be found as unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and archaea.
- Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotes are more complex, with compartmentalization provided by membrane-bound organelles. They can be found as both unicellular (e.g., yeast) and multicellular organisms (e.g., plants, animals, fungi).
In summary, prokaryotic cells are smaller, simpler, lack a nucleus, and lack membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, contain a nucleus, and possess membrane-bound organelles.
1. What is locomotion in animals?
2. What are the different methods of locomotion employed by vertebrates?
3. How do mammals move about using their legs?
4. What adaptations do animals have for movement in extreme environments?
5. How do invertebrates like insects and spiders move about?
6. Why is locomotion important for animals?
7. Can animals switch between methods of locomotion?
Answers:
1. Locomotion is the ability of living organisms to move around from one place to another.
2. Vertebrates use various methods of locomotion. For instance, birds and bats have wings that enable them to fly, while fish have fins and tails that help them swim. Mammals, including humans, have legs that allow them to walk, run, or climb.
3. Mammals move by contracting their muscles to move their leg bones. They also adjust their gait and speed depending on the terrain, incline, or other factors.
4. Animals have specific adaptations to move in extreme environments. For instance, polar bears have large, webbed paws that help them walk on ice, and animals in the desert can drink water from their food sources to conserve energy and reduce water loss.
5. Invertebrates use a variety of methods to move. For example, jellyfish and sea anemones contract and expand their muscles to propel themselves through the water, and insects and spiders have multiple legs that enable them to walk, run, or jump.
6. Locomotion is important for animals to find food, escape predators, and navigate their environments. Animals that cannot move well usually do not survive long.
7. Yes, animals can switch between methods of locomotion. For instance, some reptiles can walk or crawl on land and also swim in water.
Biceps and triceps, stability and locomotion in tetrapod, locomotion in fish, stability in fish and how it is counteracted, locomotion in birds, adaptations of birds to locomotion, fine structure of muscles, how muscles contract.
Types of skeleton, locomotion in earthworm, locomotion in insects, human skeleton, function of bones, types of muscles and their differences and joints.
Locomotion is the ability of living organisms to move around from one place to another. Animals have developed different mechanisms and body structures to enable them to move in different environments.
Vertebrates, or animals with backbones, employ various methods of locomotion. Birds and bats, for example, have wings that enable them to fly, while fish have fins and tails that help them swim. Mammals, including humans, have legs that allow them to walk, run, or climb. Other animals like snakes use their body muscles to crawl or slither.
Invertebrates, or animals without backbones, use a variety of methods to move. Jellyfish and sea anemones contract and expand their muscles to propel themselves through the water. Insects and spiders have multiple legs that enable them to walk, run, or jump.
Some animals have specific adaptations that allow them to move in extreme environments. For example, polar bears have large, webbed paws that help them walk on ice. Kangaroos use their powerful hind legs to hop across vast distances in the Australian outback.
Overall, locomotion is essential for animals to find food, escape predators, and navigate their environments.
Well discussed structured questions from national exams
Terminologies (gene, allele, dominant gene, recessive genes, homozygous, heterozygous, back cross, test cross), monohybrid inheritance, sex determination and multiple alleles (ABO blood groups)
6 A-level paper 2 revision questions for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy which is stored in the form of glucose. Oxygen is also produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis. This process plays a significant role in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Coordination in animals 30 objective revision questions and answers
in this tutorial, you will learn the laws of indices, and how to apply it to solve mathematics problems.
Remember that indices is the plural form of index, watch the video lesson and learn what it means and how to apply it to solve mathematical problems.
please click the subscription button as well as the bell icon to be notified each time I post educational videos.
#maths #multiplication #division #inverse #roots #power #index #exponents #exponential
#viral #maths #algebra #funmaths #tiktokvideo #shortvideo #mathvideos #mathslesson #mathstutor #algebra #trending #viral #maths #funmathvideos #viralmaths #algebra #shortvideo #circletheorem #logarithmic #equation #waec #2023 #2024 #necomaths #waecmaths
This video is about practicals for food tests.Please enjoy.
Title: Food Tests Practicals - Episode One: Test for Starch
Introduction:
Welcome to the first episode of Food Tests Practicals! In this episode, we will be conducting a simple test to detect the presence of starch in food items. Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is commonly found in foods such as potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta. By performing this test, we can identify if a particular food item contains starch.
Materials Needed:
1. Food items for testing (recommended: potato, bread, and rice)
2. Iodine solution
3. Test tubes
4. Dropper or pipette
5. Beaker or container for water bath
6. Water
Procedure:
1. Start by setting up a water bath. Fill a beaker or container with water and heat it until it reaches a gentle simmer.
2. Take the food items you wish to test (potato, bread, and rice) and cut small pieces of each. Ensure that the pieces are roughly the same size.
3. Label your test tubes with the names of the food items you are testing.
4. Place a piece of each food item into their respective labeled test tubes.
5. Add a few drops of iodine solution to each test tube using a dropper or pipette.
6. Observe the color change that occurs. Starch reacts with iodine to produce a dark blue or black color.
Results and Interpretation:
Positive Result - If the color of the solution changes to dark blue or black, it indicates the presence of starch in the tested food item.
Negative Result - If the color of the solution remains unchanged (brown or yellow), it suggests the absence of starch in the tested food item.
Conclusion:
In this episode of Food Tests Practicals, we performed a test to detect the presence of starch in food items using iodine solution. By observing the color change in the solution, we can determine if a food item contains starch. Starch is an essential carbohydrate in our diet, providing energy and serving as a storage form of glucose in plants. Stay tuned for more practical episodes on food tests to expand your knowledge of food science!
Questions are skillfully selected test and enhance understanding
Definition of homeostasis, mechanisms of homeostasis (negative feedback and positive feedback), components of efficient negative feed back mechanism, homeostasis of glucose, role of pancreas in homeostasis of glucose (i.e. production of insulin) and diabetes mellitus
Homeostasis is the ability of an organism or system to maintain a stable and constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment or physiological conditions. In other words, homeostasis is the process by which the body regulates and maintains equilibrium or balance within its internal environment, including temperature, pH, fluid levels, and energy metabolism.
The mechanisms of homeostasis involve feedback loops that continuously monitor and adjust internal conditions to maintain stable levels. Negative feedback loops, for example, are used to detect and correct deviations from normal conditions, such as fluctuations in body temperature or blood glucose levels. Positive feedback loops, on the other hand, amplify changes in the internal environment and are involved in processes such as childbirth and blood clotting.
The body's major organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis. The nervous system, for example, uses sensors in the body to detect deviations from normal conditions and sends signals to coordinate responses. The endocrine system uses hormones to regulate various physiological processes, including metabolism, growth and development, and fluid and ion balance. The immune system also plays a role in maintaining homeostasis by fighting off infections and other threats to the internal environment.
Dysfunction in homeostasis can lead to diseases and health problems. For example, diabetes results from a failure in the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels, while dehydration occurs when there is an imbalance in fluid and electrolyte levels. Understanding homeostasis and its mechanisms is thus crucial in preventing and treating various health conditions.
atomic masses, relative atomic masses, and relative molecular masses
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. It is commonly used in geometry, physics, and engineering to solve problems involving right triangles.
The three basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, and tangent. The sine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The tangent of an angle is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle to the cosine of the angle.
In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle, the base is the side adjacent to the angle, and the height is the side opposite to the angle. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Trigonometric functions can be used to solve various problems involving angles and sides of triangles. For example, if you know one side and one angle of a right triangle, you can use trigonometric functions to find the lengths of the other sides. Similarly, if you know the lengths of two sides, you can use trigonometric functions to find the angles of the triangle.
Trigonometry also involves concepts such as radian measure, which is an alternative way of measuring angles, and the unit circle, which is a circle with a radius of one unit used to define the values of trigonometric functions for all angles.
Overall, basic trigonometry provides tools to analyze and solve problems involving triangles, angles, and sides. It is an important branch of mathematics that has applications in various fields.
central nervous system, reflex arc, conditioned reflex, part and functions of parts of the brain, sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, position of endocrine glands in the body, hormone and their function, mechanism of hormone action
Differences between Nervous and Endocrine Systems:
1. Communication:
- Nervous System: Uses electrical impulses (action potentials) for rapid communication.
- Endocrine System: Uses chemical messengers called hormones for slower, long-distance communication.
2. Mode of Transmission:
- Nervous System: Transmits information through neurons via synapses.
- Endocrine System: Releases hormones into the bloodstream to target specific tissues or organs.
3. Speed of Response:
- Nervous System: Responds rapidly, enabling quick reflexes and immediate reactions.
- Endocrine System: Responds more slowly, with effects taking minutes to hours, but lasts longer.
4. Duration of Effect:
- Nervous System: Effects are short-lived.
- Endocrine System: Effects are long-lasting.
Action Potential:
- An action potential is a rapid electrical impulse that allows neurons to transmit signals throughout the nervous system.
- It is generated when the membrane potential of a neuron depolarizes, reaching a threshold level, causing a cascade of voltage-gated ion channels to open and initiate the action potential.
- The action potential propagates down the axon of a neuron, allowing for long-distance transmission of signals.
Impulse:
- An impulse refers to the rapid transmission of an action potential along the length of a neuron.
- It involves the depolarization and repolarization of the neuron's membrane.
- The impulse allows for the efficient and coordinated communication of signals in the nervous system.
All-or-None Law:
- The all-or-none law states that once a neuron's membrane potential reaches the threshold level, an action potential is generated and transmitted along the neuron.
- The size or intensity of the stimulus does not affect the amplitude or speed of the action potential; it either fires completely or does not fire at all.
Refractory Period:
- The refractory period is a brief period of time following an action potential when the neuron cannot generate another action potential.
- It allows the neuron to recover and reset its ion channels before firing again, ensuring proper signal transmission and preventing continuous firing.
Synapse:
- A synapse is a junction between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (such as a muscle or gland).
- It is the site where communication occurs between these cells.
- At the synapse, the electrical signal of the presynaptic neuron is converted into a chemical signal in the form of neurotransmitters.
Transmission at the Synapse:
- Transmission at the synapse involves the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron, which diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron or effector cell.
- This binding triggers a response in the postsynaptic neuron or effector cell, propagating the signal across the synapse.
Neuromuscular Junction:
- The neuromuscular junction is a specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
- It is responsible for transmitting signals from the motor neuron to the muscle, leading to muscle contraction.
Functions of Synapses:
- Mediating the transmission of signals between neurons, allowing for communication within the nervous system.
- Integrating and processing incoming signals, allowing for complex and coordinated responses.
- Modulating and amplifying signals, enabling effective communication and control of bodily functions.
- Allowing for synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for learning, memory formation, and neural adaptability.
Differences between nervous and endocrine system, action potential, impulse, none or nothing law, refractory period, synapse, transmission at the synapse, neuromuscular junction, functions of the synapses.
Differences between Nervous and Endocrine Systems:
1. Communication:
- Nervous System: Uses electrical impulses (action potentials) for rapid communication.
- Endocrine System: Uses chemical messengers called hormones for slower, long-distance communication.
2. Mode of Transmission:
- Nervous System: Transmits information through neurons via synapses.
- Endocrine System: Releases hormones into the bloodstream to target specific tissues or organs.
3. Speed of Response:
- Nervous System: Responds rapidly, enabling quick reflexes and immediate reactions.
- Endocrine System: Responds more slowly, with effects taking minutes to hours, but lasts longer.
4. Duration of Effect:
- Nervous System: Effects are short-lived.
- Endocrine System: Effects are long-lasting.
Action Potential:
- An action potential is a rapid electrical impulse that allows neurons to transmit signals throughout the nervous system.
- It is generated when the membrane potential of a neuron depolarizes, reaching a threshold level, causing a cascade of voltage-gated ion channels to open and initiate the action potential.
- The action potential propagates down the axon of a neuron, allowing for long-distance transmission of signals.
Impulse:
- An impulse refers to the rapid transmission of an action potential along the length of a neuron.
- It involves the depolarization and repolarization of the neuron's membrane.
- The impulse allows for the efficient and coordinated communication of signals in the nervous system.
All-or-None Law:
- The all-or-none law states that once a neuron's membrane potential reaches the threshold level, an action potential is generated and transmitted along the neuron.
- The size or intensity of the stimulus does not affect the amplitude or speed of the action potential; it either fires completely or does not fire at all.
Refractory Period:
- The refractory period is a brief period of time following an action potential when the neuron cannot generate another action potential.
- It allows the neuron to recover and reset its ion channels before firing again, ensuring proper signal transmission and preventing continuous firing.
Synapse:
- A synapse is a junction between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (such as a muscle or gland).
- It is the site where communication occurs between these cells.
- At the synapse, the electrical signal of the presynaptic neuron is converted into a chemical signal in the form of neurotransmitters.
Transmission at the Synapse:
- Transmission at the synapse involves the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron, which diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron or effector cell.
- This binding triggers a response in the postsynaptic neuron or effector cell, propagating the signal across the synapse.
Neuromuscular Junction:
- The neuromuscular junction is a specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
- It is responsible for transmitting signals from the motor neuron to the muscle, leading to muscle contraction.
Functions of Synapses:
- Mediating the transmission of signals between neurons, allowing for communication within the nervous system.
- Integrating and processing incoming signals, allowing for complex and coordinated responses.
- Modulating and amplifying signals, enabling effective communication and control of bodily functions.
- Allowing for synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for learning, memory formation, and neural adaptability.
structure, adaptations and functions of photosynthesis, chemistry of photosynthesis(light harvesting, electron transport and Calvin cycle), C3 and C4 plants, advantages of C4 plants over C3 plant, differences between respiration and photosynthesis.
Structure and Adaptations of Photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which captures sunlight.
- The chloroplasts have an inner membrane, outer membrane, and thylakoid membranes, where the various stages of photosynthesis take place.
- The thylakoid membranes are arranged in stacks called grana, and the fluid-filled space surrounding the grana is called the stroma.
- Adaptations of photosynthesis include the presence of large surface areas with abundant chloroplasts in leaves, and the arrangement of chlorophyll molecules in the thylakoid membranes to maximize light absorption.
Functions of Photosynthesis:
- Conversion of sunlight energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
- Production of oxygen as a byproduct, which is released into the atmosphere.
- Biosynthesis of carbohydrates and other organic compounds necessary for the plant's growth and maintenance.
Chemistry of Photosynthesis:
1. Light Harvesting: Chlorophyll absorbs photons of light energy, exciting electrons and initiating the process.
2. Electron Transport: Excited electrons are passed through a series of electron carriers within the thylakoid membranes, generating ATP and reducing NADP+ to NADPH.
3. Calvin Cycle: This occurs in the stroma and involves a series of enzyme-mediated reactions that use ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
C3 and C4 Plants:
- C3 plants: Common plants like wheat, rice, and oats that directly use the C3 pathway in photosynthesis. In this pathway, carbon dioxide is initially fixed into a three-carbon compound.
- C4 plants: Plants like corn, sugarcane, and sorghum that have an additional step before entering the C3 pathway. They first fix carbon dioxide into a four-carbon compound, helping them adapt to hotter and drier environments.
Advantages of C4 Plants over C3 Plants:
- C4 plants have a higher rate of photosynthesis and can better withstand high temperatures and low carbon dioxide conditions.
- Their unique carbon fixation process allows them to efficiently use water and nutrients, promoting their growth in arid conditions.
- C4 plants often exhibit better water use efficiency compared to C3 plants.
Differences between Respiration and Photosynthesis:
1. Respiration occurs in all living cells, while photosynthesis occurs only in plants, algae, and some bacteria.
2. Respiration involves the breakdown of glucose to produce ATP, releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct, while photosynthesis fixes carbon dioxide to produce glucose, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
3. Respiration occurs continuously, while photosynthesis typically occurs during daylight hours.
4. Respiration releases energy, while photosynthesis stores energy.
types of autotrophic nutrition, conditions necessary for photosynthesis, limiting factors of photosynthesis
Purpose, types and adaptations to different types of heterotrophic nutrition
digestion and adaptation of digestive canal
control of digestions
Properties, and uses of acids, bases, water, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and vitamins
Aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, glycolysis, Krebs cycle, basal metabolic rate, fermentation
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). It is a series of metabolic reactions that occur in the presence of oxygen (aerobic respiration) or in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
In aerobic respiration, the process takes place in the mitochondria and consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle), and the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This process yields a small amount of ATP and NADH.
Next, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it undergoes the Krebs cycle. During this cycle, pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and producing NADH, FADH2, and ATP.
The final stage is the electron transport chain, which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. NADH and FADH2 produced in previous stages donate electrons to the chain, creating a flow of electrons that generates a proton gradient. This gradient drives ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen and includes processes such as alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. These processes allow cells to continue generating small amounts of ATP without oxygen but are less efficient than aerobic respiration.
Overall, cellular respiration is a crucial process for organisms to obtain energy from nutrients and sustain various cellular activities.
properties of enzymes, factors affecting enzymes, lock and key hypothesis, enzyme inhibitors, anabolic reactions, catabolic reactions
Diffusion, osmosis, active transport, phagocytosis and pinocytosis for A-level students
describes physical and chemical properties of cobalt and nickel
Chemistry of Cobalt:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Cobalt has an atomic number of 27 and an atomic weight of 58.933 g/mol. It is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal with a high melting point of 1495°C and a boiling point of 2870°C.
2. Oxidation states: Cobalt can exhibit various oxidation states, including +2, +3, and +4. The +2 state is the most common and stable, while the +3 and +4 states are less common.
3. Chemical reactivity: Cobalt is a moderately reactive metal, similar to iron. It reacts slowly with oxygen in the air to form cobalt(II) oxide (CoO). It also reacts with a variety of acids and non-metals, such as sulfur and halogens.
4. Cobalt compounds: Cobalt forms a multitude of compounds, such as cobalt chloride (CoCl2), cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2), and cobalt sulfate (CoSO4). These compounds find applications in various fields, including catalysts, pigments, and batteries.
5. Biological importance: Cobalt is an essential element for some living organisms. It is a critical component of vitamin B12 (cobalamin), which is necessary for proper functioning of the nervous system, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production.
6. Magnetic properties: Cobalt is known for its magnetic properties. It is one of the few naturally occurring magnetic elements and can be magnetized to produce permanent magnets.
7. Alloys: Cobalt forms alloys with other metals, such as cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) and cobalt-nickel (Co-Ni) alloys. These alloys have excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, making them useful in applications like aerospace, orthopedic implants, and turbine blades.
Chemistry of Nickel:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Nickel has an atomic number of 28 and an atomic weight of 58.693 g/mol. It is a silvery-white metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel has a melting point of 1455°C and a boiling point of 2730°C.
2. Oxidation states: Nickel commonly exhibits two oxidation states, +2 and +3. The +2 state is the more stable and prevalent form.
3. Chemical reactivity: Nickel undergoes slow oxidation in air, forming a thin oxide layer. It is resistant to corrosion and is utilized in various applications where corrosion resistance is crucial, such as stainless steel.
4. Nickel compounds: Nickel forms a range of compounds, including nickel chloride (NiCl2), nickel sulfate (NiSO4), and nickel oxide (NiO). These compounds have applications in electroplating, catalysts, and ceramics.
5. Biological importance: Nickel is not considered an essential nutrient for most organisms but has some biological activity. It is a cofactor for certain enzymes and plays a role in enzymatic processes.
6. Alloy formation: Nickel is widely used in alloy formation. It forms alloys with metals like iron, chromium, and copper, leading to the production of stainless steel, superalloys, and various other alloys with improved mechanical and thermal properties.
7. Industrial applications: Nickel and its alloys find extensive use in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction, due to their excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and heat resistance.
Understanding the chemistry of cobalt and nickel is crucial in fields such as materials science, metallurgy, catalysis, and biochemistry. It enables the development of new materials and compounds, enhances industrial processes, and contributes to advancements in various technological applications.
properties of iron such reaction with air, water, chlorine acid, qualitative analysis,stability of oxidation states 2 and 3
Iron is a transition element that belongs to the d-block in the periodic table. Here are some key aspects of the chemistry of iron:
1. Atomic and physical properties: Iron has an atomic number of 26 and an atomic weight of 55.845 g/mol. It is a silvery-gray metal with a high melting point of 1538°C and a boiling point of 2862°C. Iron is a paramagnetic material, meaning it is weakly attracted to magnetic fields.
2. Oxidation states: Iron can exhibit various oxidation states, but the most common are +2 (ferrous) and +3 (ferric). The +2 state is more stable in aqueous solutions, while the +3 state is more prevalent in solid compounds.
3. Chemical reactivity: Iron is a moderately reactive metal. It readily reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture to form iron oxides. This reaction is known as rusting. Iron also reacts with acids, halogens, and sulfur, among other elements.
4. Iron compounds: Iron forms various compounds, including iron oxide (Fe2O3), iron sulfide (FeS), iron chloride (FeCl2 and FeCl3), and iron carbonate (FeCO3). These compounds find applications in industries like construction, manufacturing, and medicine.
5. Biological importance: Iron is an essential nutrient for most living organisms. It plays a critical role in oxygen transport (through hemoglobin and myoglobin), energy metabolism, DNA synthesis, and enzyme activity.
6. Alloy formation: Iron forms alloys with other elements, such as carbon (to produce steel), nickel (to produce stainless steel), and cobalt (to produce magnets). These alloys have enhanced properties, including improved strength, corrosion resistance, and magnetic properties.
7. Redox reactions: Iron can readily undergo redox reactions, switching between the +2 and +3 oxidation states. This property is crucial in many biological processes and industrial applications.
8. Geological occurrence: Iron is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust. It is commonly found in the form of hematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), and siderite (FeCO3).
Studying the chemistry of iron is crucial in various disciplines, including materials science, environmental science, biology, medicine, and geology. It helps us understand the behavior of iron and its compounds, develop new materials, improve industrial processes, and maintain human health.
physical and chemical properties of manganese, reaction with water, air, oxidation properties of manganese VII, confirmatory tests of manganese II ions
The chemistry of manganese involves the study of the properties, reactions, and compounds of the element manganese (Mn), which belongs to the transition metal group in the periodic table. Here are some key aspects of the chemistry of manganese:
1. Oxidation states: Manganese exhibits various oxidation states ranging from -3 to +7. The most common oxidation states are +2, +4, and +7.
2. Chemical reactivity: Manganese is a moderately reactive metal. It readily reacts with halogens, sulfur, and many other non-metallic elements. It also reacts with acids to produce salts and hydrogen gas.
3. Manganese compounds: Manganese forms various compounds such as oxides (e.g., manganese dioxide), sulfides (e.g., manganese sulfide), halides (e.g., manganese chloride), and complex ions (e.g., permanganate ion).
4. Catalytic properties: Manganese, particularly in its higher oxidation states (e.g., MnO2), exhibits excellent catalytic activity. It is used as a catalyst in many chemical reactions, such as the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
5. Biological importance: Manganese is an essential trace element for many organisms, including plants, animals, and humans. It plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including enzyme activation, energy metabolism, and antioxidant defense.
6. Oxidation-reduction reactions: Manganese can undergo oxidation-reduction reactions by switching between different oxidation states. This ability is utilized in redox reactions and electron transfer processes.
7. Coordination chemistry: Manganese forms complex compounds with ligands in coordination chemistry. These compounds have applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and environmental science.
8. Geological occurrence: Manganese is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. It is commonly found in ores, such as pyrolusite (MnO2) and rhodochrosite (MnCO3).
Studying the chemistry of manganese is important for understanding its properties, applications, and environmental impact. It has wide-ranging implications in fields such as materials science, environmental science, medicine, and industrial processes.
Describes variation of electronegativity, electropositivity, atomic radii, ionization energies, electron affinities and melting points in the periodic table
Properties of the earth.structure of the earthSpinning and Rotation of the earthTheories of continental driftF.B Tailor’s theory of continental driftCriticism of F.B Tailor’s theory of continental driftTheory of sea flow spreadingThe Evidence in support of seafloor spreading Alfred Wegner’s theory of continental driftRelevancy/Evidences to support Wegner’s theory
The Earth, Continental Drift, and Earthquakes are interconnected processes and phenomena that occur on our planet. Let's take a closer look at each of them individually.
1. The Earth: The Earth is the third planet from the Sun and is composed of several layers, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The Earth's surface is primarily covered by oceans and continents. It has a diverse range of landscapes, climates, and ecosystems, making it a unique and dynamic planet.
2. Continental Drift: Continental drift refers to the movement of Earth's continents over time. The theory of continental drift was first proposed by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century. It suggests that the continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangaea, which slowly broke apart and moved to their current positions. The process of continental drift is driven by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface, which leads us to the next point.
3. Tectonic Plates: The Earth's outer layer, known as the lithosphere, is divided into several large and small tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them and are constantly moving. The movement of tectonic plates is responsible for various geologic phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the creation of mountain ranges.
4. Earthquakes: Earthquakes occur when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, causing the ground to shake. Most earthquakes are a result of the movement of tectonic plates. When the tectonic plates collide, slide past each other, or separate, they generate stress, which accumulates over time. Once the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, it is released in the form of seismic waves, causing an earthquake. Earthquakes can range from minor tremors to major, destructive events that can result in loss of life and damage to infrastructure.
Understanding the Earth, continental drift, and earthquakes is crucial for studying the dynamic nature of our planet. It helps us understand the distribution of landmasses, the formation of mountain ranges, the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic activity, and the overall behavior of the Earth's crust.
Theories explaining formation of block mountain or horst
Formation of a block mountain by compression forces
Formation of a block mountain by tension forces
Formation by relative sinking
Fault scarps/ fault escarpments.
Grabens
Fault guided valleys
Tilt block land scape
Crustal warping
Faulting
The Rift Valley
• The Tension force theory by Gregory
• The compression force by Wayland
• Vertical displacement theory by Dixey
Importance of rift valley
Mineral
Rocks
The process responsible for the formation of igneous rocks in East Africa
Plutonic rocks/ Abyssal rocks:
Hypabyssal/intermediate rocks:
Volcanic rocks/extrusive rocks:
Characteristics of Igneous rocks
Importance/uses of igneous rocks
Characteristics of sedimentary rocks
Importance of sedimentary rocks
Characteristics of metamorphic rocks
Importance of metamorphic rocks
Influence of igneous rocks on landform development in East Africa
Influence of Rock structure on the development of drainage patterns in East Africa.
1. Rectilinear or Trellis drainage pattern
2. Parallel drainage pattern
3. Dendritic and radial drainage patterns.
4. Radial drainage pattern
The relationship between rock hardness and types of slope formation in East Africa
Agricultural production in Monsoon Asia
Favorable Factors intensive agricultural production in Monsoon Asia
Problems faced by agricultural production in Monsoon Asia
Steps being taken to solve the problems of agricultural production in Monsoon Asia
Factors responsible for low level of agricultural productivity in tropical Africa
Agricultural communes in china
Characteristics of communes
Factors that lead to development of agricultural communes in China
Contributions of commune farming in China
Collective farming
Main characteristics of collective farming
Positive contributions/Advantages of collective farming
Ujamaa system in Tanzania
Benefits of the Ujamaa system
Shortcomings of Ujamaa system
Small holding farming
Characteristics of small holding farms
Advantages of small scale farming
Disadvantages of small scale farming
Growing of palm oil trees in Nigeria
Benefits of growing palm oil trees in Nigeria
Factors favoring growing of Palm oil trees in Nigeria
Challenges facing palm oil farmers
Measures being taken to increase palm oil production in Nigeria
Cocoa farming in Ghana
Benefits of growing cocoa to Ghana
Factors favoring growing of cocoa in Ghana
Measures being taken to increase cocoa production in Ghana
Characteristic of plantation farming
Plantation farming in Kwazulu-Natal
Plantation farming in Liberia
Extensive wheat farming in Canada and North America
Factors that favors plantation/extensive farming
Challenges of plantation/extensive farming
Positive contributions/Merits of Plantation/extensive farming
Demerits/Negative contributions of Plantation/extensive farming
The reasons for rapid forest destruction tropical rain forests.
Effects of deforestation on the environment.
Measure being taken to combat deforestation
Temperate coniferous forests
Characteristics of Temperate coniferous forests
Factors that have favored development of the temperate coniferous forests
Differences between boreal forests and tropical rain forests.
Contributions of forestry to the economy of a country
Characteristics of tropical rainforest
Factors that favor the growth of tropical rainforest
Factors favoring exploitation of tropical rain forests
Factors that limit exploitation of tropical forests
Tourism definition
Tourism in California, South Africa, Kenya, and Tanzania
Positive and negative contributions of tourism industry
Problems facing tourist industry in developing countries
Problems facing the tourism industry in developed countries
Factors that influence population distribution
Effects/contrbutions of high population
Population problems in developing countries (Uganda)
Possible solutions to the population problems in developing countries
Definitions of population, population census. The importance of population census in the economy. Factors which influence migration of people, Determinants of population growth rate, Population distribution in the world, The population distribution in Africa: nigeria, Egypt, Kenya, China, Canada, India,
UACE 250/2 geography paper 2 topic:advantages of road and railways transport, ,contributions of road and railway transport, problems facing road and railtransport in Africa
Mr .Nyonjo Khalid said the new curriculum is much better because a child leaves school when she/he has learnt something to do with hands.
This episode breaks down skeletal tissue starting with cartilage. Please learn, and ensure that you note down.
osmotic pressure and calculation
Defines colligative properties giving example. discusses freezing point depression with worked examples, limitations of colligative properties
Describes boiling point elevation and calculations
Describes the lowering of osmotic pressure with calculations
Calculating solubility product, common ion effect
Solubility product constant (Ksp) is a thermodynamic equilibrium constant that describes the degree to which a sparingly soluble compound dissolves in water. It is equal to the product of the concentrations of the ions raised to the powers of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation representing the dissolution of the compound. For example, consider the dissolution of a sparingly soluble salt MX at equilibrium:
MX (s) ⇌ M^+ (aq) + X^- (aq)
The solubility product expression for this reaction is:
Ksp = [M^+][X^-]
where [M^+] and [X^-] are the concentrations of the dissolved ions in the equilibrium mixture. The value of Ksp depends only on temperature and is a measure of the maximum amount of dissolved ions that can exist in a saturated solution of the salt.
If the ion concentrations in a particular solution are greater than Ksp, the salt will precipitate out of the solution until it reaches equilibrium again. On the other hand, if the ion concentrations are less than Ksp, the solution is unsaturated and additional salt can dissolve until saturation is reached. The Ksp value allows us to predict the solubility behavior of a salt and also to determine its molar solubility (the concentration of the dissolved ions) at equilibrium.
terminologies in in thermodynamic
Certainly! Here are some additional terminologies used in advanced level thermochemistry:
1. #Enthalpy: The total heat energy content of a system at constant pressure.
2. #InternalEnergy: The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of the particles within a system.
3. #StandardState: The defined set of conditions under which thermodynamic properties are measured and compared.
4. #EnthalpyofFormation: The change in enthalpy that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
5. #EnthalpyofCombustion: The change in enthalpy that occurs when one mole of a substance is completely burned in excess oxygen.
6. #EnthalpyofReaction: The change in enthalpy that occurs during a chemical reaction, typically expressed in kJ/mol.
7. #HeatofSolution: The enthalpy change that occurs when a solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution.
8. #StandardEnthalpyofReaction: The enthalpy change that occurs during a reaction when all reactants and products are in their standard states.
9. #StandardEnthalpyofFormation: The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states, with all substances in their standard states as reactants and products.
10. #BondDissociationEnergy: The energy required to break a specific bond in a gaseous molecule.
11. #EnthalpyDiagram: A graphical representation of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction, showing the potential energy of the reactants and products.
12. #EntropyChange: The change in entropy that occurs during a chemical reaction, usually expressed in J/mol·K.
13. #GibbsFreeEnergyChange: The change in Gibbs free energy that occurs during a chemical reaction, indicating the spontaneity and direction of the reaction.
14. #EquilibriumConstant: The ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations at equilibrium for a chemical reaction, indicating the extent of the reaction.
15. #ThermodynamicCycle: A series of thermodynamic processes that returns a system to its initial state, often used to determine specific energy changes.
These terminologies are commonly used in advanced level thermochemistry to analyze and quantify the energy changes and thermodynamic properties associated with chemical reactions and systems.
Terminologies;- concave mirror, convex mirrors, center of curvature, radius of curvature, principal focus, focal length, pole of the mirror, principal axis, paraxial rays; parabolic mirrors, real and virtual images, properties of images formed by concave and convex mirrors; uses of concave and convex mirrors.
Fully discussed common examination questions
Incident rays, reflected ray, normal, laws of reflection, types of reflection, Image formation in plane mirror, properties of image formed by plane mirror, location of an image formed by plane mirror by no parallax, formation of multiple images by thick plane mirror.
Sources of light, transparent medium, translucent medium, opaque medium, rays, types of beams, Rectilinear propagation of light, experiments to show that light travels in straight line, shadows from point source and extended source of light, eclipses of the sun and moon, image formation in pinhole camera, properties of images formed by pinhole camera, factors affecting images formed by pinhole camera, lens camera, differences between pinhole and lens camera, differences between lens camera and the eye.
Production and transmission of sound waves, experiment to show that transmission of sound waves requires material medium, factors affecting speed of sound waves, Quality of sound i.e. pitch, loudness and timbre
Sound waves are mechanical waves that propagate through a medium by compressing and rarefying the particles of the medium. They are created by the vibration of an object or source, which causes particles in the medium to vibrate and transfer energy.
Key characteristics of sound waves include:
1. Frequency: The frequency of a sound wave refers to the number of cycles or vibrations it completes in one second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz). Higher frequencies result in higher-pitched sounds, while lower frequencies produce lower-pitched sounds.
2. Amplitude: The amplitude of a sound wave represents the maximum displacement of the particles in the medium from their resting position. It determines the loudness or intensity of a sound. Greater amplitude results in a louder sound, while smaller amplitude produces a softer sound.
3. Wavelength: The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions of the wave. It is inversely proportional to the frequency of the wave. Longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies, while shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies.
4. Speed: The speed of sound refers to the rate at which sound waves travel through a medium. It depends on the properties of the medium, such as temperature, density, and elasticity. In dry air at room temperature, sound travels at approximately 343 meters per second.
Sound waves can be transmitted through different mediums, including air, water, and solids. They propagate in all directions and can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, and absorbed by various objects and surfaces they encounter.
Sound waves are responsible for our perception of sound and have numerous applications, including:
1. Communication: Sound waves enable us to communicate through speech, music, and other forms of audio transmission.
2. Music: Sound waves are the basis of music, allowing us to enjoy melodies, harmonies, and rhythms.
3. Sonar: Sound waves are used in sonar systems for navigation and underwater detection by emitting sound and analyzing its reflection.
4. Medical Imaging: Techniques like ultrasound employ sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues in medical diagnosis and monitoring.
5. Noise cancellation: Sound waves can be manipulated to cancel or reduce unwanted sounds in noise cancellation technology.
By understanding the properties, behaviors, and applications of sound waves, we gain insights into the phenomena and principles underlying our auditory experiences and the practical use of sound in various domains.
Definition of a wave, differences between mechanical and electromagnetic waves, differences between longitudinal and transverse waves, terminologies of a wave i.e., crest, trough, cycle, wavelength, period, frequency, and wave velocity, worked examples.
At the Ordinary level, waves are a fundamental topic in physics. Here are some key areas covered when studying waves at this level:
#Waves #PropertiesOfWaves #WaveTypes #WavePropagation #WaveBehavior #WaveInterference #WaveReflection #WaveRefraction #WaveDiffraction #SoundWaves #LightWaves
1. #Waves:
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium or empty space. They can be classified as mechanical waves, such as sound waves that require a medium for propagation, or electromagnetic waves, like light waves that can travel through a vacuum.
2. #PropertiesOfWaves:
Waves have several characteristics, including amplitude (the maximum displacement from equilibrium), wavelength (the distance between two successive points in a wave), and frequency (the number of complete waves passing a given point per second).
3. #WaveTypes:
Different types of waves include transverse waves and longitudinal waves. Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, while longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to the wave's direction.
4. #WavePropagation:
Wave propagation refers to how waves spread or travel through a medium or empty space. Mechanical waves, like water waves or sound waves, require a medium, while electromagnetic waves, including light waves and radio waves, can propagate through a vacuum.
5. #WaveBehavior:
Waves can undergo behaviors such as reflection (bouncing off a surface), refraction (bending when passing from one medium to another), diffraction (bending around obstacles or through gaps), and interference (interaction between two or more waves).
6. #WaveInterference:
Wave interference occurs when two or more waves meet at the same point in space. Constructive interference happens when their amplitudes add up, resulting in a larger wave. Destructive interference occurs when their amplitudes cancel each other out, leading to a smaller or zero wave.
7. #WaveReflection:
Wave reflection happens when waves encounter a boundary or barrier and bounce back. The angle of incidence (the angle at which the wave strikes the boundary) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which the wave bounces off the boundary).
8. #WaveRefraction:
Wave refraction occurs when waves pass from one medium to another and change speed, causing their direction to bend. This bending is determined by the change in the wave's speed and the angle at which it approaches the boundary between the two media.
9. #WaveDiffraction:
Wave diffraction refers to the bending or spreading of waves as they encounter obstacles or pass through narrow openings. Diffraction allows waves to spread out and bend around corners, enabling phenomena like sound reaching around objects or light passing through a small gap.
10. #SoundWaves:
Sound waves are mechanical waves that result from the vibration of particles in a medium, typically air. They can travel through gases, liquids, and solids, and are responsible for our perception of sound.
11. #LightWaves:
Light waves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum and can travel through a vacuum or a transparent medium. They exhibit properties of both waves and particles (photons) and are responsible for our perception of sight.
These #tags cover the key topics and concepts taught at the Ordinary level when studying waves. Understanding these areas will provide a foundation for further exploration of waves and their various applications in science and technology.
Definition of electromagnetic induction, demonstration of electromagnetic induction using a straight wire and a solenoid, predicting the direction of current using Fleming's right rule, Applications of electromagnetic induction in d.c. motor, d.c. generator and a.c generator. Transformers and power transmission
effect of magnetic field on current carrying conductor, Fleming's left hand rule, Magnetic field of current carrying conductor in magnetic field of a permanent magnet
Definition of electromagnet;
Uses of electromagnets in electric bell, telephone receiver, moving coil loud speaker, and relay switch
definition of magnetism, uses of magnets, properties of magnets, magnetic domain theory, methods of magnetization( i.e. single stroke, double stroke, electrical and induction methods), method of demagnetization (i.e. heating, hitting, electrical methods,), storing a magnet , soft and hard magnetic substances
Structure, Functions, and adaptations of parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem and phloem for A -level students
epithelial and connective tissues, squamous, cuboidal, columnar tissue, endocrine tissue, connective tissues
Drawings of plants and animal cell; functions of parts of plants and animal cells, differences between plants and animal cells. suitable for advanced level and institutions.
Although plants and animals are both living organisms, there are significant differences between the cells found in each of them.
Plant cells have some unique features that distinguish them from animal cells:
1. Cell wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, which provides structural support and protection for the cell. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
2. Chloroplasts: Plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll and convert sunlight into energy. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
3. Large central vacuole: Plant cells have a large central vacuole that occupies a significant portion of the cell. The vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste products and helps maintain cell turgidity. Animal cells may have smaller vacuoles, but they are not as prominent as in plant cells.
4. Plasmodesmata: Plant cells are interconnected by tiny channels called plasmodesmata, which allow for the transport of nutrients and signals between adjacent cells. Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata.
In contrast, animal cells have some distinguishing features:
1. Centrioles: Animal cells often contain centrioles, which are involved in cell division and the formation of spindle fibers. Plant cells lack centrioles.
2. Lysosomes: Animal cells have lysosomes, which are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. Lysosomes break down waste materials and cellular debris. Plant cells may have vacuoles with some similar functions but do not have true lysosomes.
3. Cilia and flagella: Animal cells often have cilia or flagella, which are hair-like structures involved in cellular movement. Plant cells do not have cilia or flagella, although some algae, which are plant-like organisms, may have similar structures.
Despite these differences, plant and animal cells also share many similarities. Both types of cells have a nucleus that contains the genetic material (DNA), as well as similar membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This energy is then stored as potential energy and used by organisms for various metabolic activities.
The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle).
Light-dependent reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts and require light energy. The key steps involved in this stage are:
1. Absorption of light: Chlorophyll and other pigments in the thylakoid membrane absorb photons of light. This energy is used to excite electrons in chlorophyll.
2. Electron transport chain: Excited electrons from chlorophyll are passed along a series of electron carriers, losing energy in the process. This energy is used to pump hydrogen ions (H+) across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient.
3. ATP synthesis: The proton gradient created is used to drive ATP synthase, an enzyme that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This process is called chemiosmosis.
4. Generation of reducing power: Excited electrons from chlorophyll are also used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH, another molecule that stores energy.
Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and do not require light directly. The key steps involved in this stage are:
1. Carbon fixation: CO2 from the atmosphere is captured and added to a 5-carbon molecule called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), forming an unstable 6-carbon molecule. This process is catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco.
2. Reduction: The 6-carbon molecule is quickly split into two 3-carbon molecules called 3-phosphoglycerate (PGA). ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to convert PGA into a 3-carbon sugar called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
3. Regeneration: Some G3P molecules are converted back into RuBP, while others are used to synthesize glucose and other organic molecules.
Overall, photosynthesis is a crucial process for sustaining life on Earth as it provides oxygen for respiration and serves as the primary source of energy for most living organisms.
Organs of neck and muscles on the chest, abdominal structures in undisturbed form, veins from digestive system, arteries to digestive system, urinogenital system, diaphragm, visceral structures of the chest in undisturbed form and blood vessels in the neck and chest region.
classification, external structures functions and adaptations, Ecology
preparation alkynes for vicinal dihalidespreparation of ethyne from carbonpreparation of long chain alkynesreaction of alkynes alkynes, ethyne, propynes, butynwith hydrogen chloride and hydrogen bromidesreaction of alkynes, ethyne, propynes, butyne with chlorine and bromines
Preparation of alkenes from alcoholspreparation of alkenes from alkylhalides
## Preparation of Alkenes from Alcohols and Alkyl Halides:
There are several methods for preparing alkenes from alcohols and alkyl halides. Here are the two most common ones:
**1. Dehydration of Alcohols:**
This method involves removing a water molecule from an alcohol to form an alkene. There are two main types of dehydration reactions:
- **Acidic dehydration:** This reaction uses concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid as a catalyst. The alcohol must have at least one beta-hydrogen (a hydrogen atom on the carbon atom next to the hydroxyl group). This reaction follows the **Saytzeff rule**, which states that the more substituted alkene will be the major product.
- **Thermal dehydration:** This reaction uses heat (around 300°C) and often involves passing the alcohol vapor over alumina as a catalyst. This method has fewer regioselectivity issues than acidic dehydration, but it often leads to a mixture of products.
**2. Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides:**
This method involves removing a hydrogen halide (like HCl or HBr) from an alkyl halide to form an alkene. There are also two main types of dehydrohalogenation reactions:
- **E2 elimination:** This reaction uses a strong base, such as potassium hydroxide or sodium ethoxide, as a catalyst. The base abstracts a proton from the beta-hydrogen, while the halide ion leaves, forming an alkene. The major product follows the **Zaitsev rule**, which is similar to the Saytzeff rule.
- **E1 elimination:** This reaction is less common and requires strong heat instead of a base. It typically occurs with tertiary alkyl halides and follows a different mechanism than E2 elimination.
**Additional points to consider:**
* The specific method used for preparing an alkene depends on the starting material, the desired product, and other factors like availability of reagents and reaction conditions.
* Both dehydration and dehydrohalogenation reactions can be regioselective, meaning that the position of the double bond in the alkene product can be controlled to some extent.
* Safety precautions are essential when working with concentrated acids, strong bases, and organic solvents.
I hope this information helps! Feel free to ask if you have any further questions or need more details on specific aspects of these reactions.
Carbonium ionsreaction of alkenes with hydrogen bromide in presence a peroxideozonolysis of alkenespolymerization of alkenes
reaction of alkenes with chlorine, bromine and iodinereaction of propene, ethene, 2-methylpropene with water, halogens, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid
Alkenes part 1
examples of alkenes, reduction of alkene, reaction of alkenes with dilute potassium permanganate, electrophylic addition reaction, reaction of alkenes with halogens, chlorine, bromine and iodine
Properties of alkeness
sources ofalkenes
Nomenclature of alkanes
Definitions of organic chemistry
Hydrocarbons
Functional groups,
Homologous series
Isomerism
An introduction to the tangent and velocity problems. Using the slope of the secant line to approximate the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a given point. Also, using the average velocity to approximate the instantaneous velocity of an object at a specific time. An exciting start to the journey of calculus! #tangentline #tangentandvelocityproblems #calculus1 #mathtvwithprofessorv #mathprofessor #youtubemath #mathvideos #calculus #calculusvideos #calculushelp #tangentlinetoacurve #averagevelocity #instantaneousvelocity #algebra #precalculus #mathtutor
Don't forget to LIKE, Comment, & Subscribe!
xoxo,
Professor V
https://linktr.ee/mathtvwithprofessorv
Calculus 2 Lecture Videos on Integration:
Integration by parts: https://youtu.be/0klrkpMUsXA
Tabular Integration: https://youtu.be/pzhJciqIrzw
Trigonometric integrals: https://youtu.be/0MqaL3fwPu4
Trigonometric Substitution: https://youtu.be/rAH-dRxQ4o0
Partial Fraction Decomposition: https://youtu.be/mT25uSspHIU
Strategy for Integration: https://youtu.be/P_smvpnX3_g
Improper Integrals: https://youtu.be/Q0zD3GjXJ1s
Trig Review:
Unit Circle: https://youtu.be/nl84YXi1_3A
Trig Identities: https://youtu.be/SLVrNGi1Br0
Sum and Difference Formulas: https://youtu.be/9kC8gwkxf6A
Double Angle & Half-Angle Formulas: https://youtu.be/EaF57Y4B2uY
Calculus 3 Video Lectures:
https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLl-Np5U6u5E65pR
#mathtvwithprofessorv #integration #partialfractions #partialfractionmethod #partialfractiondecomposition #trigonometricsubstitution #trigintegrals #trigsubstitution #integrals #integralcalculus #calculus2 #calculusvideos #calculus2videos #integralvideos #trigonometricintegrals #math #youtubemath #mathvideos #mathtutor #mathprofessor #calculusvideos #integrationbyparts #integralcalculus
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCokuhoh5N_B0ZxHcE
Socials:
IG: @mathtvwithprofessorv
TikTok: @mathtvwithprofessorv
I'm also an Amazon influencer, so feel free to support and shop:
https://amazon.com/shop/mathtvwithprofessorv
EXCITING NEWS: You can now sign up for my Patreon at the link below!
https://www.patreon.com/mathtvwithprofessorv
My Patreon is a place for students to have access to exclusive ad-free content not available on my YouTube channel! Access to the library of additional videos, worksheets, and more is available with the "Star Pupil Package" tier for just $9.99/month (USD).
https://www.patreon.com/mathtvwithprofessorv
*This video is copy protected and cannot be downloaded or used in any capacity without my permission.*
In this video , we look at how to derive the equation of motion of a simple pendulum using the concepts of calculus of variations
I had a request for a spicier integral of the day, so I hope this fits the bill! Enjoy!
Don't forget to LIKE, Comment, & Subscribe!
xoxo,
Professor V
https://linktr.ee/mathtvwithprofessorv
Calculus 2 Lecture Videos on Integration:
Integration by parts: https://youtu.be/0klrkpMUsXA
Tabular Integration: https://youtu.be/pzhJciqIrzw
Trigonometric integrals: https://youtu.be/0MqaL3fwPu4
Trigonometric Substitution: https://youtu.be/rAH-dRxQ4o0
Partial Fraction Decomposition: https://youtu.be/mT25uSspHIU
Strategy for Integration: https://youtu.be/P_smvpnX3_g
Improper Integrals: https://youtu.be/Q0zD3GjXJ1s
Trig Review:
Unit Circle: https://youtu.be/nl84YXi1_3A
Trig Identities: https://youtu.be/SLVrNGi1Br0
Sum and Difference Formulas: https://youtu.be/9kC8gwkxf6A
Double Angle & Half-Angle Formulas: https://youtu.be/EaF57Y4B2uY
Calculus 3 Video Lectures:
https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLl-Np5U6u5E65pR
#mathtvwithprofessorv #integration #partialfractions #partialfractionmethod #partialfractiondecomposition #trigonometricsubstitution #trigintegrals #trigsubstitution #integrals #integralcalculus #calculus2 #calculusvideos #calculus2videos #integralvideos #trigonometricintegrals #math #youtubemath #mathvideos #mathtutor #mathprofessor #calculusvideos #integrationbyparts #integralcalculus
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCokuhoh5N_B0ZxHcE
Socials:
IG: @mathtvwithprofessorv
TikTok: @mathtvwithprofessorv
I'm also an Amazon influencer, so feel free to support and shop:
https://amazon.com/shop/mathtvwithprofessorv
EXCITING NEWS: You can now sign up for my Patreon at the link below!
https://www.patreon.com/mathtvwithprofessorv
My Patreon is a place for students to have access to exclusive ad-free content not available on my YouTube channel! Access to the library of additional videos, worksheets, and more is available with the "Star Pupil Package" tier for just $9.99/month (USD).
https://www.patreon.com/mathtvwithprofessorv
*This video is copy protected and cannot be downloaded or used in any capacity without my permission.*
Joining high school can be an exciting but also overwhelming experience. Here's some general guidance to help you navigate your new journey:
Academics:
Get organized: Develop a system for managing your homework, assignments, and deadlines. A planner, calendar app, or notebook can be helpful.
Find your learning style: Do you learn best by listening, reading, or doing? Knowing your style will help you find effective study methods.
Don't be afraid to ask for help: If you're struggling in a subject, don't hesitate to ask your teacher or a tutor for help.
Challenge yourself: Step outside your comfort zone and consider taking advanced classes or electives that interest you.
Balance is key: While academics are important, make sure to leave time for activities and hobbies you enjoy.
Social Life:
Be open-minded: High school is a great time to meet new people from diverse backgrounds. Don't be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and connect with others.
Join clubs and activities: Get involved in activities you enjoy, whether it's sports, music, or student government. This is a great way to make friends and explore your interests.
Be respectful: Treat everyone with kindness and respect, even if you don't always agree with them.
Find your support system: Surround yourself with positive people who make you feel good about yourself. This could be friends, family, or teachers.
Personal Growth:
Discover your passions: Explore different activities and interests to find what you're truly passionate about.
Develop good habits: Time management, self-discipline, and healthy communication are all essential life skills.
Embrace challenges: High school will present its share of challenges, but view them as opportunities to learn and grow.
Seek guidance: Don't be afraid to ask for help from trusted adults like counselors, teachers, or family members.
Remember, you are not alone: Everyone experiences ups and downs in high school. Talk to friends, family, or a counselor if you're feeling overwhelmed.
Additional Tips:
Get involved in your community: Volunteering and participating in community events is a great way to give back and gain valuable experience.
Stay organized: This includes staying organized with your belongings, your schedule, and your mind.
Take care of yourself: Make sure to get enough sleep, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly.
Enjoy the experience: High school is a time for learning, growing, and making memories. Relax, have fun, and make the most of it!
Remember, everyone's high school experience is different. Find what works best for you and don't be afraid to ask for help along the way. Best of luck!
In this video, I take you through the topic trigonometry.
You will be able to learn how use trigonometrical identities to solve equations in trigonometry and also to prove and derive unique identities in trigonometry.
Worked examples from U.A.C.E UNEB Question Bank have also been included in this video.
This video is suitable to A-level students in Senior Five and Six offering Principle Mathematics as part of their combination. E.g. (PCM, BCM, PEM, PMT, PMA, MEG, MET, MEF, MEA e.t.c.)
Maths made simple
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. It is useful for solving problems in various fields such as physics, engineering, and astronomy. Trigonometry involves the use of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent to calculate angles and distances in triangles. It also includes concepts such as the unit circle, Pythagorean theorem, and inverse trigonometric functions. Trigonometry has practical applications in navigation, surveying, and even the design of video games and animations.
In this video, I have tried to answer all Questions of UNEB Sub ICT 2023 Paper 1. Hopefully, it helps you in your revision, and those who didn't do the paper can learn more from it as well.
I welcome comments on guidance in case a certain Roman (Question) was not well addressed.
Subscribe and Share
Thank You
This videos elaborates how to work with composite functions
This lecture has been viewed about 17 million times. About 1 million times on MIT's OCW, 7 million times in the channel "For the Allure of Physics" and about 9 million times in this channel. Walter Lewin puts his life on the line to demonstrate that he is a strong believer in the conservation of energy. He explained why the sky is blue, why the clouds are white and why sunsets are red. Great demonstrations! MIT video streamed this lecture in real time. It was viewed live by about 25 thousand people all over the world.
OMG!
#WalterLewin #physics
The narrower the pipe section, the lower the pressure in the liquid or gas flowing through this section. This paradoxical fact, following from the law of conservation of energy, is called the Bernoulli principle or law.
The scales of the universe refer to the different sizes at which objects and phenomena exist in the cosmos. Here are some commonly used scales of the universe, ranging from the smallest to the largest:
1. Quantum Scale: This scale deals with the behavior of subatomic particles, such as quarks, leptons, and bosons. It is described by quantum mechanics and includes phenomena like particle interactions, wave-particle duality, and quantum entanglement.
2. Atomic and Molecular Scale: At this scale, objects such as atoms and molecules exist. It includes the study of atomic structure, chemical bonding, and molecular interactions. Fields like chemistry and molecular biology operate at this scale.
3. Cellular and Biological Scale: This scale encompasses the study of living organisms and their cellular components. It includes cells, organelles, and biological molecules like DNA, proteins, and enzymes. Biology and genetics are primarily concerned with this scale.
4. Human Scale: This scale relates to the size and dimensions of the human body and objects that we commonly interact with. It includes human anatomy, physiology, and various human-made structures such as buildings and vehicles.
5. Planetary Scale: At this scale, celestial bodies like planets, moons, asteroids, and comets exist. It includes the study of their formation, geology, atmosphere, and interaction with other bodies in the solar system.
6. Stellar Scale: This scale encompasses stars and their properties, such as their size, mass, temperature, and brightness. Stellar evolution, fusion reactions, and the life cycle of stars are studied at this scale.
7. Galactic Scale: At this scale, galaxies exist, which are vast collections of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. It includes the study of galaxy formation, structure, dynamics, and the interactions between galaxies.
8. Cosmic Scale: This scale deals with the large-scale structure of the universe, including galaxy clusters, superclusters, and cosmic voids. It involves studying the distribution of matter and the large-scale properties of the universe, such as its expansion and the cosmic microwave background radiation.
9. Universal Scale: This is the largest scale encompassing the entire observable universe. It includes all matter, energy, space, and time. Understanding the origin, evolution, and fate of the universe itself is the primary focus at this scale.
These scales help scientists categorize and study objects and phenomena based on their sizes and characteristics, allowing us to better comprehend the vastness and complexity of the universe.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of the lesson, a learner should be able to;
Mention at least four communication devices and their use
Define an adjective
Describe communication devices using adjectives and modifiers
Use comparatives to compare at least three pairs of devices
Welcome to our S.2 Mathematics lesson where we dive into the intriguing world of Linear Inequalities. 📈
In this lesson, we will explore two key aspects:
1. **Solving Linear Inequalities:** We will unravel the art of solving linear inequalities, providing you with the tools and techniques to handle a variety of inequality problems.
2. **Representing Linear Inequalities Graphically:** Discover the power of visualization as we learn how to represent linear inequalities graphically. This graphical representation adds a whole new dimension to understanding inequalities.
📋 **Lesson Highlights:**
- Understanding the basics of linear inequalities.
- Step-by-step problem-solving techniques for solving linear inequalities.
- Introduction to the number line and its role in representing inequalities.
- Drawing and interpreting graphs of linear inequalities.
📊 **Why Learn Linear Inequalities?**
Linear inequalities play a crucial role in various fields, from economics and engineering to everyday decision-making. Mastery of this topic is a valuable skill in problem-solving.
📚 **Additional Resources:**
- Practice exercises to reinforce your understanding.
Join us in this engaging lesson to build a strong foundation in linear inequalities. Stay tuned for more math insights and don't forget to hit the "Subscribe" button to keep up with our lessons. Your mathematical journey begins here! 🧮📚
Linear inequalities are mathematical expressions that compare two quantities using inequality symbols such as < (less than), > (greater than), ≤ (less than or equal to), or ≥ (greater than or equal to). These inequalities involve linear functions, meaning every term in the inequality has a degree of 1.
For example, consider the linear inequality 2x + 3 < 7. This inequality states that the expression 2x + 3 is less than 7. To solve this inequality, we can follow these steps:
1. Subtract 3 from both sides: 2x + 3 - 3 < 7 - 3
Simplified: 2x < 4
2. Divide both sides by 2: (2x) / 2 < 4 / 2
Simplified: x < 2
Therefore, the solution to the linear inequality 2x + 3 < 7 is x < 2. This means that any value of x less than 2 would satisfy the inequality.
Linear inequalities can also involve variables on both sides of the inequality symbol. For example, consider the linear inequality 3x - 2 ≥ 5x + 1. To solve this inequality, we can follow similar steps:
1. Subtract 5x from both sides: 3x - 2 - 5x ≥ 5x + 1 - 5x
Simplified: -2x - 2 ≥ 1
2. Add 2 to both sides: -2x - 2 + 2 ≥ 1 + 2
Simplified: -2x ≥ 3
3. Divide both sides by -2 and reverse the inequality symbol: (-2x) / -2 ≤ 3 / -2
Simplified: x ≤ -3/2
Therefore, the solution to the linear inequality 3x - 2 ≥ 5x + 1 is x ≤ -3/2. This means that any value of x less than or equal to -3/2 would satisfy the inequality.
The equations of linear motion are used to understand the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object moving in a straight line. There are four main equations of linear motion, which are:
1. s = ut + 1/2 at^2 - This equation relates the distance traveled s by an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and time t.
2. v = u + at - This equation relates the final velocity v of an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and time t.
3. v^2 = u^2 + 2as - This equation relates the final velocity v of an object to its initial velocity u, acceleration a, and the distance traveled s.
4. s = (u + v) t / 2 - This equation relates the distance traveled s by an object in terms of its initial velocity u, final velocity v, and time t.
Here,
s = distance traveled by the object
u = initial velocity of the object
v = final velocity of the object
a = acceleration of the object
t = time taken for the motion
These four equations can be used to solve a variety of problems related to linear motion. For example, if we know the initial velocity, acceleration, and time taken by an object, we can use the first equation to calculate the distance traveled by the object. Similarly, if we know the initial and final velocities and the acceleration, we can use the third equation to calculate the distance traveled by the object.
Linear motion refers to the motion of a particle or an object in a straight line. The object moves along a path without any change in direction. The speed or velocity of the object may vary, but its direction remains constant. A common example of linear motion is a car traveling along a straight road.
On the other hand, nonlinear motion refers to the motion of a particle or an object in a curved or non-straight path. In nonlinear motion, the path of the object is not a straight line, and it may change direction at any point. The speed or velocity of the object may also vary.
Nonlinear motion can be divided into two main categories: uniform circular motion and accelerated motion. In uniform circular motion, the object moves in a circular path with a constant speed but changing direction. A common example of uniform circular motion is a satellite orbiting around the Earth.
In accelerated motion, the speed or velocity of the object changes with time. The object may accelerate in a straight line or in a curved path. A common example of accelerated motion is a car accelerating from rest and then coming to a stop.
Overall, the main difference between linear and nonlinear motion is the path of the object. In linear motion, the object moves along a straight path, while in nonlinear motion, the path of the object may be curved or non-straight.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a simple sugar) and oxygen. It is a crucial biological process that occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
During photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by pigments in the chloroplasts, primarily chlorophyll. This energy is used to power a series of chemical reactions that take place in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle).
In the light-dependent reactions, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy carriers are used in the next stage of photosynthesis.
In the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH are utilized to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. This process involves a series of chemical reactions that use enzymes to catalyze the formation of glucose. The glucose produced can be used by the plant as an energy source or stored as starch for later use.
Photosynthesis not only provides energy-rich glucose for the plant but also produces oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is released into the atmosphere and is vital for supporting aerobic respiration in many organisms.
Overall, photosynthesis is an essential process that allows plants, algae, and certain bacteria to convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It plays a crucial role in sustaining plant life and maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Additionally, photosynthesis acts as the primary source of energy for most ecosystems on our planet.
Autotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which an organism synthesizes its own food using simple inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide and water, with the help of energy from sunlight or inorganic chemical reactions. Autotrophs are organisms that have the ability to produce organic compounds from inorganic sources.
There are two main types of autotrophs: photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs use sunlight as a source of energy and are able to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds by the process of photosynthesis. Examples of photoautotrophs include plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
Chemoautotrophs, on the other hand, obtain their energy from chemical reactions involving inorganic compounds, such as sulfur, nitrogen, or iron. They can use the energy from these reactions to convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds. Examples of chemoautotrophs include some bacteria and archaea.
Autotrophic nutrition is important for the biosphere because it forms the basis of the food chain. Autotrophs are the primary producers that provide the energy and organic compounds essential for the survival of all other organisms. Through photosynthesis, autotrophs also release oxygen into the atmosphere, which is utilized by many organisms for respiration.
Overall, autotrophic nutrition is a unique mode of nutrition that enables organisms to produce their own food without relying on other organisms. It plays a vital role in sustaining life on Earth and maintaining ecological balance.
Electrical potential
emf
Potential difference
Types of cells
Ordinary level Current Electricity is a branch of physics that focuses on the study of electric currents and their behavior in circuits. It is typically taught at the Ordinary level (O-level), which is a secondary school level of education.
In this subject, students learn about the fundamental concepts and principles of electricity, such as electric charge, electric current, electric potential difference (voltage), and electric resistance. They also study the behavior of these parameters in different types of circuits, such as series circuits and parallel circuits.
Some of the main topics covered in Ordinary level Current Electricity include:
1. Electric circuits: Students learn about the components of an electric circuit, such as resistors, capacitors, and batteries. They study the flow of electric charge in a closed loop and how to calculate the total resistance in a series or parallel circuit.
2. Ohm's Law: Ohm's Law relates the current flowing through a conductor to the voltage across it and the resistance of the conductor. Students learn how to apply Ohm's Law to calculate various quantities related to current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit.
3. Electric power and energy: Students learn about the concepts of power and energy in electrical circuits. They study how to calculate the power dissipated or consumed by various components in a circuit and understand the relationship between power, current, and voltage.
4. Electrical safety: Students are taught about the importance of electrical safety and precautions to be taken when working with electricity. They learn about the potential hazards associated with electric shocks and how to prevent accidents.
5. Circuit diagrams: Students learn how to interpret and draw circuit diagrams, which are graphical representations of electrical circuits. They understand the symbols used for different components and how to analyze circuits based on their diagrams.
Throughout the course, students are also exposed to practical activities and experiments to reinforce their theoretical understanding of current electricity. They learn how to use electrical measuring instruments, such as ammeters and voltmeters, to measure current and voltage in circuits.
Overall, Ordinary level Current Electricity provides students with a foundational understanding of the principles and applications of electric currents in circuits. It serves as a basis for further studies in physics and related fields, including Advanced level (A-level) and university-level courses.
Definition of a function
Examples of functions
Solving functions
Mappings and relations are concepts in mathematics that involve the relationship between two sets or groups of elements.
A mapping, also known as a function, is a relation between two sets in which each element from the first set (domain) is paired with exactly one element from the second set (codomain). In other words, a mapping assigns each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain.
For example, consider the mapping f: {1, 2, 3} -> {a, b, c}, where f(1) = a, f(2) = b, and f(3) = c. This mapping assigns each element in the domain {1, 2, 3} to a unique element in the codomain {a, b, c}.
Mappings can also be represented using tables, graphs, or algebraic expressions. They are widely used in various mathematical concepts, such as calculus, algebra, and discrete mathematics.
A relation, on the other hand, is a general concept that describes any connection or association between elements of two sets. Relations do not necessarily have to be one-to-one or onto like mappings. They can be many-to-one, one-to-many, or even many-to-many.
For example, consider the relation R = {(1, a), (1, b), (2, c), (3, a)}. This relation represents the connections between elements of the set {1, 2, 3} and the set {a, b, c}. In this case, the element 1 is related to both a and b, and hence, it is a many-to-many relation.
Relations can also be represented using tables, graphs, or algebraic expressions. They are used in various areas of mathematics, such as number theory, algebraic structures, and set theory.
In summary, mappings and relations are essential concepts in mathematics that describe the relationships between elements of two sets. Mappings, also known as functions, assign each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain, while relations describe general connections or associations between elements of two sets, which can be one-to-one, onto, many-to-one, one-to-many, or even many-to-many.
Mappings and relations are concepts in mathematics that involve the relationship between two sets or groups of elements.
A mapping, also known as a function, is a relation between two sets in which each element from the first set (domain) is paired with exactly one element from the second set (codomain). In other words, a mapping assigns each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain.
For example, consider the mapping f: {1, 2, 3} -> {a, b, c}, where f(1) = a, f(2) = b, and f(3) = c. This mapping assigns each element in the domain {1, 2, 3} to a unique element in the codomain {a, b, c}.
Mappings can also be represented using tables, graphs, or algebraic expressions. They are widely used in various mathematical concepts, such as calculus, algebra, and discrete mathematics.
A relation, on the other hand, is a general concept that describes any connection or association between elements of two sets. Relations do not necessarily have to be one-to-one or onto like mappings. They can be many-to-one, one-to-many, or even many-to-many.
For example, consider the relation R = {(1, a), (1, b), (2, c), (3, a)}. This relation represents the connections between elements of the set {1, 2, 3} and the set {a, b, c}. In this case, the element 1 is related to both a and b, and hence, it is a many-to-many relation.
Relations can also be represented using tables, graphs, or algebraic expressions. They are used in various areas of mathematics, such as number theory, algebraic structures, and set theory.
In summary, mappings and relations are essential concepts in mathematics that describe the relationships between elements of two sets. Mappings, also known as functions, assign each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain, while relations describe general connections or associations between elements of two sets, which can be one-to-one, onto, many-to-one, one-to-many, or even many-to-many.
Vegetative propagation
business paternship
This Video details how to handle and manage project work in the new lower secondary Curriculum
Identify potential sources of stress
Early recognition of signs & symptoms and work on the issues
Look at practical stress management techniques.
Identify a range of coping strategies.
Put emphasis on the benefits of balancing work with personal life.
Use strategies that help one manage their workload.
Promote sharing experiences in order to build a supportive social group while encouraging collaboration
ordinary organic chemistry
learning Advanced level Maths
KEY AREAS IN ENTREPRENEURSHIP PAPER ONE
STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY
NUMERICAL METHODS
MECHANICS
New Curriculum
Competency based
Generic skills
Builders frame work
Created by @hakimtheblackbutterfly #tiktok #trending #shortsfeed #newvideo #youtubeshorts #instagram #subscribe @youtubecreater47 @youtubecreators @rkcreationsvlog @Biology made easy#biology#cytology
😍😍😍
😍😍😍
😍😍😍
😍😍😍😍
.
This video talks about the definition of the enthalpy of atomisation and how it helps calculate the Bond enthalpy, sublimation enthalpy, etc., in various cases.
00:00- Introduction
2:35- Relationship between atomisation enthalpy and bond enthalpy
4:30- Worked example
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Thermodynamics” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 11 Chemistry” here - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
This video talks about the definition of the standard enthalpy of combustion. It also helps us identify the relationship between the standard enthalpy of combustion and the calorific value for a given fuel. This helps us compare different fuels.
00:00- Introduction
2:14- Is combustion enthalpy always negative?
2:34- Comparing fuels using combustion enthalpy values.
4:13- Calculating enthalpy of formation using combustion enthalpy values.
Practice this concept - “https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
Check out more videos and exercises on “Thermodynamics” - https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/physical-chemi
To get you fully ready for your exam and help you fall in love with “Chemistry”, find the complete bank of exercises and videos for “Class 11 Chemistry” here -https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/class-11-chemi
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by
Jitin Nair
TV LESSON SS3 is a Lagos state online class for SS3 student in preparation for WAEC.
Subscribe- be the first to view our latest videos
Connect with WazobiaMax TV on social media:
Follow WazobiaMax TV on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/wa...
Follow WazobiaMax TV on instagra m: https://www.instagram.com/w...
Follow #WazobiaMax TV on Twitter: https://twitter.com/wazobiamax
This episode gives you a detailed introduction of a subtopic Histology under a topic of Cell Biology with more emphasis on Simple Epithelial Tissue.
This episode is setting a pace for a series of episodes that are about the same topic subtopic that u need to watch to get a complete doze of content.
May you subscribe(if you haven't), like the videos,comment and share the links with friends
This video breaks down areolar tissue as the simplest connective tissue.please Enjoy.
In this video, we look in detail at standard enthalpy change of reaction. I discuss what this means and how to carry out the calculation. I give you two examples to try yourself before taking you through the correct answers. I also explain to you what the units of standard enthalpy change of reaction actually mean.This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
In this video, we look at how to determine the standard enthalpy change of a reaction. First I take you through the experimental procedure. I then explain to you how to correct the results to take into account heat losses from the experimental setup. Finally, I show you how to carry out the calculation.This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
You can find all my A Level Chemistry videos fully indexed at https://www.freesciencelessons.....co.uk/a-level-revis
In this video, I explain how to determine the standard enthalpy change of combustion for a liquid fuel. First I show you the method. Then I take you through the calculation. Finally, I explain why the standard enthalpy change of combustion that we determine may be different to published values.
This video is aimed at the UK A Level Chemistry specifications. Students studying International A Level Chemistry will need to check their specification.
Image credits
Spirit Burner
https://upload.wikimedia.org/w....ikipedia/commons/9/9
Xofc, CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0), via Wikimedia Commons
Hess's law, also known as the law of constant heat summation, is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics that states that the total enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is independent of the pathway taken, as long as the initial and final states are the same. In simpler terms, it doesn't matter how many steps a chemical reaction takes, the overall heat absorbed or released will always be the same.
This law is based on the concept of **enthalpy**, which is a thermodynamic property that combines a system's internal energy and the amount of work it can perform on its surroundings due to changes in pressure and volume. Enthalpy is often denoted by the symbol **H**.
Hess's law has numerous applications in chemistry, particularly in thermochemistry, which deals with the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. It allows chemists to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction even if it cannot be measured directly, by breaking it down into a series of simpler steps for which the enthalpy changes are known.
Here's a visual representation of Hess's law:
[Image of Hess's law diagram]
**Example:**
Consider the combustion of methane (CH₄) to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O):
CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) ΔH = -890.3 kJ
However, it is difficult to measure the enthalpy change for this reaction directly in a single step. Instead, we can break it down into a series of hypothetical steps for which the enthalpy changes are known:
1. Combustion of hydrogen to form water vapor:
H₂(g) + ½O₂(g) → H₂O(g) ΔH = -285.8 kJ (multiply by 2)
2. Condensation of water vapor to form liquid water:
H₂O(g) → H₂O(l) ΔH = -44.0 kJ
By summing the enthalpy changes for these two steps, we can calculate the enthalpy change for the overall combustion reaction:
ΔH = (-285.8 kJ/mol) x 2 + (-44.0 kJ/mol) = -890.6 kJ/mol
This value is in excellent agreement with the experimental value of -890.3 kJ/mol, demonstrating the validity of Hess's law.
Hess's law is a powerful tool that allows chemists to predict the enthalpy changes for a wide variety of chemical reactions, even if they cannot be measured directly. It is a cornerstone of thermochemistry and has numerous applications in fields such as chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental science.
The dreaded Hess's cycle I hear you cry! Hopefully this video will put those Hess's demons to rest. Take a look to find out how you use a Hess's cycle and how to draw them correctly in order to work out enthalpy of reaction, combustion and formation.
A level Chemistry
Energetics
Enthalpy Change
Exothermic and Endothermic
Reaction Profiles
Combustion
Formation
Standard Conditions
Hess' Law
Bond Energy
Physical Chemistry | Year 1
In this video, we explore more about a unique type of animal tissue called connective tissue with more focus on the breakdown of the different types.
Please enjoy, watch other episodes, and Share with colleagues and friends
Talk to Tr OSBERT NUWARINDA
+256705353517/+256779114179
osbertnuwa94@gmail.com
Get yourself a copy of biology book written by Tr.OSBERT NUWARINDA
1. Ordinary biology Made Easy (Good biology book for research for O'level)
2. Advanced Biology Demystified vol1 &vol 2 ( With good precise but enriching content of Advanced Level Biology)
In this episode, we expound more on the compound Epithelial Tissue. Just watch till the end and I tell you what,! you need to watch out for the next episode is really waoo.
watch, enjoy, and share. don't forget to subscribe Incase you haven't.
@nuwarindaosbertug9724
The first week video contents.
In this episode, we breakdown glandular tissue, types, examples and look at the structures of different glands. you don't have to miss it. I know you are going to enjoy it like never before.
Next video is about connective tissue also explained in totality. Just sit and enjoy the learning.
Investing Basics for Educators: Building Wealth for a Brighter Future
As an educator, you dedicate your life to shaping the minds of the future. But what about your own future? Investing can be a powerful tool for educators to build wealth and secure a brighter financial future.
Why should educators invest?
*Financial security: Investing can help you reach your financial goals, whether it's retirement, buying a home, or paying for your children's education.
Beat inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your money over time. Investing can help your money grow faster than inflation, protecting your purchasing power.
* **Compound interest:** The magic of compound interest is often described as "earning interest on interest." Over time, even small investments can grow significantly thanks to compound interest.
* **Early start advantage:** The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow. Educators often have stable jobs and steady income, making them prime candidates for early investing.
Investing Basics for Beginners:
1. Set your financial goals:
* What are you hoping to achieve with your investments?
* Do you want to save for retirement, a down payment on a house, or your children's college education?
* Different goals will require different investment strategies.
2. Understand your risk tolerance:
* How comfortable are you with the possibility of losing money?
* Some investments are riskier than others, but they also have the potential for higher returns.
* It's important to choose investments that match your risk tolerance.
3. Diversify your portfolio:
* Don't put all your eggs in one basket!
* Spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, can help reduce your risk.
4. Invest regularly:
* Even small contributions can add up over time.
* Setting up a regular investment plan can help you stay on track.
5. Seek professional advice:
* If you're new to investing, it's a good idea to seek professional advice from a financial advisor.
* They can help you create a personalized investment plan that meets your needs and goals.
Resources for Educators:
National Education Association: The NEA offers a variety of resources on financial planning for educators, including webinars, articles, and calculators.
American Federation of Teachers: The AFT also offers resources on financial planning for educators, including a retirement calculator and investment guide.
Securities and Exchange Commission: The SEC provides investor education resources, including information on different types of investments, how to read financial statements, and how to avoid scams.
Investing can seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. By starting early, setting realistic goals, and diversifying your portfolio, you can build a solid foundation for your financial future. As an educator, you invest in your students every day. Now, it's time to invest in yourself.
Solving simultaneous equations using geogebra
This is the best video to get started with the Swahili language!
https://bit.ly/3iRtq0X Click here to learn Swahili twice as fast with FREE PDF!
↓Check how below↓
Step 1: Go to https://bit.ly/3iRtq0X
Step 2: Sign up for a Free Lifetime Account - No money, No credit card required
Step 3: Achieve Your Learning Goal and master Swahili the fast, fun and easy way!
In this video, we will teach you the most common 2000 swahili words that you must know if you're a an absolute beginner. This is THE place to start if you want to learn Swahili, and improve both your listening and speaking skills.
Get started with Swahili language now! https://bit.ly/3iRtq0X
Follow us here:
■ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SwahiliPod101
■ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/SwahiliPod101
■ Twitter: https://twitter.com/SwahiliPod101
Also, please LIKE, SHARE and COMMENT on our videos! We really appreciate it. Thanks!
#beginners #vocabulary #swahili #learnswahili #swahililanguage #swahilipod101
Finally get fluent in Swahili with PERSONALIZED lessons and the best free resources: https://bit.ly/41DovaK ↓ Check how below ↓
Step 1: Go to https://bit.ly/41DovaK
Step 2: Sign up for a Free Lifetime Account - No money, No credit card required
Step 3: Start learning Swahili the fast, fun and easy way!
With this video compilation you'll be able to catch up with the best lessons of 2023, and review Swahili phrases to master the language!
You've decided to start learning Swahili, so let's build up your vocabulary! In this video, you'll learn some of the most important words and phrases in the Swahili language. If you want to start learning Swahili, this video is made for you. Our hosts express themselves in simple Swahili, with English subtitles. This video will challenge your listening comprehension skills and help you progress in your Swahili study.
Let us help you through this 2023 Recap video compilation as you continue learning Swahili! This is the fastest, easiest way to pick up basic Swahili!
Click here to get started with the Swahili language: https://bit.ly/41DovaK
Also, please LIKE, SHARE and COMMENT on our videos! We really appreciate it. Thanks!
This video is part of Voice of America's teacher education efforts. See the playlist here:
https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLd9hCvj34W5gd1C
For more teaching resources, see: Let's Teach English https://learningenglish.voanews.com/p/6764.html
In this lecture , we prove the Bayes theorem , a very fundamental part of probability .
A Level Physics Advanced Information Revision : ) Experimental skills in materials are important in the OCR Advanced Information but also relevant to other exam boards.
Please note that is not a complete list and many many different variation of experiments could come up in practicals.
Full in depth playlist of online lessons on materials: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
Note: springs in series and parallel should be included in this video as well. Please see this here:
https://youtu.be/WMHC4txjK0k
Chapters:
00:00 Intro
00:15 Tensile and Compressive Forces
00:58 Hooke's Law
02:25 Hooke's Law experiment
04:27 Work Done by a spring and Elastic Potential Energy
06:38 Stress strain
08:45 Ultimate Tensile Strength
09:48 Young's Modulus
10:48 Experiment to determine Young's Modulus
17:06 Ductile material, elastic and plastic deformation
17:57 Ductile material - Stress and Strain Graph
19:26 Brittle Material - Stress and Strain Graph
20:07 Rubber and Polyethene - Stress and Strain Graph
This is excellent A Level Physics revision for all exam boards including OCR A Level Physics, AQA A level Physics, Edexcel A Level Physics, CIA Cambridge International A Level Physics, Eduqas etc.
Forces in physics refer to the interactions between objects that cause changes in their motion or shape. They are described using Newton's laws of motion and are crucial in understanding the behavior and motion of objects in the physical world. Here are some common types of forces in physics:
1. Gravitational Force: This force is responsible for the attraction between objects with mass. It is the force that keeps planets in orbit around the sun and objects grounded on the Earth.
2. Normal Force: The normal force is the force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it. It acts perpendicular to the surface, preventing objects from falling through it.
3. Frictional Force: Friction is the resistance that opposes motion when two objects come in contact. It occurs due to the roughness of surfaces. Frictional force acts parallel to the surfaces in contact and can either be static (preventing motion) or kinetic (opposing motion).
4. Tension Force: Tension is the force exerted by a string, rope, or a similar object when it is pulled at both ends. It transfers force uniformly along its length and is responsible for maintaining the integrity of the object.
5. Applied Force: An applied force is the force exerted on an object by a person or object. It can be used to push, pull, or move an object in various directions.
6. Spring Force: When an elastic object, such as a spring, is compressed or stretched, it exerts a force according to Hooke's law. This force is directly proportional to the displacement from the object's equilibrium position.
7. Electrical Force: Electrical forces exist between charged particles, such as electrons and protons. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract.
8. Magnetic Force: Magnetic forces result from the interaction between moving charged particles (currents) or magnetic fields. Magnets can attract or repel each other based on their poles.
9. Buoyant Force: Buoyant force acts on objects immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) and is directed upward. It is responsible for the ability of objects to float in a fluid and is determined by the density of the fluid and the displaced volume.
These are just a few examples of forces in physics. Understanding and analyzing these forces is essential in the study of mechanics and other branches of physics, allowing us to predict and explain the behavior of objects in various scenarios.
Resolving forces in depth video: https://youtu.be/GqyI3zl9P_oArchimedes Principle in depth video: https://youtu.be/mDavwJOiYJYChapters:00:00 F=ma, The net force02:18 The Newton02:40 Free Body Diagrams, Types of Forces08:05 Net Force Example Question11:48 Drag16:06 Experiment: Motion of a ball through a viscous liquid18:32 Resolving Forces on a slope21:42 Centre of gravity, experiment23:48 Moments26:20 Non perpendicular Moments29:05 The Principle of Moments30:44 Force Couples and Torque32:00 Triangle of forces34:19 Density and Pressure35:00 Pressure at a height, h.37:00 Archimedes PrincipleThis is excellent A Level Physics revision for all exam boards including OCR A Level Physics, AQA A level Physics, Edexcel A Level Physics, CIA Cambridge International A Level Physics, Eduqas etc.
Join my free Physics Newsletter: https://zphysicslessons.net/about
My Physics Workbooks: https://zphysicslessons.net/my-workbooks
Full list of my revision videos:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
My online lessons on motion:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
Chapters:
00:00 Independence of vertical and horizontal motion
01:31 Vertical and horizontal components
02:55 How the components vary
04:44 Calculating the maximum height
07:17 Maximum Range
This is excellent A Level Physics revision for all exam boards including OCR A Level Physics, AQA A level Physics, Edexcel A Level Physics, CIA Cambridge International A Level Physics, Eduqas etc.
Get my Uncertainty Workbook: https://koji.to/k/9uCs
Teacher Version (for your entire institution): https://koji.to/k/9uCx
All of my revision videos:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
Please also revise:
Graphical methods:
https://youtu.be/tMkSM6gFKWM
Uncertainty from a data set:
https://youtu.be/JIJf_aNUDaw
Foundations of Physics complete playlist with more examples and online lessons on uncertainties:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
Chapters:
00:00 Intro
00:18 Absolute Uncertainties
01:33 Percentage Uncertainties
03:44 Combining Uncertainties
04:14 Adding or Subtracting
06:31 Multiplying or Dividing
08:21 Raising to a power
My Physics Workbooks: https://zphysicslessons.net/my-worksheets
Next step: Vectors practice questions: https://youtu.be/tMr--psNVxM
Part 1 Foundations of Physics: https://youtu.be/WOckc29sZJA
All the Maths for A Level Physics: https://youtu.be/neBotgd2PKA
Credit: Music for the intro: "At the top", provided by Camtasia included Royalty Free Music
Chapters:
00:00 Intro
00:15 Scalars and Vectors
03:09 Distance and displacement
04:51 adding parallel vectors
05:39 adding perpendicular vectors
08:47 resolving vectors
14:46 adding non-perpendicular vectors - scale diagram
16:31 adding non-perpendicular vectors - sine and cosine rules
20:47 adding non-perpendicular vectors - resolution
Join my free Physics Newsletter: https://zphysicslessons.net/about
My Physics Workbooks: https://zphysicslessons.net/my-workbooks
Part 2: All of projectile Motion:
https://youtu.be/WRWFpYeETHM
Instantaneous velocity video: https://youtu.be/aV47J1Leam4
Chapters:
00:00 Intro
00:37 Distance and displacement
01:55 Average speed and velocity
03:52 Instantenous velocity and the gradient of the tangent
06:39 Displacement time graphs and distance time graphs
07:43 Acceleration
09:16 the area under a velocity time graph is displacement
10:10 SUVAT equations and examples
17:04 Falling under gravity
18:17 Calculating the maximum height
21:38 An experiment to determine g, method 1
26:42 An experiment to determine g, method 2
27:45 Proofs and derivations of the SUVAT equations
36:00 Stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance
This is excellent A Level Physics revision for all exam boards including OCR A Level Physics, AQA A level Physics, Edexcel A Level Physics, CIA Cambridge International A Level Physics, Eduqas etc.
Join my free Physics Newsletter: https://zphysicslessons.net/about
My Physics Workbooks: https://zphysicslessons.net/my-workbooks
A rather long video covering the section on Quantum Physics on the OCR Physics A specification, however applicable to all exam boards. Remember, after you have revised the content - time for practice questions! : )
Check out all of my revision videos:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLSygKZqfTjP
This is excellent A Level Physics revision for all exam boards including OCR A Level Physics, AQA A level Physics, Edexcel A Level Physics, CIA Cambridge International A Level Physics, Eduqas etc.
Chapters:
00:00 Photons
01:26 Energy of a Photon
03:06 Base Unit of Planck's constant, h
04:40 The Electronvolt, eV conversion factors
06:24 Photoelectric Effect, Work Function, Threshold Frequency
10:03 The Gold Leaf Electroscope Experiment
13:50 Einstein's Photoelectric Effect Equation
19:13 Why Maximum Kinetic Energy?
20:27 Graphs
22:19 Wave Particle Duality - Electron Diffraction
23:40 De Broglie Wavelength
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of the properties, relationships, and measurement of 2D and 3D shapes. In 2D geometry, we focus on the properties and relationships of flat shapes such as points, lines, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles.
Points are the basic building blocks of geometry. They define the position and location of objects in 2D space. A line is a straight path with infinite length that connects two points. An angle is the space between two intersecting lines or planes.
Triangles are 2D shapes that are formed by connecting three lines. They have three sides, three angles, and three vertices. Based on the length of their sides and angles, triangles are categorized into scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles.
Quadrilaterals are 2D shapes that have four sides and four vertices. The most common quadrilaterals are squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids. These shapes have unique properties that define their symmetry, angles, and side lengths.
Circles are 2D shapes that are defined by a center point and a radius. They have an endless number of points on their circumference, and all of these points are equidistant from the center of the circle.
In 2D geometry, we use various tools and techniques to measure and calculate the properties of these shapes. For example, we use formulas to calculate the perimeter and area of triangles and quadrilaterals, and we use measurements to calculate the radius, circumference, and area of circles.
Overall, 2D geometry plays a fundamental role in many areas of math and science, including engineering, architecture, and physics. Understanding the principles and properties of 2D shapes helps us to better understand and analyze the world around us.
This compilation of our Napoleonic Wars series covers the period from 1809 to the Emperor's abdication in 1814. Along the way we encounter the horrors of the French occupation of Spain and Portugal, Napoleon's disastrous invasion of Russia, and the great struggle for German in 1813. The series concludes with arguably Napoleon's finest campaign - his doomed defence of Paris in 1814.
Support Epic History TV on Patreon from $1 per video, and get perks including ad-free early access & votes on future topics https://www.patreon.com/EpicHistoryTV
👕 Buy EHTV t-shirts, hoodies, mugs and stickers here! https://teespring.com/en-GB/st....ores/epic-history-tv
Visit our online bookshop to find great books on this and other topics:
https://uk.bookshop.org/shop/epichistorytv
As a bookshop.org affiliate we earn from qualifying purchases while donating 10% of sales to support independent bookshops!
Thank you to our series partner Osprey Publishing https://ospreypublishing.com/
Thank you to Nuneaton Museum & Art Gallery for kind permission to use 'The Battle of Vitoria' painting by James Prinsep Beadle.
Special thanks to Alexander Averyanov for kind permission to use his paintings 'Battle of Smolensk' , 'Bivouac', 'Artilleryman's Exploits', 'Prince Pyotr Bagration at Borodino: The Last Counterattack', 'Horse Guards at the Battle of Borodino', 'The Fighting for Shevardino Redoubt', 'The Fighting for Bagration Flèches', 'Maloyaroslavets', 'At Gorodnya 25 October 1812', 'Council of War at Gorodnya'.
Special thanks to Egor Zaitsev for kind permission to use his painting 'Prayer Before the Battle of Borodino'.
📚Recommended reading (as an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases):
📖 Campaign: Borodino 1812 by Philip Haythornthwaite https://geni.us/YNVnu
📖 Combat:French Guardsman vs Russian Jäger 1812-14 https://geni.us/rWnOT
📖 Napoleon's Guard Infantry by Philip Haythornthwaite https://geni.us/sbj92uT
📖 The Napoleonic Wars by Todd Fisher http://geni.us/R5ZI9c
📖 Salamanca 1812: Wellington Crushes Marmont by Ian Fletcher https://geni.us/h0Ha
📖 The Cossacks 1799 - 1815 by Laurence Spring https://geni.us/mW1x2
📖 Lützen & Bautzen 1813: The Turning Point by Peter Hofschröer https://geni.us/NS4fkL
📖 Leipzig 1813: The Battle of the Nations https://geni.us/fZqo
📖 1813: Leipzig - Napoleon & the Battle of the Nations by Digby Smith https://geni.us/GMqpsG1
🎶🎶 Music from Filmstro: https://filmstro.com/?ref=7765
Get 20% off an annual license with this exclusive code: EPICHISTORYTV_ANN
🎶 Additional music from Kevin MacLeod (incompetetch.com):
'Egmont Overture'; 'Intrepid', 'Long Note Three'; 'Song of the Volga Boatmen'; 'Trio for Violin Viola and Piano'
Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
#epichistorytv #napoleonicwars #napoleon
An artificial intelligence (AI) system engaged in a live, public debate with a human debate champion at Think 2019 in San Francisco (watch replay). At an event sponsored by IBM Research and Intelligence Squared U.S., the champion debater and IBM’s AI system, Project Debater, began by preparing arguments for and against the resolution, “We should subsidize preschool.” Both sides then delivered a four-minute opening statement, a four-minute rebuttal, and a two-minute summary.
https://www.ibm.com/blogs/rese....arch/2019/02/ai-deba
These are Full Audio Books of the Bible Acts thru Revelation (King James Version) I use calm & relaxing ambient background music (A paid licensed track from "Soothing Relaxation" Peder B. Helland) Who I highly recommend for his great talents as a composer of music for whatever need you may have for background tracks for projects.
Click this Link to visit his website: soothingrelaxation.com
And this is his Youtube Link:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCjzHeG1KWoonmf9d5
Narrated by Max McLean who is the "Official Voice of the Listeners Bible". He has been nominated for four awards from the Audio Publishers Association for his narration of The Listener’s Bible. His creative work has been cited with distinction by the New York Times, Washington Post, Boston Globe, Chicago Tribune, Wall Street Journal, and CNN to name a few media outlets.
This is the Link for His Website:
https://listenersbible.com/about-max-mclean/
I've given special attention to produce these files with high quality sound, speed & tone/pitch. For the Best ambient experience, Headphones are recommended.
These are great to listen to as you fall asleep, meditate, or just for relaxing background noise at the office or home. The video's also make a great screensaver also. All video footage used in these are copyrighted, created and produced by myself (Gospel Productions by Joe Hackney) all rights reserved. If you would like to share these videos, please copy and paste this full description into your description. PLEASE DO NOT RE-UPLOAD THESE VIDEOS AS IF THEY WERE CREATED BY YOU.
May you be blessed and grow spiritually as you listen to the Word of God.
~Joseph P. Hackney
Mark 16:15 Internet Ministries &
Gospel Productions by Joe Hackney
You can also follow my other ministry pages on these Social Networks Below
https://www.facebook.com/Gospe....lProductionsbyJoeHac
https://www.facebook.com/mark1....615ministries.wordpr
https://www.pinterest.com/joehackney71/_created/
https://www.facebook.com/10000....9387599255/videos/27
Want to score a 1500 or higher on the SAT® Exam? Having trouble finding time to prepare? UWorld is here to help!
Start your FREE TRIAL : collegeprep.uworld.com
Eternity Network International
-------------------------------------------------------------
➤Video original and produced exclusively by Christocentric Message
➤Speaker: Apostle Joshua Selman
-------------------------------------------------------------
Full Video:
Subscribe to this YouTube channel and hit the notification bell to be notified whenever we upload a new video: https://www.youtube.com/christocentricmessagehq
You can download free unlimited audio messages of Apostle Joshua Selman from their website (link below)
https://t.me/christocentricmessage
When making these videos, our purpose is to make quality educational motivational videos and share these with our viewers.
🔴NOTE: Christocentric Message is not in any way in Partnership with Eternity Network Internation, Neither do we represent them
🔴CONNECT WITH US 🔴
Facebook-https://www.facebook.com/christocentricmessage
Instagram-https://instagram.com/christocentric_message
Twitter- https://twitter.com/MChristocentric
Telegram- https://t.me/christocentricmessage
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please to connect directly or officially with Apostle Joshua Selman or His Ministry kindly use the following Official Social Media Handle:
Public Relations:
+2348147214444
+2349077777853
+2349150227448
Counseling/Prayer:
+2348075770001
Protocol:
+2347087777765
Media:
+2348100289892
Finance:
+2349065996660
Instagram: (@Koinoniaglobal)
https://instagram.com/koinoniaglobal
Facebook:
https://facebook.com/koinoniaglobal
Twitter:
https://twitter.com/koinoniaeni
YouTube:
https://YouTube.com/c/koinoniaglobal
----------------------------------------------------------
To easily get messages shared on this page, search for these:
apostle joshua selman
apostle joshua selman sermons
apostle joshua selman 2021
apostle joshua selman worship songs
apostle joshua selman prayer
apostle joshua selman live
apostle joshua selman midnight prayers
apostle joshua selman messages
apostle joshua selman praying in tongues
apostle joshua selman songs
apostle joshua selman holy spirit
apostle joshua selman wife and family
apostle joshua selman tongues of fire
apostle selman 2021
apostle selman live
apostle selman joshua
joshua selman
joshua selman message
koinonia global
koinonia abuja
koinonia apostle joshua selman
koinonia live stream
koinonia global live
koinonia abuja live
koinonia messages by apostle joshua selman
Equation of State of an Ideal Gas
NOTE: at the end, the conversion between Kelvin and Celsius should use 273 rather than 237.
1 + 1 = 3 Proof | Breaking the rules of mathematics.
One plus one equals three is possible only by breaking the rules of mathematics. 1+1=3 is not supported by mathematical logic. These strange results may come by the mistake during the calculations. This viral math tricks video is given here to show a message that a single mistake in mathematical calculations can lead to a destructive result.
The second part of this video containing how to prove 2+2 = 5. Two plus two equals five is an old mathematical illusion that also proves that a mistake in the calculation can make different results. 2+2=5 viral math problem may puzzle anyone. But if someone carefully watches the 2+2=5 video, there is a mistake in the calculation. The secret of 2+2=5 is hidden in its calculation. The ground rules of mathematics were not followed in 2+2=5 calculations.
The third part of this video shows how easy to multiply anything by 11. This fun of mathematics video is intended to show you a message that a simple mistake in mathematical calculations may lead to wrong results.
------------------------------------------------------------
Subscribe Matescium: https://youtube.com/c/matescium?sub_confirmation=1
------------------------------------------------------------
Watch other interesting videos on Matescium
Hacking Someone’s age: https://youtu.be/HW8TQ3JVGmA
You can solve it within 10 seconds: https://youtu.be/MfeqLjhZAYE
Mathematics ca prove anything: https://youtu.be/DYDMudoi_mw
5 5 5 = 6 How | 6s Challenge | Part 2: https://youtu.be/NbJGLIYA-6A
0 0 0 = 6 How | 6s Challenge: https://youtu.be/io0WIBzx_jU
------------------------------------------------------------
Thanks for watching it.
#1+1=3 #mathtricks #viralmath #1+1=3mathtrick #1+1=3How #1+1=3Proof
politics, business, motivational speakers in Uganda, bobiwine, museven, best schools in Uganda , best teachers in Uganda, best historians in Uganda,#school
Demonstration of the calculations of the resultant force and direction for a concurrent co-planar system of forces.
This video demonstrates the tabular method for 2d systems.
Get more lessons like this at http://www.tebtalks.comIn this lesson, you will learn an introduction to physics and the important concepts and terms associated with physics 1 at the high school, college, or university level.We will review Newton's laws of motion, projectile motion, force, energy (potential and kinetic energy), gravitation, momentum, collisions and more.
Signup for your FREE trial to The Great Courses Plus here: http://ow.ly/s2UK30r2D3q
Five areas of physics worth remembering: Classical mechanics, energy and thermodynamics, electromagnetism, Relativity, and Quantum Mechanics. Classical mechanics - two main concepts worth knowing. The first is Newton’s second law: F= ma: Force equals mass times acceleration. If you apply a force to a fixed mass, it tells you how much acceleration you will get. And knowing acceleration which is the change in velocity, you can make predictions.
The second equation is the law of universal gravitation. it allows us to determine the motion of heavenly bodies. It says that the gravitational attraction between two bodies is the product of their masses divided by the distance between them squared, times a constant, called Newton’s gravitational constant.
Energy is not a vector like force or momentum, but it is just a number. Work is closely related to energy. It is force times distance traveled. Energy for most objects consists of kinetic energy plus potential energy. KE is the energy of motion, It is KE = ½ M V^2 – the more mass you have and/or the more velocity you have, the more energy you have.
Gravitational potential energy is expressed as PE = m g h – mass times the gravitational acceleration times the height. The total energy of an object is both Kinetic energy plus potential energy. Potential energy can take many forms. Gasoline or petrol has chemical potential energy. Important: Energy is always conserved. It is not created or destroyed. It only changes form.
Thermodynamics is the study of work, heat, and energy on a system. We showed energy is how much work you could do. But another form of energy is thermal energy. If a car is moving and you apply the brakes, the kinetic energy of the car gets converted to thermal energy, created by friction of the car’s brakes. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of atoms in a system. Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of atoms in a system.
Entropy is a measure of disorder, or more accurately, the information required to describe the micro states of a system. The 2nd law of thermodynamics states that entropy of an isolated system can never decrease. Energy at lower entropy can do more work than energy at high entropy. The one way flow of Entropy seems to be the only reason we have a forward flow of time.
Electromagnetism is the study of the interaction between electrically charged particles. The essentials are in Maxwell’s equations. If you have a static object with a charge, it will affect only other charges. If you have a static magnet, it will affect only other magnets. It will not affect charges. But if you have a moving charge, it will affect a magnet. And if you have a moving magnet, it will affect a charge. The constants mu naught and epsilon naught are the permeability and permittivity of free space. These two constants determine the speed of light because they measure the resistance of space to changing electric and magnetic fields.
Special Relativity: Einstein presumed that the speed is the same in any frame of reference. This was one of the postulates.
The second postulate was principle of relativity - the laws of physics are the same for all observes who are moving at the same velocity relative to each other. Einstein showed that the only way these can be true is if time was not fixed, but was relative.
General relativity: Later Einstein showed using the same assumptions, there would be no way to tell if you were in an accelerating reference frame or standing stationary on earth. A flashlight beam will bend in gravity. But since light always takes the shortest path between any two points, this means that space-time itself is bending.
Quantum mechanics: Three principles are important. First by Max Planck, says that energy is not continuous, but is quantized. The amount of energy equals the frequency of the radiation times Planck's constant. Using this, Einstein later showed that a photon is both a wave and a particle.
The second is the Heisenberg's uncertainty principle: you cannot know both a particle’s exact position and it’s exact momentum at the same time. For a particle with mass, this means if you know exactly where a particle is, you don’t know how fast going. If you know exactly how fast it’s going, you don’t know where it is.
#allphysics
#arvinash
Schrodinger's equation: prior to measurement, quantum systems are in superposed states. This means that their properties can only be expressed as a wave function. A wave function simplified, is a set of probabilities. So in a hydrogen atom, you can’t know where to find the electron in advance. All you can know is the probability of where you might find it, if you measured it. Prior to measurement, all quantum systems are waves of probabilities. This is not a limitation of our measuring devices. It is a limitation of reality.
Become a patron: https://www.patreon.com/bePatron?u=17543985
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the 4 states of matter such as solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Solids have a definite shape and volume. Liquids have a definite volume but not a definite shape since they assume the shape of the container. Gases do not have a definite volume or shape. Solids and gases are fluid which mean they have the ability to flow. Plasma is an ionized gas that can conduct electricity. Solids and liquids have a relatively high density and gases have a low density.
Organic Chemistry Tutor - Playlists: https://www.video-tutor.net/
Subscribe To My YouTube Channel: https://bit.ly/37WGgXl
E-Book & E-mail Newsletter: https://www.video-tutor.net/math-and-science-ebook.html
Chemistry Tutors: https://bit.ly/3PRCtSh
Useful Textbooks: https://www.amazon.com/shop/th....eorganicchemistrytut
Chemistry - Basic Introduction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-KfG8kH-r3Y
Scientific Notation Review: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZtB0vJMGve4
Significant Figures Review: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l2yuDvwYq5g
Unit Conversion Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eK8gXP3pImU
Accuracy and Precision: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0IiHPKAvo7g
Density Practice Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9CKDQE35qXQ
Pure Substances & Mixtures: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OHhnm2p5G3o
Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eI-tmv4DLEk
Physical and Chemical Changes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YE2xaMsoGFU
Solids, Liquids, Gases, & Plasma: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9TVOlTolKFA
Physical Vs Chemical Properties: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gH1R87ahFvA
Law of Conservation of Mass: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eBTNzScLUg4
Law of Definite Proportions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ly0ywRdVG_M
Law of Multiple Proportions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sxE95VOY-YY
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sNQsdrqsD_s
Cathode Ray Tube Experiment: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i6zyPOSreCg
Atoms - Basic Introduction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=acdkMeEKCNQ
Cations and Anions Explained: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aAV2DMAI5f8
Diatomic Elements & Molecules: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gi337Mx7wTc
Elements, Atoms, & Molecules: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pSJeMJaCkVU
Protons, Neutrons, & Electrons: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=65dDZulPhtg
Average Atomic Mass: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JT18bDAadQ0
What Are Isotopes? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bagegEZBtOs
Ionic and Covalent Bonding: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uDFLHTDJ4XA
Naming Molecular Compounds: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3agUL7-ezXk
Writing Formulas - Molecular Compounds: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KrJnnwLDY6o
Naming Ionic Compounds: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rSgduXqhhU
Writing Formulas - Ionic Compounds: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GJ4Mds0CWLE
Writing Formulas - Polyatomic Ions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=stu2omPRvbs
Introduction to Moles: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EowJsC7phzw
Resource Links: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chemistry Help: https://bit.ly/44YpRg6
Useful Chemistry Notes: https://etsy.me/3PoX0fe
Online Courses: http://bit.ly/3RqVN9Z
Buy Now, Pay Later: https://bit.ly/46gRXVg
Affordable Furniture: https://www.wayfair.com/
Car Insurance Student Discount: https://on.gei.co/3rlkHgz
Affiliate Marketing Disclaimer: Some of the links associated with this video may generate affiliate commissions on my behalf. As an amazon associate, I earn from qualifying purchases that you may make through such affiliate links.
This physics video tutorial explains the concept behind Newton's First Law of motion as well as his second and third law of motion. This video contains plenty of examples and practice problems. This video is useful for high school and college students studying physics.
Physics Basic Introduction and Final Exam Review:
https://www.video-tutor.net/ph....ysics-basic-introduc
Here is a list of topics on Newton's 3 Laws of Motion:
1. Newton's First Law of Motion - An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
2. Second Part of Newton's First Law of Motion - An object in motion will continue in motion unless acted on by a net force
3. The net force is zero when an object moves with constant velocity
4. Newton's 1st Law of Motion Examples & Demonstrations - Ball rolling on a rough surface with friction such as a carpet vs a ball rolling on a smooth surface such as ice with very little kinetic friction.
5. Earth moves continually in space - lack of frictional forces
6. Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force = Mass times acceleration
7. Newton's 2nd Law of Motion - Force is proportional to mass and acceleration. Mass and acceleration are inversely related when the force applied is constant.
8. Newton's Third Law of Motion - Action Reaction Pairs. For every action force, there is an equal but opposite reaction force.
9. Newton's 3rd Law of Motion Examples - Astronaut throwing a ball in space. Fisherman throws a package out into see and experiences a recoil velocity.
10. Impulse equals force multiplied by time
11. Momentum - Mass in Motion. Momentum equals mass times velocity.
12. Scalar vs Vector Quantities - Magnitude and Direction
13. Impulse - Momentum Theorem
14. Variation of Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force is the rate of change of momentum
15. Applied Force, Frictional Force, Normal Force vs Weight Force
16. How to calculate Final Velocity / Speed Using Acceleration
17. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity
18. One Dimension Kinematics Formulas
Physics - Basic Introduction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b1t41Q3xRM8
Physics 1 Formulas: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E8C06X-v0_A
Newton's 1st Law of Motion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fr5EMXZaujc
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ee6CHn0MRKE
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TxhESW6YtOg
Mass Vs Weight: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LB_WoV071vc
Free Body Diagrams: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52R61aSWHg0
Normal Force Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uyJTwljKSJ4
Elevator Physics Problem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sVVKpRvuNG0
Net Force Physics Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tfAJDST3cjo
What Is a Normal Force? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fRQq4_ry9-Q
Static Friction and Kinetic Friction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIBeeW1DSZg
Contact Forces: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iin29KFE4So
Tension Force Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F5oqJ5t-pa4
Types of Forces: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E626-DiQgRs
Inclined Planes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ufgY237M5KQ
Simple Machines: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WI8j3UlR-SE
Pulley Physics Problems: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N6IhkTjWrd4
The Pulley - Simple Machines: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GAegAHnfkMs
The Lever - Simple Machines: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0HSJx3CHZJ4
Mechanical Advantage: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SPTNKnCqlW4
What Is a Force? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vZ0ehaOEZKE
The 4 Fundamental Forces: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k1jaDh97Q_g
Physics Forces Review: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pL2YfC-22Uc
Physics 1 Final Exam Review: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CwkhvFlNFp0
introduction to physics
The modern periodic table is based on the periodic law: "The chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number." Let's see how is this different from Mendeleev's periodic table and how this solves for its predecessor's limitations.
More free lessons & practice https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/in-in-class-10
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Ram Prakash
Delta TV is an independent, impartial and honest television station, which is people centered designed to offer timely, accurate and relevant information to guide the audiences and advertisers on how best to meet their development needs and aspirations.
Delta TV is a business enterprise committed to deliver quality programming, befitting the intentions and value for money of the targeted consumers of services/products.
Professionalism, Hard work, Innovativeness and Team work are the backbone of the survival of the station with every one committing the best of their capability for success.
A speech refers to an informal or formal talk given to an audience. Giving a speech allows you to address a group of people to express your thoughts and oftentimes, your opinion.
The ability to pass Biology exams lies in writing and rewriting notes, questions and answers to internalise the concepts, improve on spellings and writing.
The ability to pass Biology exams lies in writing and rewriting notes, questions and answers to internalise the concepts, improve on spellings and writing.
In this video you will learn about the Biological practical and how to attempt questions.
Practical Chemistry with Experiments. Chemistry is the science of experiments. Scientific concepts can be easily understood by performing ...
The cosine rule, also known as the law of cosines, relates all 3 sides of a triangle with an angle of a triangle. It is most useful for solving for missing information in a triangle. For example, if all three sides of the triangle are known, the cosine rule allows one to find any of the angle measures.
Let's explore the ideas of redox reactions
Khan Academy is a free learning platform for Class 1-12 students with videos, exercises, and tests for maths, science, and more subjects. Our content is aligned to CBSE syllabus and available in Hindi, English, and many more regional languages.
Experience the joy of easy, seamless, accessible learning anywhere, anytime with Khan Academy.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/khanacademy
As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Created by Jitin Nair
Do you desire to receive greater revelation from God's Word? David Diga Hernandez shares 5 Bible study keys you can apply right now. If you’re a beginner in Bible study, these keys will increase your ability to understand God’s Word.
Did you enjoy this? Watch my sermon “How to CLEARLY Hear the Holy Spirit's Voice” by clicking here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMdXQtu-kis&list=PLyPy6sEo_wifRjopDQf_YvKFi7go2Ej-U&index=4
______________________________
📩 Sign up to receive updates, free content, and more from David via email: http://www.davidhernandezministries.com/email
______________________________
🟢 Make a one-time donation to help fund our livestreams, content, events, and more: http://www.davidhernandezministries.com/donate
______________________________
🤝 Become a monthly ministry supporter. Partner with David for as low as $15 a month: http://www.davidhernandezministries.com/partner
______________________________
🗓 Upcoming Events - Come experience the presence and power of the Holy Spirit. See David's ministry event schedule: http://www.davidhernandezministries.com/events
______________________________
📚 David’s books and ministry apparel: https://www.davidhernandezministries.com/shop
______________________________
Receive Livestream text alerts. Text LIVE to 747474
______________________________
Receive ETV content right to your phone. Text ETV to 747474
______________________________
00:00 - Introduction
00:29 - 5 Simple Keys to Studying the Bible
00:46 - Key #1: Revelation of the Holy Spirit
07:07 - Key #2: Dedication to Reading the Word
11:42 - Do You Feel Like You're Not Understanding What You Read?
15:50 - Key #3: Observation & Interpretation
22:05 - A Helpful Study Method: Macro - Micro - Macro
32:19 - Why Are There Chapters and Verses in the Bible?
40:22 - Key #4: Meditation on the Word of God
41:57 - Is it Hard for You to Remember What You Read?
50:05 - Key #5: Application - Apply the Scripture
55:16 - Receive This Prayer
58:32 - You Can Get Involved
#encountertv #daviddigahernandez #viralrevival #bible #bibleteaching #biblestudy #biblestudytools
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Africa
00:03:07 1 Prehistory
00:03:16 1.1 Paleolithic
00:06:57 1.2 Emergence of agriculture and desertification of the Sahara
00:11:23 1.3 Central Africa
00:12:11 1.4 Metallurgy
00:14:05 2 Antiquity
00:14:57 2.1 Ancient Egypt
00:19:50 2.2 Nubia
00:23:09 2.3 Carthage
00:25:58 2.3.1 Role of the Berbers
00:27:58 2.4 Somalia
00:28:38 2.5 Roman North Africa
00:34:02 2.6 Aksum
00:36:32 2.7 West Africa
00:38:51 2.8 Bantu expansion
00:40:17 3 Medieval and Early Modern (6th to 18th centuries)
00:40:29 3.1 Sao civilization
00:41:29 3.2 Kanem Empire
00:43:26 3.3 Bornu Empire
00:45:53 3.4 Shilluk Kingdom
00:46:33 3.5 Baguirmi Kingdom
00:47:03 3.6 Wadai Empire
00:47:54 3.7 Luba Empire
00:49:22 3.8 Lunda Empire
00:50:54 3.9 Kingdom of Kongo
00:53:48 3.10 Horn of Africa
00:53:57 3.10.1 Somalia
00:56:43 3.10.2 Ethiopia
00:58:37 3.11 North Africa
00:58:46 3.11.1 Maghreb
01:04:18 3.11.2 Nile Valley
01:04:26 3.11.2.1 Egypt
01:08:25 3.11.2.2 Sudan
01:08:32 3.11.3 Christian and Islamic Nubia
01:11:35 3.12 Southern Africa
01:12:15 3.12.1 Great Zimbabwe and Mapungubwe
01:15:47 3.12.2 Namibia
01:16:35 3.12.3 South Africa and Botswana
01:16:44 3.12.3.1 Sotho–Tswana
01:17:23 3.12.3.2 Nguni peoples
01:18:03 3.12.3.3 Khoisan and Afrikaaner
01:20:15 3.13 Southeast Africa
01:20:24 3.13.1 Prehistory
01:20:50 3.13.2 Swahili coast
01:23:42 3.13.3 Urewe
01:25:19 3.13.4 Madagascar and Merina
01:27:23 3.13.5 Lake Plateau states and empires
01:27:43 3.13.5.1 Kitara and Bunyoro
01:28:54 3.13.5.2 Buganda
01:29:53 3.13.5.3 Rwanda
01:31:05 3.13.5.4 Burundi
01:31:44 3.13.6 Maravi (Malawi)
01:32:41 3.14 West Africa
01:32:49 3.14.1 Sahelian empires & states
01:32:52 3.14.1.1 Ghana
01:34:41 3.14.1.2 Mali
01:38:08 3.14.1.3 Songhai
01:41:28 3.14.1.4 Sokoto Caliphate
01:42:55 3.14.2 Forest empires and states
01:43:04 3.14.2.1 Akan kingdoms and emergence of Asante Empire
01:47:03 3.14.2.2 Dahomey
01:48:42 3.14.2.3 Yoruba
01:51:15 3.14.2.4 Benin
01:52:59 3.14.2.5 Niger Delta and Igbo
01:54:24 4 19th century
01:54:33 4.1 Southern Africa
01:56:29 4.2 Nguniland
01:58:44 4.3 Voortrekkers
02:00:32 4.4 European trade, exploration and conquest
02:05:44 4.5 France versus Britain: the Fashoda crisis of 1898
02:06:45 4.6 European colonial territories
02:08:27 5 20th century
02:10:00 5.1 World War I
02:12:41 5.2 World War II: Political
02:16:46 5.2.1 French Africa
02:18:18 5.3 World War II: Military
02:20:42 5.4 Post-war Africa: decolonization
02:21:51 5.4.1 East Africa
02:22:33 5.4.2 North Africa
02:24:53 5.4.3 Southern Africa
02:25:45 5.4.4 West Africa
02:26:47 5.5 Historiography of British Africa
02:29:05 6 See also
Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago.
Learning by listening is a great way to:
- increases imagination and understanding
- improves your listening skills
- improves your own spoken accent
- learn while on the move
- reduce eye strain
Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone.
You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCuKfABj2eGyjH3ntP
You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through:
https://github.com/nodef/wikipedia-tts
"The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing."
- Socrates
SUMMARY
=======
The history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and – at least 200,000 years ago – anatomically modern humans (Homo sapiens), in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. The earliest known recorded history arose in the Kingdom of Kush, and later in Ancient Egypt, the Sahel, the Maghreb and the Horn of Africa.
Following the desertification of the Sahara, North African history became entwined with the Middle East and Southern Europe while the Bantu expansion swept from modern day Cameroon (West Africa) across much of the sub-Saharan continent in waves between around 1000 BC and 0 AD, creating a linguistic commonality across much of the central and Southern continent.
During the Middle Ages, Islam spread west from Arabia to Egypt, crossing the Maghreb and the Sahel. Some notable pre-colonial states and societies in Africa include the Ajuran Empire, D'mt, Adal Sultanate, Warsangali Sultanate, Kingdom of Nri, Nok culture, Mali Empire, Songhai Empire, Benin Empire, Oyo Empire, Ashanti Empire, Ghana Empire, Mossi Kingdoms, Mutapa Empire, Kingdom of Mapungubwe, Kingdom of Sine, Kingdom of Sennar, Kingdom of Saloum, Kingdom of Baol, Kingdom of Cayor, Kingdom of Zimbabwe ...
😇😍
😍
#youtubeshorts #dancevideo #viral
😇
😜
marriage
Project-based learning (PBL) or project-based instruction is an instructional approach designed to give students the opportunity to develop knowledge and skills through engaging projects set around challenges and problems they may face in the real world.
In this lecture , we look at how to deal with shortest distance problems usingEuler's differential Equation
To gather with Love and perfect Unity====
REACH US @ 336-747-3348 or Email:sautiyauamshotv@gmail.com
UNVA IMYIFATIRE YURUBYIRUKO RWIKIGIHE [Agira ati Abasore nabakobga twifashe nabi murikigihe iyunvire
To gather with Love and perfect Unity=
Thanks to all those that shares our videos may God bless ya'll
To gather with Love and perfect Unity====
REACH US @ 336-747-3348 or Email:sautiyauamshotv@gmail.com
#AmahoroTVMJ256 #JOHNUMCOFFICIAL
PLEASE SHARE AND SUBSCRIBE AND IF U AHVE ANYCOMMENTS DON'T HESITATE TO COMMENTS DOWN BELLOW OR CONTACT US @336-740-2824
OR Email: sautiyauamshotv@gmail.com
LETS GATHER WITH UNITY AND LOVE
KEEP SHARING AND SUBSCRIBING AND GOD WILL BLESS YOU!!!
To gather with Love and perfect Unity====
SUBSCRIBE
Tusigeuze maumbile ya Asili yetu tunapofanya hivo ni chukizo mbere ya Mungu.
Hari byinchi Umwuka wera adufasha niyompanvu tumukenye. Ibyakozwe. 1:8
Share to all the youth
Continue subscribing to this YouTube channel and also don't forget to tap 🔔
😍
Amateka yabibiriya
This video is about finding the square root of a surd by first converting it into a perfect square. i have applied the techniques on the example sqrt(3-2*sqrt(2))
In this lecture, we derive Euler's Differential Equation that will help us in our next lectures,. wish you the best as you watch this video
Project-based learning is an instructional approach where students learn by actively engaging in real-world projects. These projects are typically interdisciplinary and require students to apply their knowledge and skills to solve a problem or complete a task.
What is PBL?
Project Based Learning (PBL) is a teaching method in which students learn by actively engaging in real-world and personally meaningful projects.
In Project Based Learning, teachers make learning come alive for students.
Students work on a project over an extended period of time – from a week up to a term– that engages them in solving a real-world problem or answering a complex question. They demonstrate their knowledge and skills by creating a public product or presentation for a real audience.
As a result, students develop deep content knowledge as well as critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, and communication skills. Project Based Learning unleashes a contagious, creative energy among students and teachers.
And in case you were looking for a more formal definition...
Project Based Learning is a teaching method in which students gain knowledge and skills by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to an authentic, engaging, and complex question, problem, or challenge.
Watch Project Based Learning in Action
These 7-10 minute videos show the Gold Standard PBL model in action, capturing the nuts and bolts of a PBL unit from beginning to end.
Project-based learning in chemistry teaching is an instructional approach where students actively engage in real-world, hands-on projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills in chemistry. Instead of traditional lecture-based teaching, project-based learning focuses on student-centered learning, where students take ownership of their learning and work collaboratively to solve problems or complete projects.
In chemistry, project-based learning can involve various activities such as conducting experiments, designing and building models, analyzing data, researching and presenting findings, and solving chemical problems. These projects are often interdisciplinary, integrating concepts from other subjects like physics, biology, and environmental science.
The goal of project-based learning in chemistry teaching is to provide students with a deeper understanding of chemical concepts and principles, as well as develop their critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration skills. By working on authentic, real-world projects, students can see the relevance and application of chemistry in their everyday lives, making the learning experience more meaningful and engaging.
Some examples of project-based learning in chemistry teaching include:
1. Designing and conducting an experiment to investigate the effect of different variables on a chemical reaction.
2. Creating a model or simulation to understand the behavior of atoms and molecules.
3. Researching and presenting a project on the environmental impact of a specific chemical or chemical process.
4. Collaborating with peers to solve a chemical problem or design a solution to a real-world issue.
5. Analyzing and interpreting data from a chemical analysis or experiment to draw conclusions and make predictions.
Overall, project-based learning in chemistry teaching promotes active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, while also fostering creativity, collaboration, and communication among students.
Topology is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and structures of spaces. In university mathematics, topology is typically studied as a subfield of analysis or geometry.
In topology, the focus is on studying the properties of spaces that are preserved under continuous transformations, such as stretching, bending, and twisting. The main objects of study in topology are topological spaces, which are sets equipped with a collection of subsets called open sets. These open sets satisfy certain axioms, such as being closed under finite intersections and arbitrary unions.
Topology is applied in various areas of mathematics, including analysis, geometry, algebra, and differential equations. It provides a framework for studying the properties of functions, continuity, convergence, compactness, connectedness, and many other concepts that are fundamental in mathematical analysis. In geometry, topology is used to study the properties of shapes and surfaces, such as their curvature, dimensionality, and topological invariants.
Topology also has applications in other fields, such as physics, computer science, and engineering. For example, in physics, topology is used to study the properties of space-time and the behavior of particles. In computer science, topology is applied in areas such as network analysis, data visualization, and algorithm design. In engineering, topology optimization is used to find the optimal layout or configuration of structures or systems to achieve certain performance criteria.
Overall, topology provides a powerful mathematical framework for studying the properties and structures of spaces, and its applications extend to various areas of mathematics and beyond.
Watch Trace & Julia defy gravity in this episode of DNews Labs!
Help support DNews Labs by completing this one-question survey - http://bit.ly/dlabssurvey
Watch More DNews Labs ►►►► http://dne.ws/1NIjeVw
____________________
DNews is dedicated to satisfying your curiosity and to bringing you mind-bending stories & perspectives you won't find anywhere else! New videos twice daily.
Watch More DNews on TestTube http://testtube.com/dnews
Subscribe now! http://www.youtube.com/subscri....ption_center?add_use
DNews on Twitter http://twitter.com/dnews
Trace Dominguez on Twitter https://twitter.com/tracedominguez
Julia Wilde on Twitter https://twitter.com/julia_sci
DNews on Facebook https://facebook.com/DiscoveryNews
DNews on Google+ http://gplus.to/dnews
Discovery News http://discoverynews.com
Download the TestTube App: http://testu.be/1ndmmMq
Episode 1: Why Black Africans Were Historically Viewed As A Threat ?
The view that Black Africans were historically viewed as a threat is a complex issue with multiple factors. One significant factor is the history of colonialism and the European conquest of Africa. European powers colonised Africa for its natural resources, and the perception of Africans as "primitive" or "uncivilised" was used to justify the exploitation and subjugation of African peoples.
Another factor is the transatlantic slave trade, which saw millions of Africans forcibly taken from their homes and transported to the Americas as slaves. The dehumanization of Africans as property and the violent treatment they received from their slave owners further reinforced the perception of Africans as a threat.
Additionally, racism and prejudice against Black people have been pervasive throughout history and continue to be a problem today. This bias has often led to the assumption that Black people are inherently violent or dangerous, perpetuating the stereotype of the "angry Black man" or "aggressive Black woman."
In short, the perception of Black Africans as a threat has deep roots in history, including colonialism, slavery, and ongoing prejudice and discrimination. It is a complex issue that requires a nuanced understanding of history and culture to fully grasp.
============================
Let's come together in reasonable dialogue to honor our ancestors and reclaim the world through an African lens. Join me as we delve into African history, culture, and worldview to better understand their relevance to our lives today. By sharing our thoughts and knowledge, we can pave the way for a new culture of awareness and reclaim our story. As the African Diaspora saying goes, "I am because we are, and we are because I am."
#blackscreenstatus #blackamerica #slavery
This stream is created with #PRISMLiveStudio
This stream is created with #PRISMLiveStudio
This stream is created by Tebtalks
This stream is created with #PRISMLiveStudio
In this tutorial we shall guide you on how to get started with EXCEL (NEW TRICKS 2023)
FOR MORE RELATED VIDEOS PLEASE FOLLOW US ON OUR SOCIAL MEDIA PLATFORMS
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCEAlDOqZwPpDLshDE
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/gousetech
Twitter: https://twitter.com/GoUseTech2
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/go-use-tech-0a871123b/
Tebtalks: https://tebtalks.com/@1662457783922720
Whatsap: https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=%2B256779113920&text&type=phone_number&app_absent=0
Email: usetech.go@gmail.com
Thanks for the support
Regards
NABASA JONATHAN
FOUNDER GO-USE TECH
jnabasa135@gmail.com, +256 779113920
some people feel no interest of going back to Africa for some reasons
__________
But i think home will be home forever
I don't know what you think
drop your comment
down please
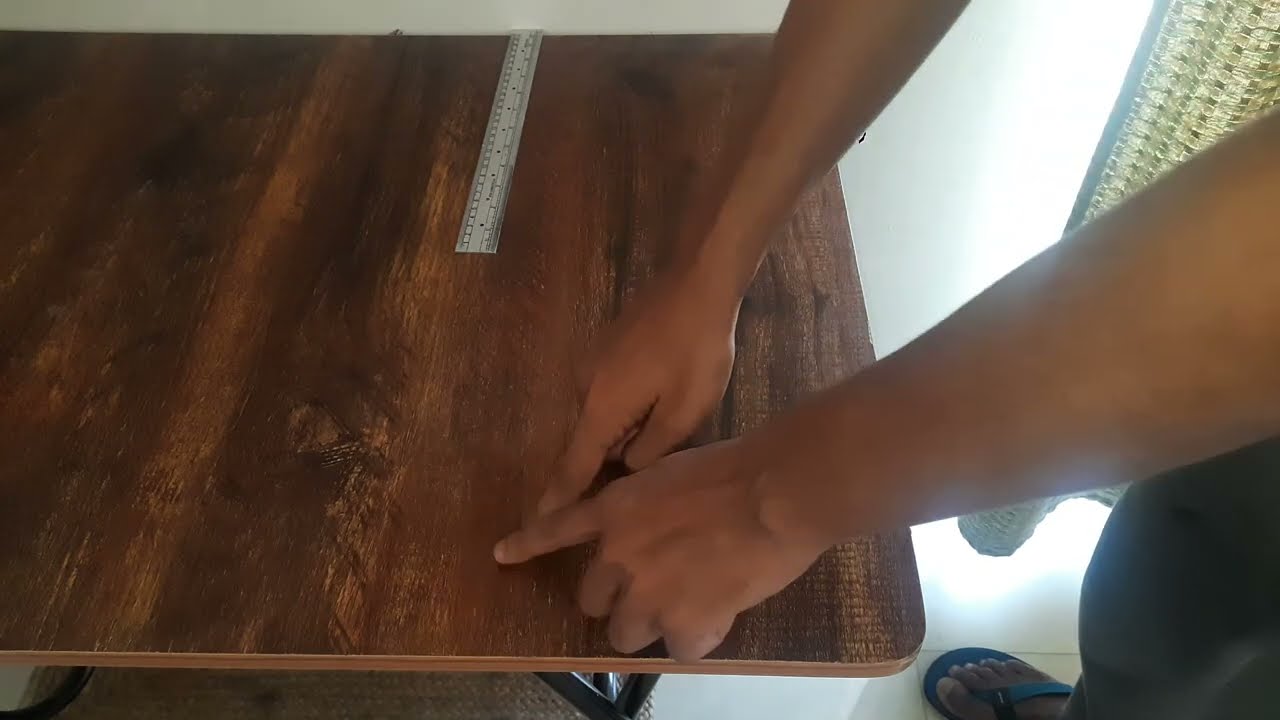
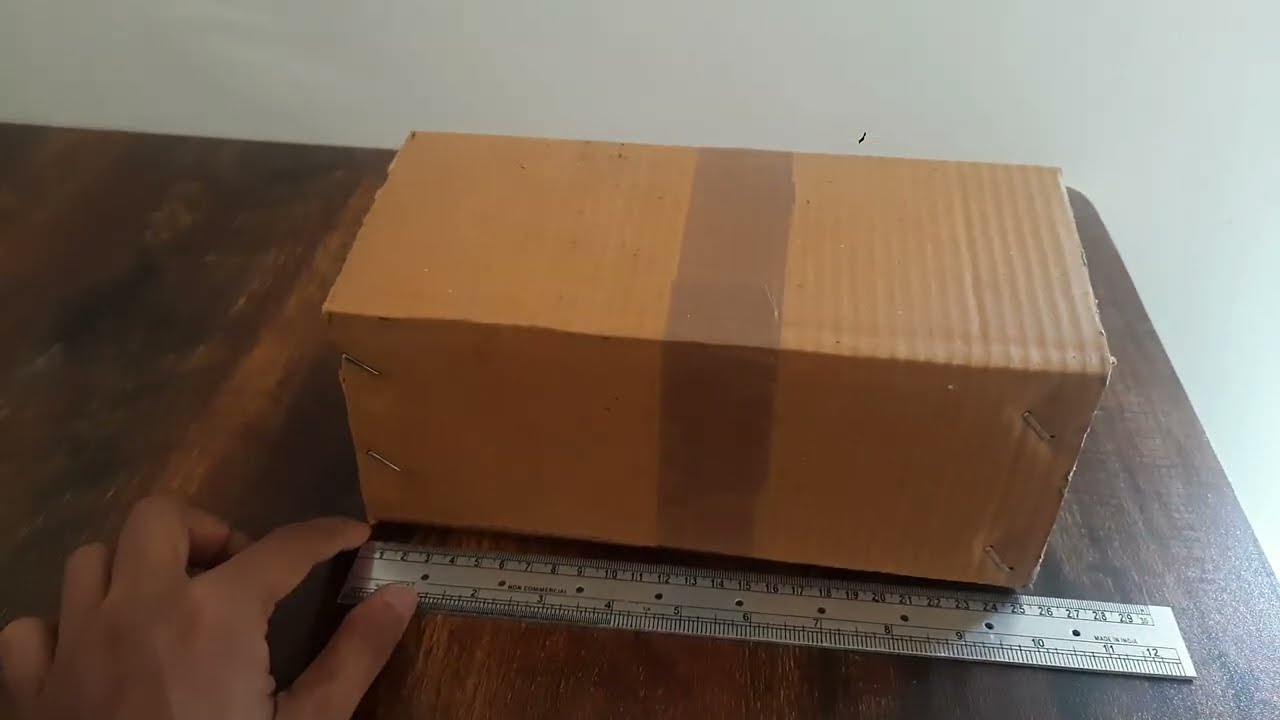
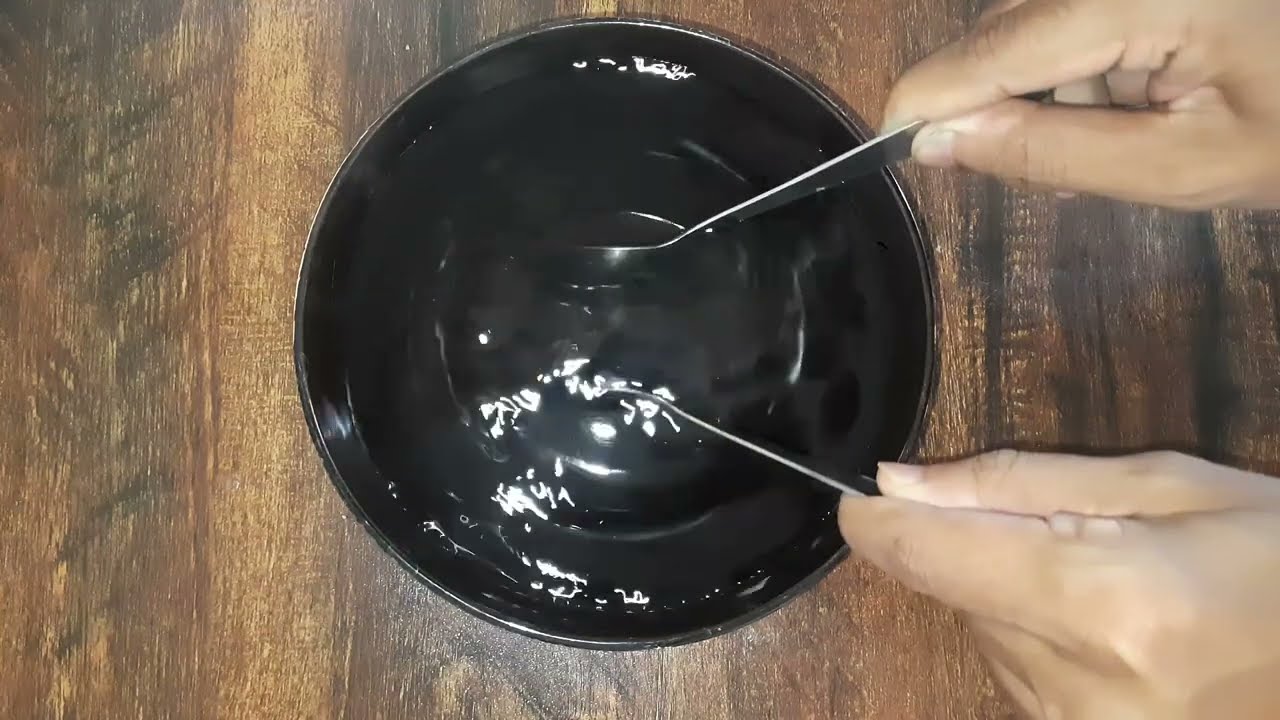
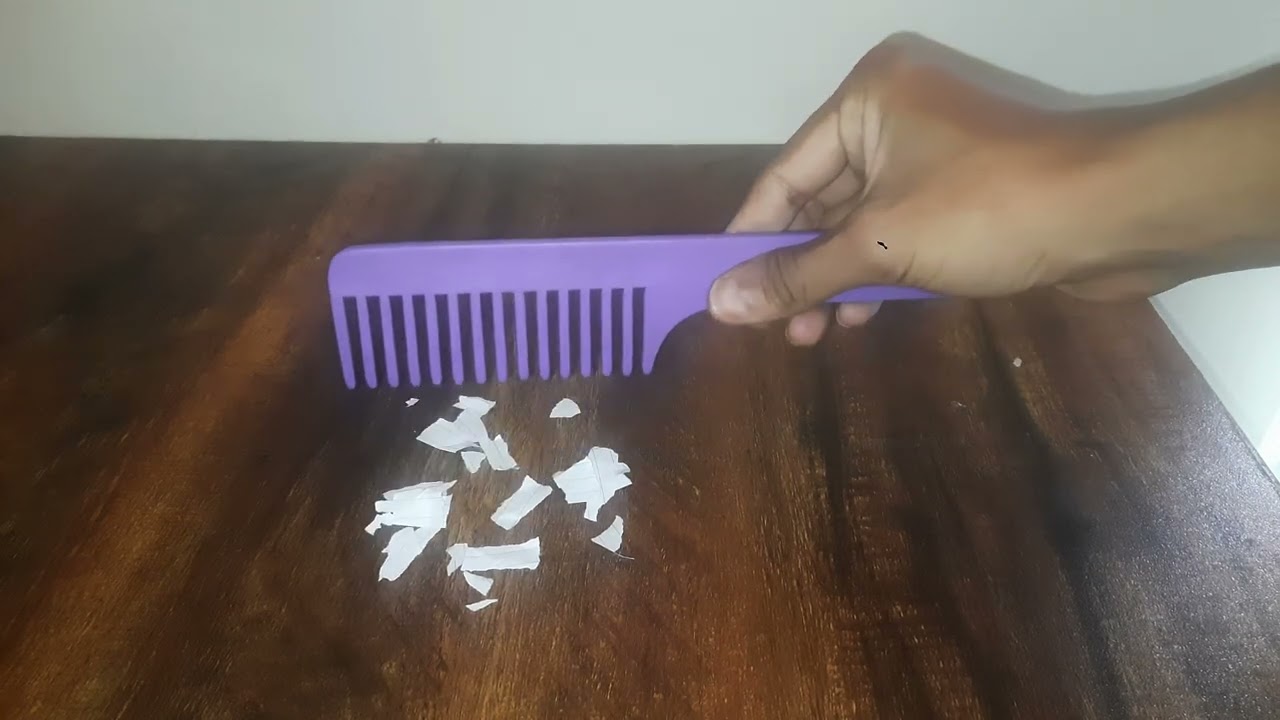
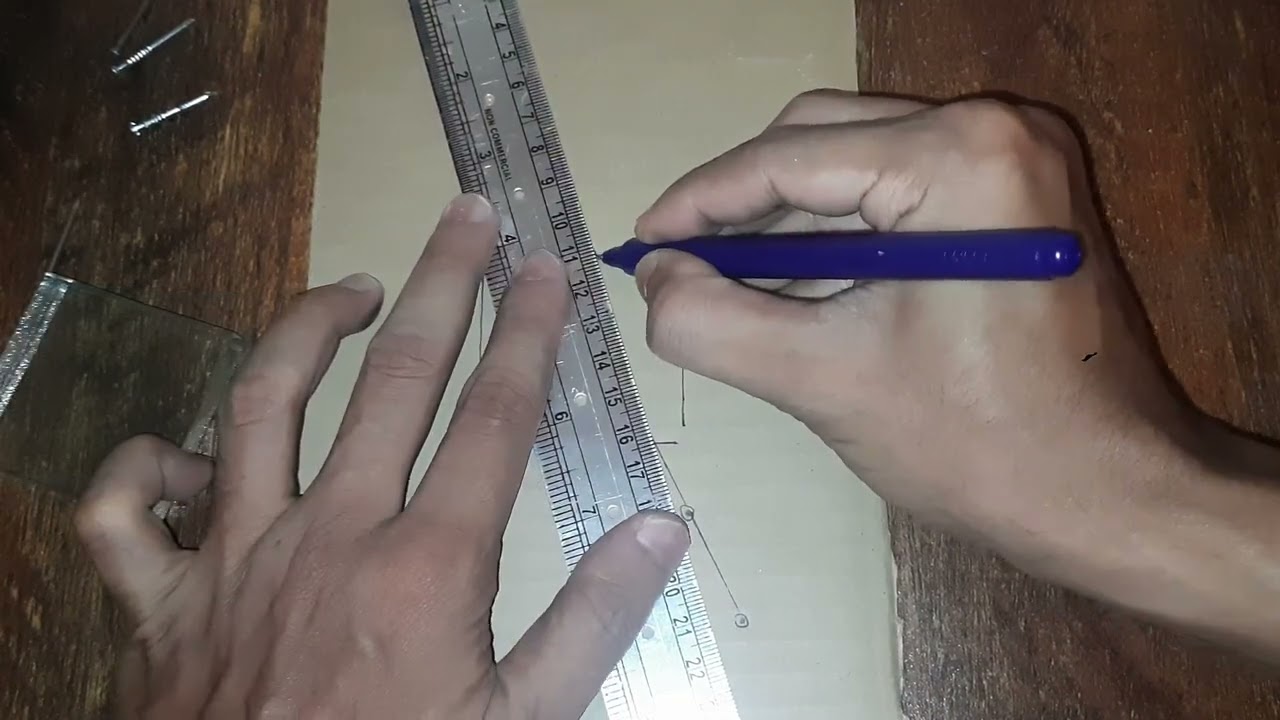
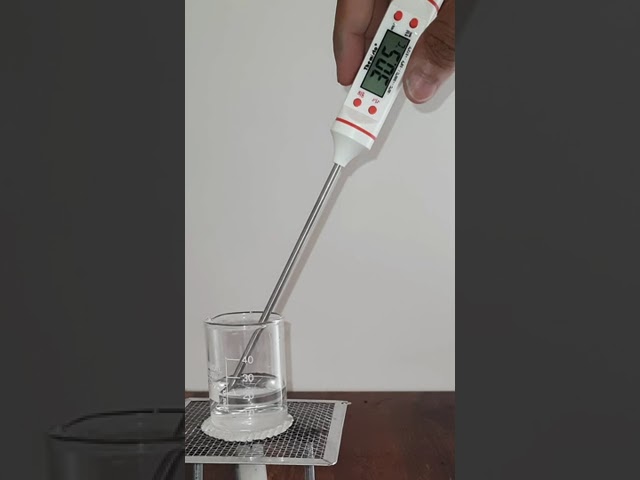






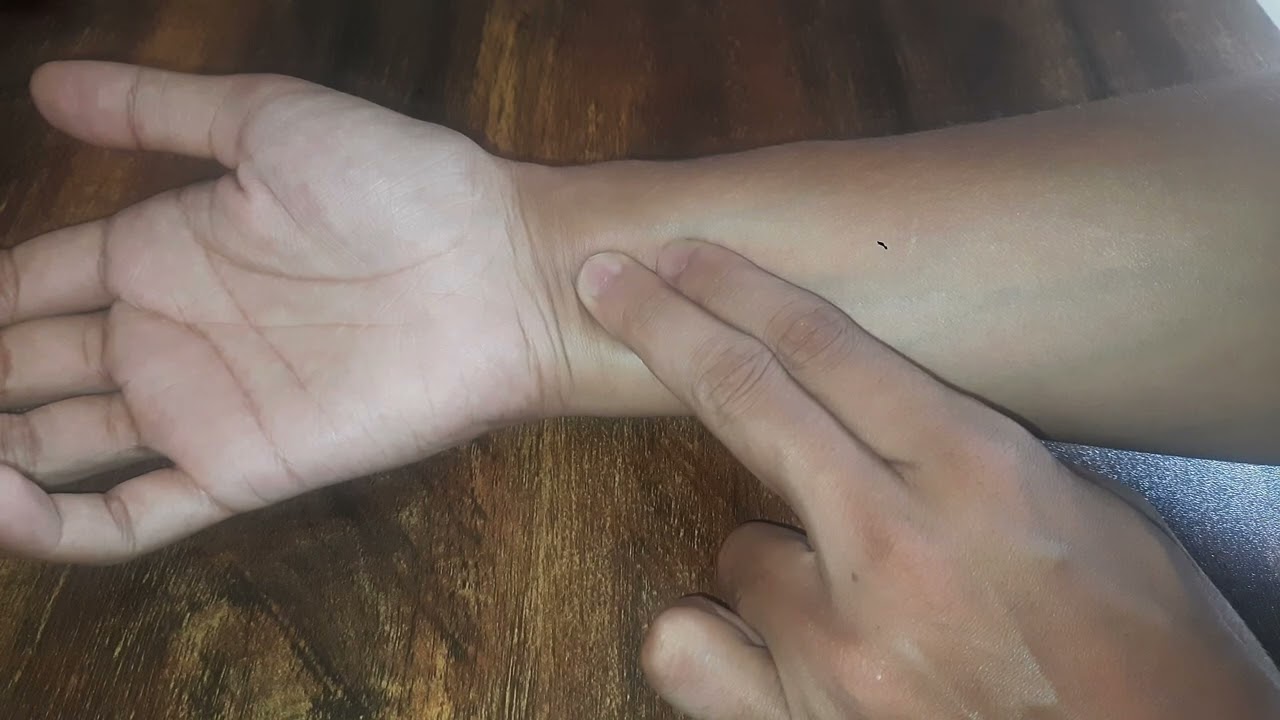























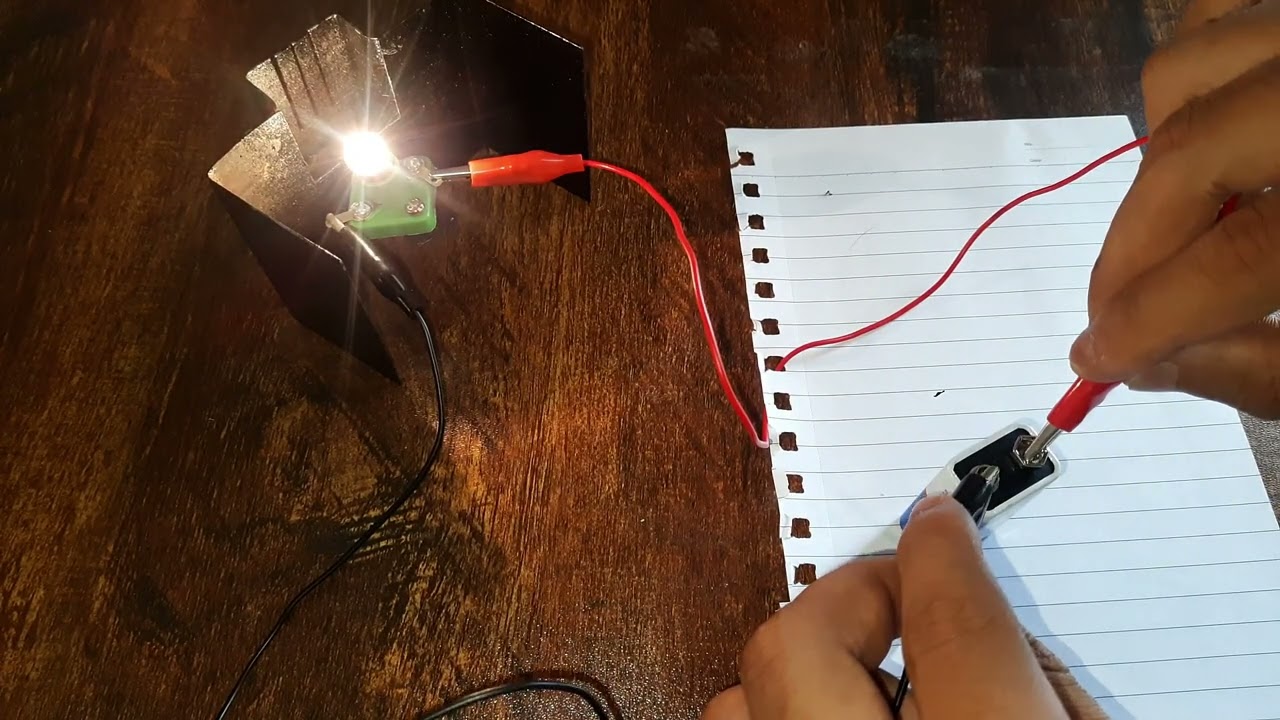







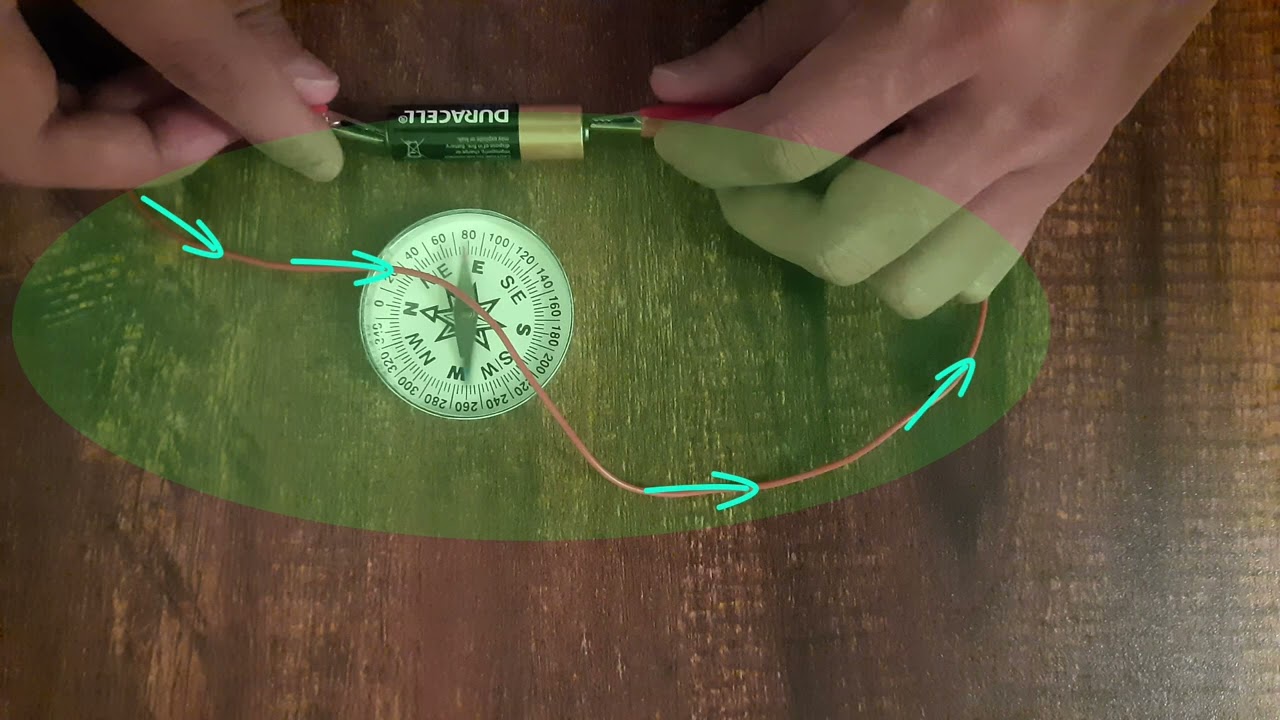
















































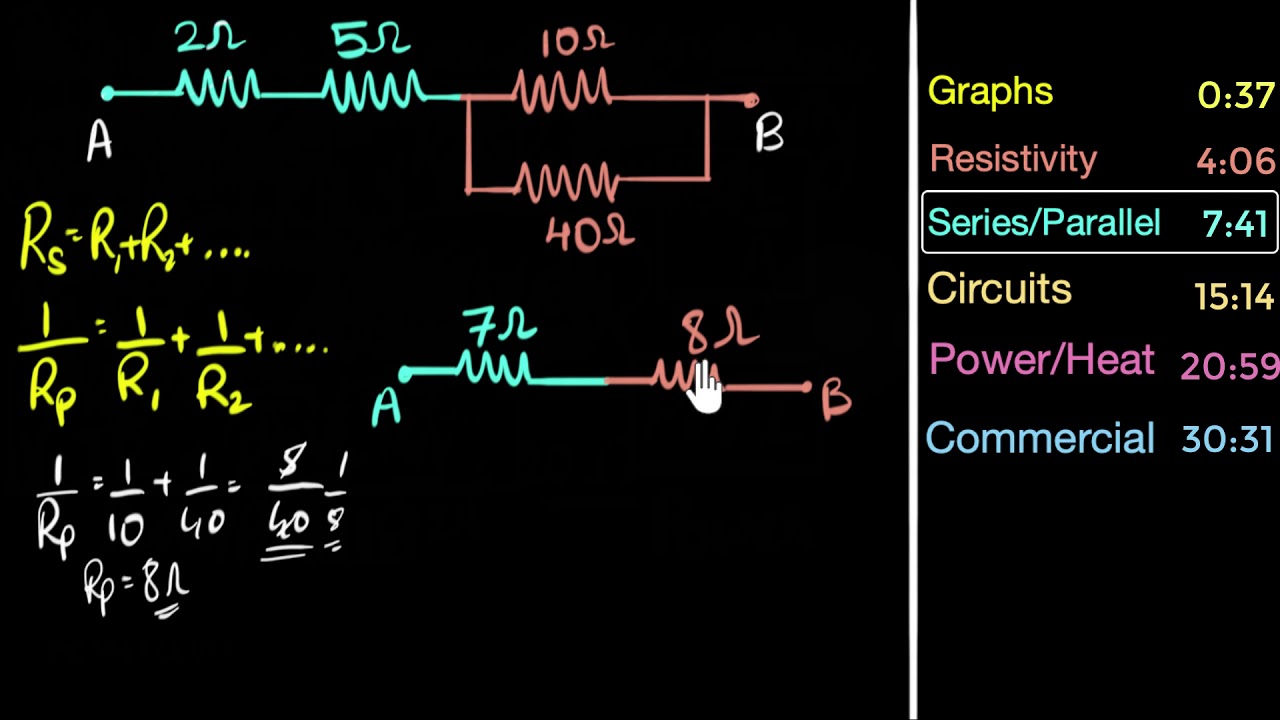



![1.5 Factoring a Cubic Polynomial - [ax^3 + bx^2 +cx +d] (Special Case with Grouping)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/mXdAiJY7YfY/maxresdefault.jpg)




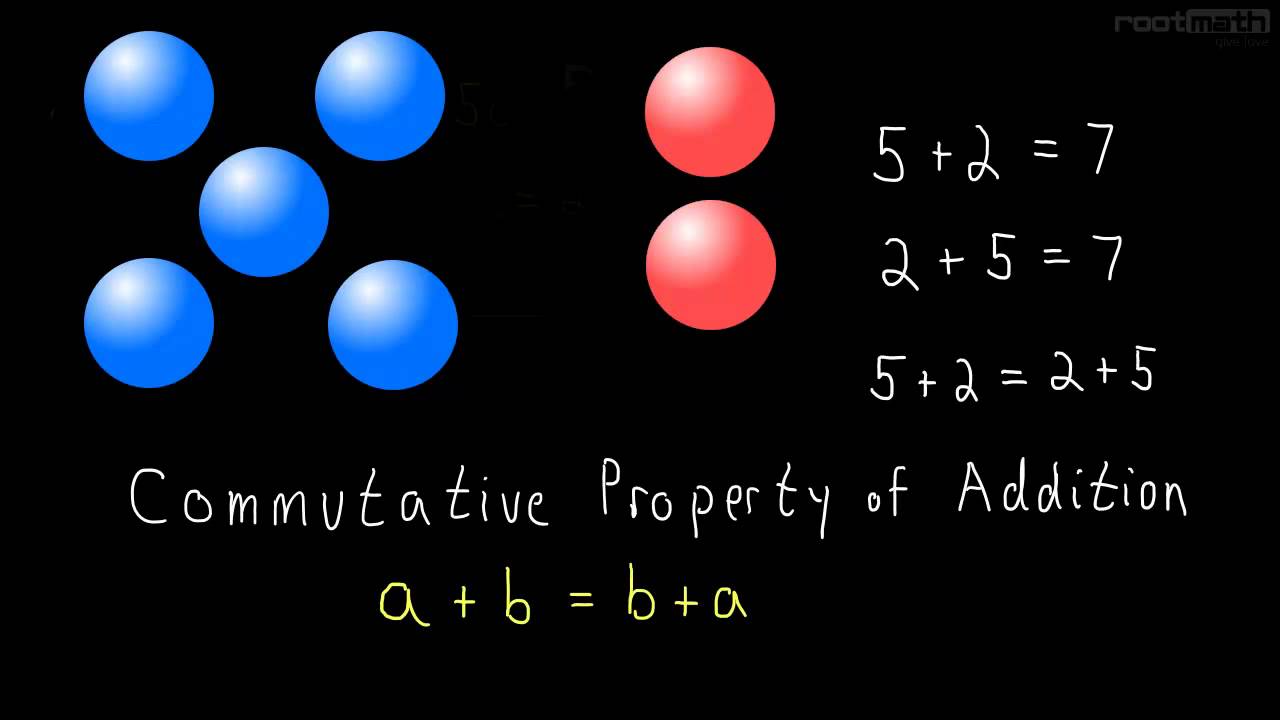



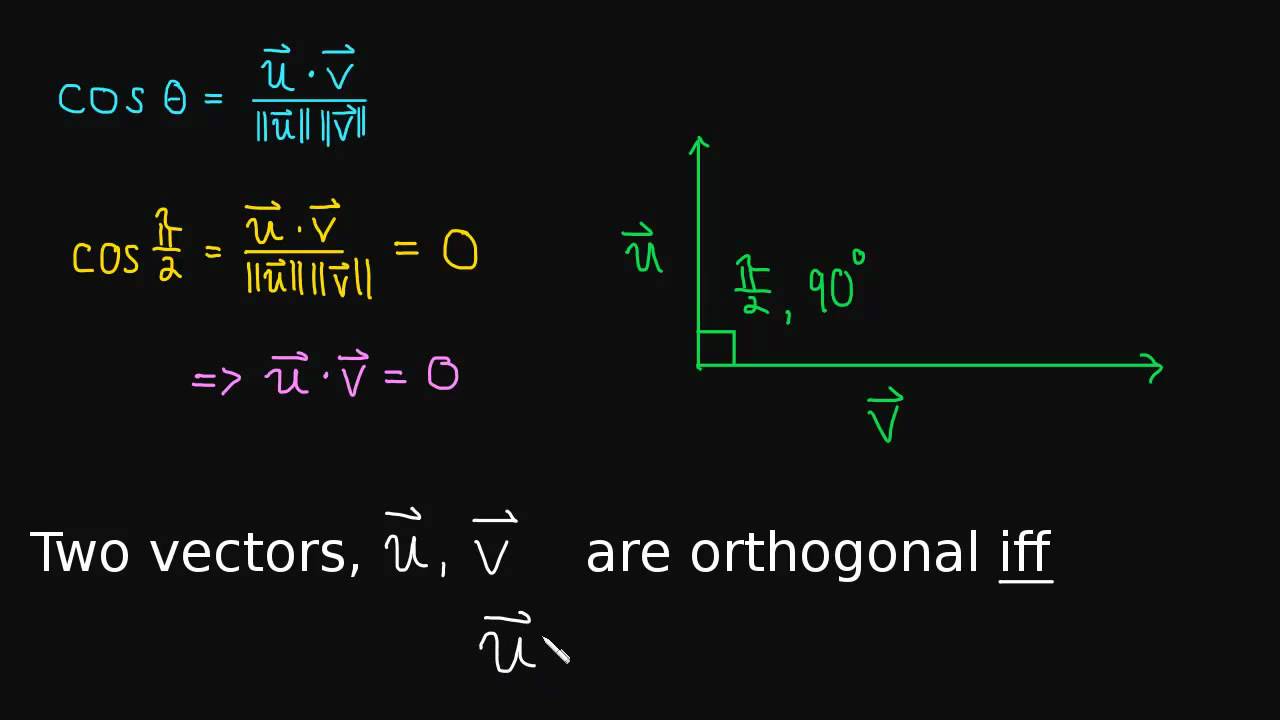








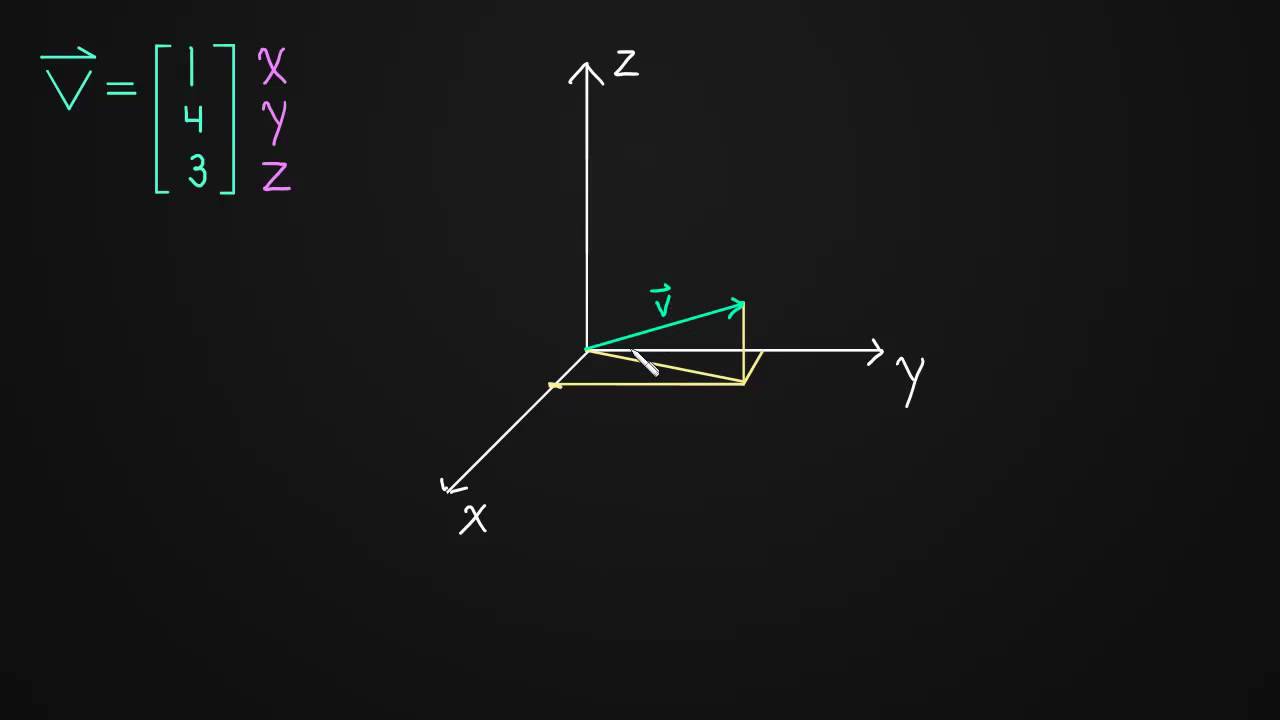


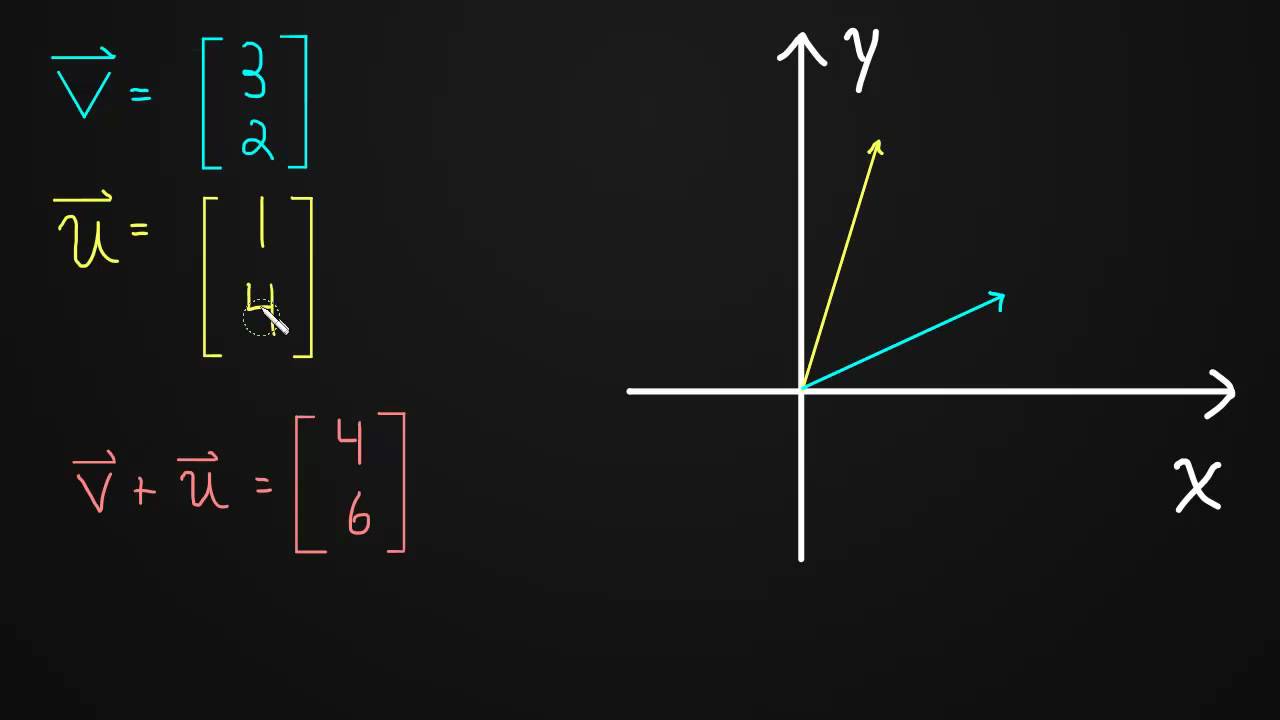

![3.2 Finding Critical Numbers [Example 5]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/h2YwPGCVgPc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![3.2 Finding Critical Numbers [Example 4]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/joCSKCFwpC0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![3.2 Finding Critical Numbers [Example 3]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m_aV6K5wzNg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![3.2 Finding Critical Numbers [Example 2]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bc8pEURcUfs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![3.2 Finding Critical Numbers [Example 1]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/x0Zkx33G_Lk/maxresdefault.jpg)



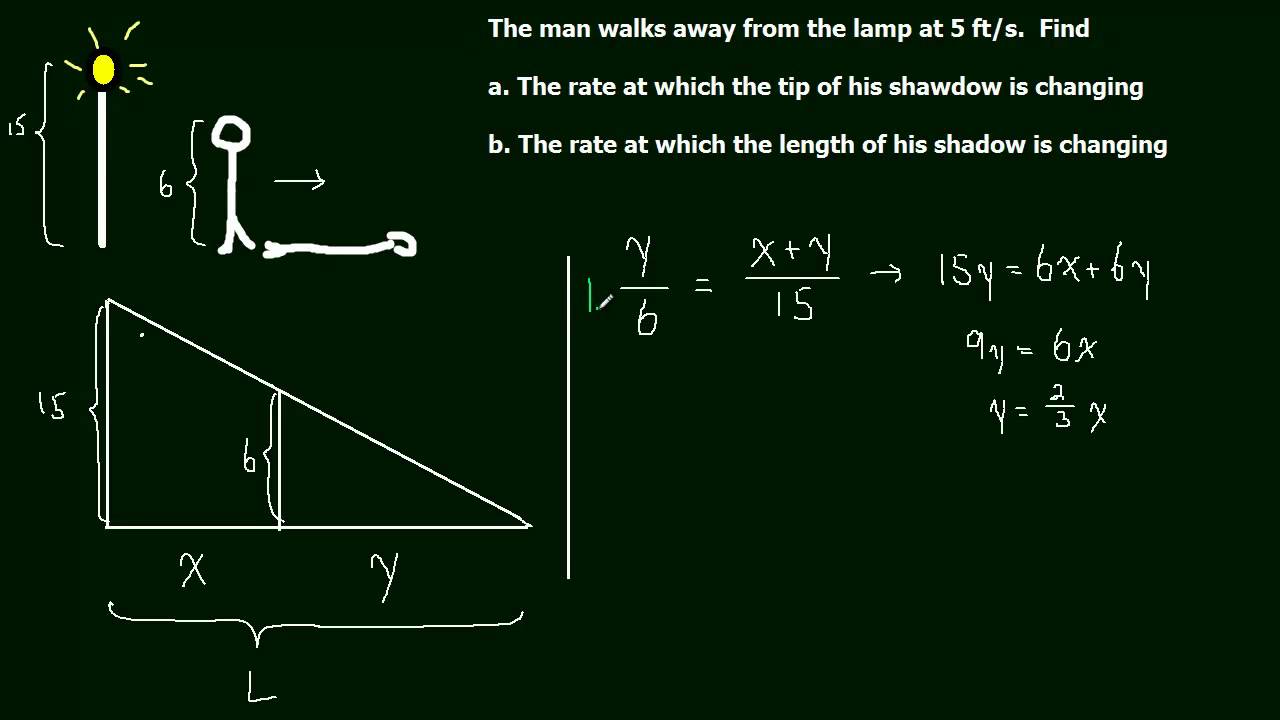


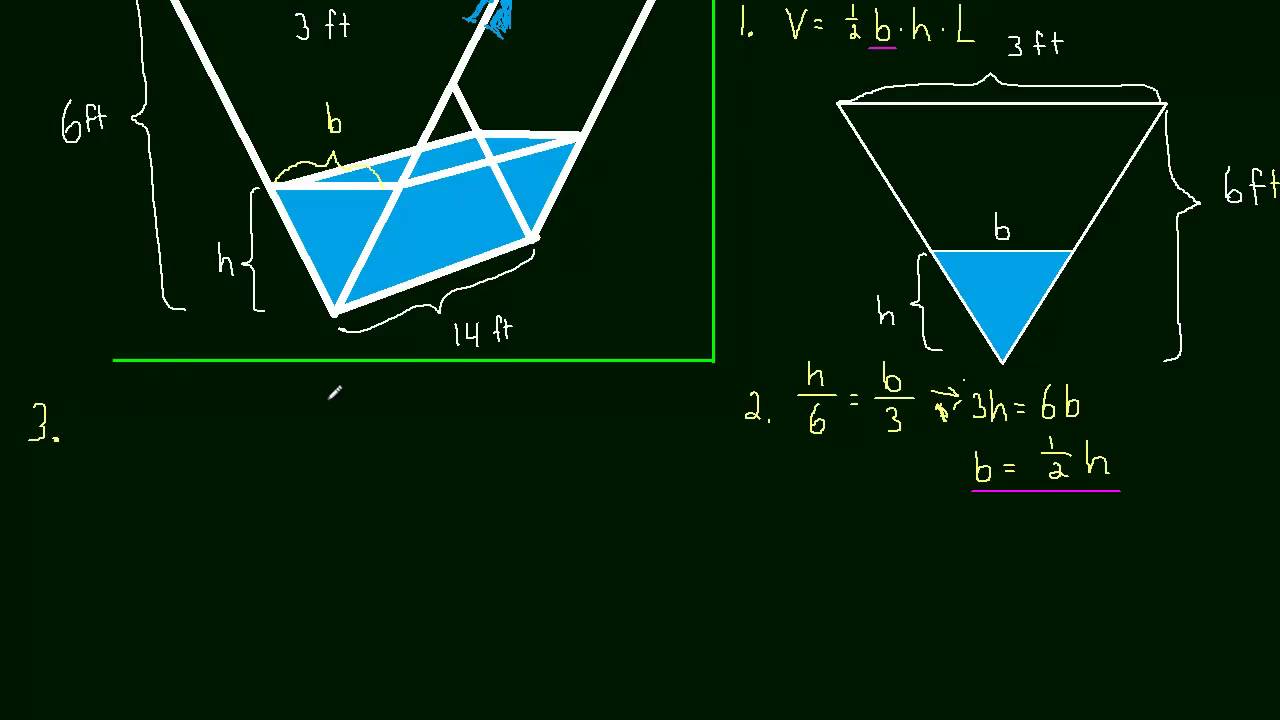













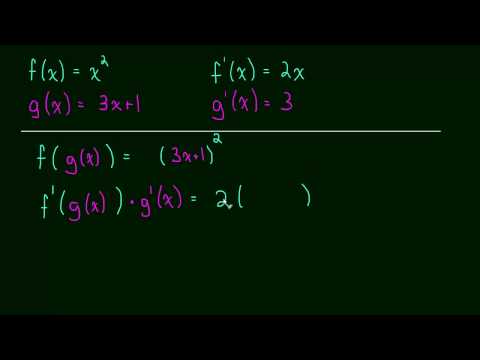

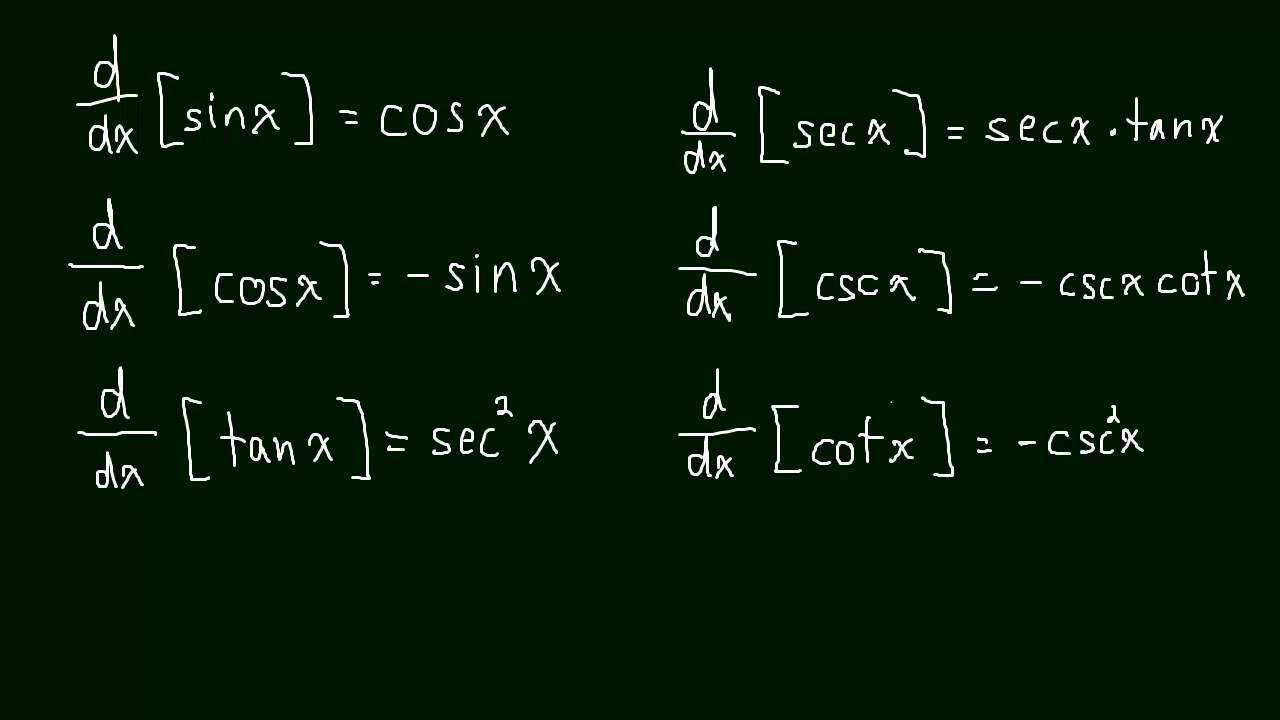

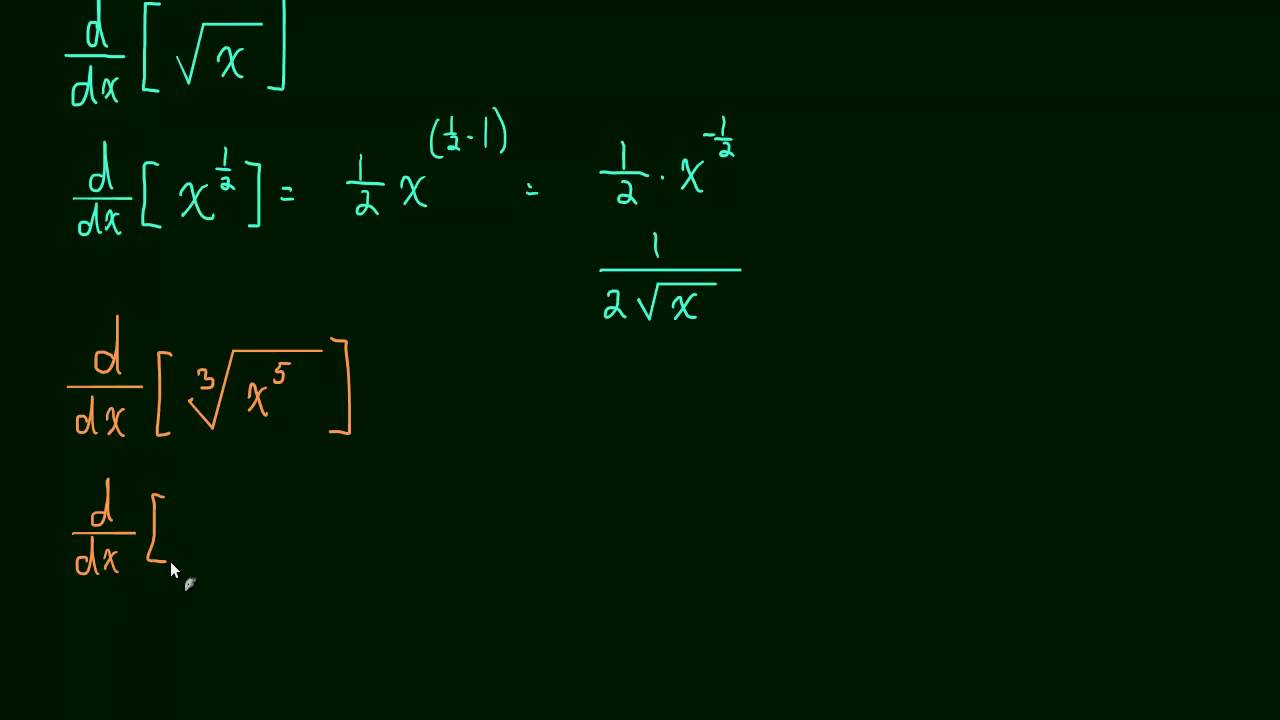





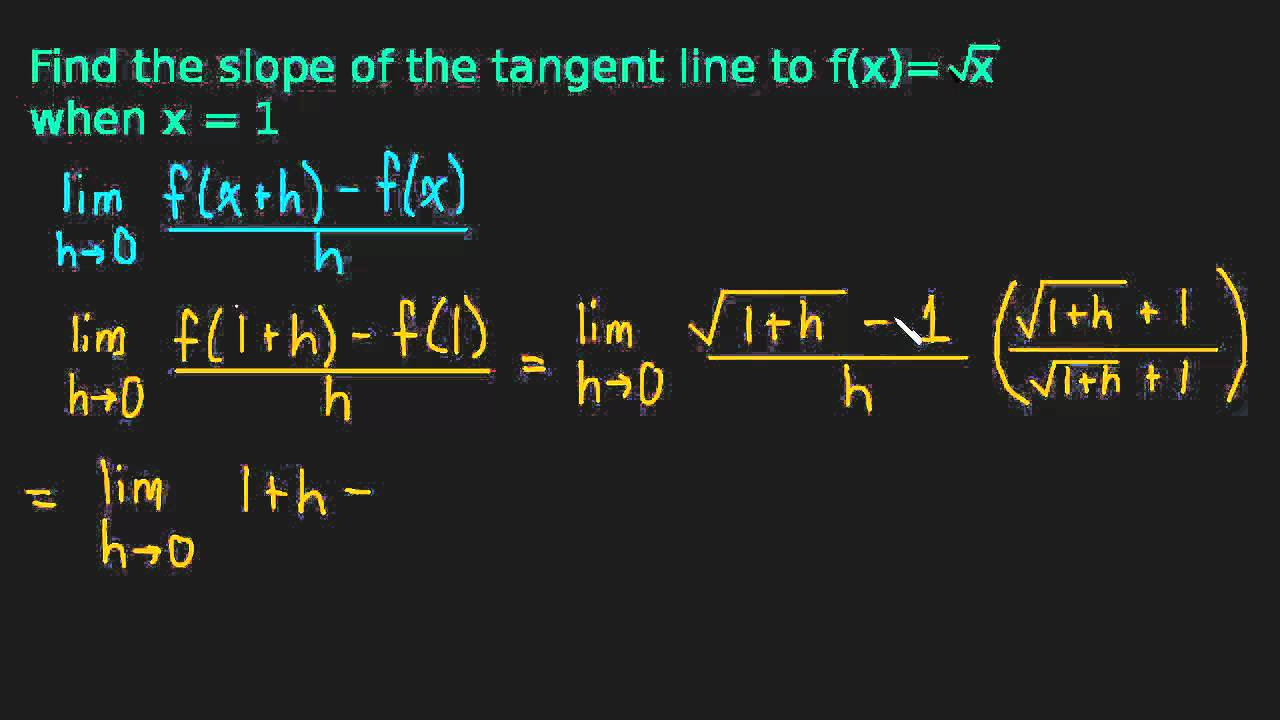


![1.9 Problem Solving [02]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/F3oXMU4JhX0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.9 Problem Solving [01]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Vs6b_E_jg5s/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.9 Geometry of [1 - cos(x)/x]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fiapFlevWDU/maxresdefault.jpg)

![1.6 Trig Limits [03] Proof of sinx/x](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vz9_102nL8M/maxresdefault.jpg)





![1.7 Epsilon Delta Limit Definition [03] (example 1)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/q-tJ8bdJiyg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.7 Limit Definition - Epsilon Delta [02]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eT891yEkzhU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.7 Limit Definition - Epsilon Delta [01] (NEW)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PkHX3p5YqaA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.6 Trig Limits [02] (tanx/x & sin3x/x)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-_FGrN2eN_c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.6 Trig Limits [01] (1-cosx/x)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QVL470BIJeY/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.5 Solving Limits [03] (Fractions)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pfaQkRflAHs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.5 Solving Limits [02] (Rationalization)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/iVLyE_UEfxs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.5 Solving Limits [01] (Factoring)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ubRTCZiFkpY/maxresdefault.jpg)

![1.3 Limits that Fail to Exist [03] - sin(1/x)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PRUBqgJnN-E/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.3 Limit that Fails to Exist [02] - 1/x^2](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DGnR49P-xf0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![1.3 Limits that Fail to Exist [01] - |x|/x](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fU7JNYBxiaY/maxresdefault.jpg)























![HL Doppler effect equations [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SBXywnv74ks/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Doppler effect in astrophysics [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LgMMD8--BrQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Doppler effect introduction [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EEIvwf633Io/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Resonance and damping [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yoAQfbj6P9Q/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Phase difference in standing waves [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TljrSY5_szA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Standing waves [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/AzRiqxM--ag/maxresdefault.jpg)
![HL Multiple slit interference [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TgiUSCHpQDs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![HL Single slit diffraction [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fJ5S6tBgK8c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Young's double slit diffraction [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MFJUVWhhi50/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Interference [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PiA_7USyHa8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Diffraction [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PPRuDFhee4M/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Reflection and refraction [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/U-8HQZuYLD8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Phase angle with travelling waves [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1E0t6yvIhlk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Properties of waves [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Cb9jUOFDBiE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![HL Energy equations for SHM [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Nh-Xc7x0xHU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![HL Example with more advanced SHM [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MzTrimvWvpQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![HL SHM phase angle and more detailed equations [IB Physics HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Hl2WacAdwYg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Simple harmonic motion example [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TRADuuGKwv4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Simple harmonic motion and angular frequency [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QxhnCMfrl2U/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Simple harmonic motion SHM basics [IB Physics SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vzpX-LzZDKg/maxresdefault.jpg)

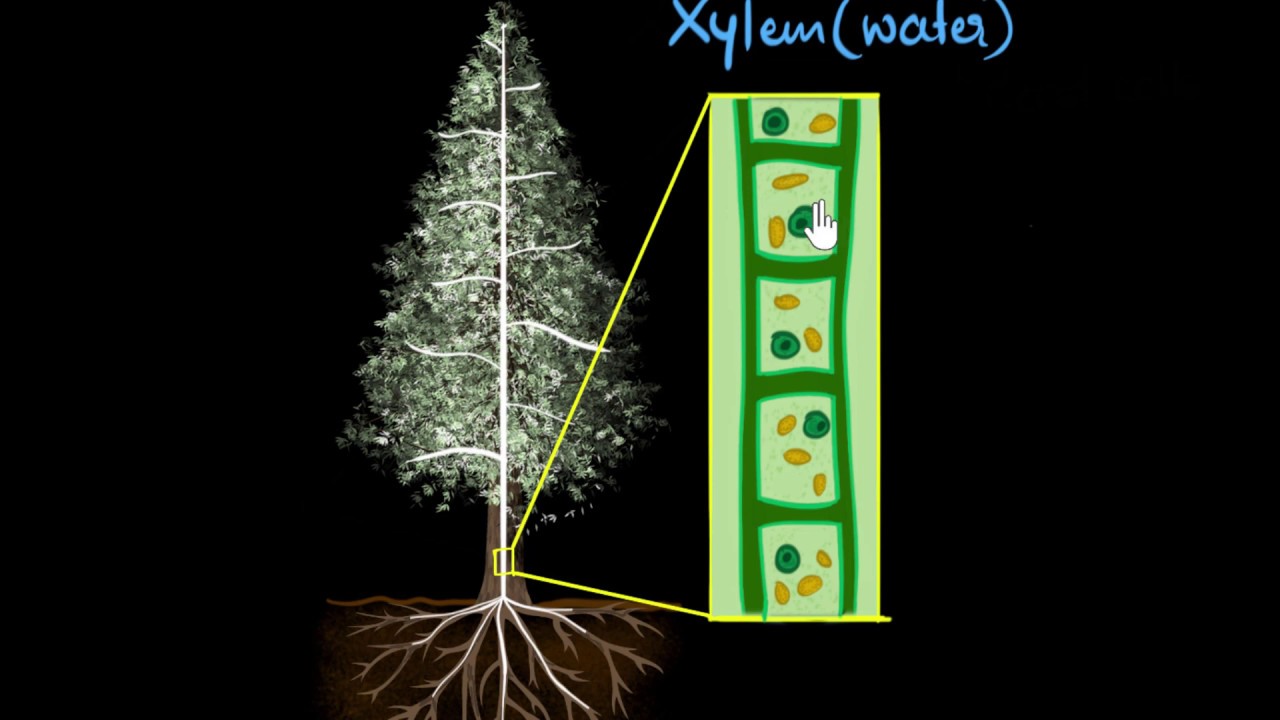



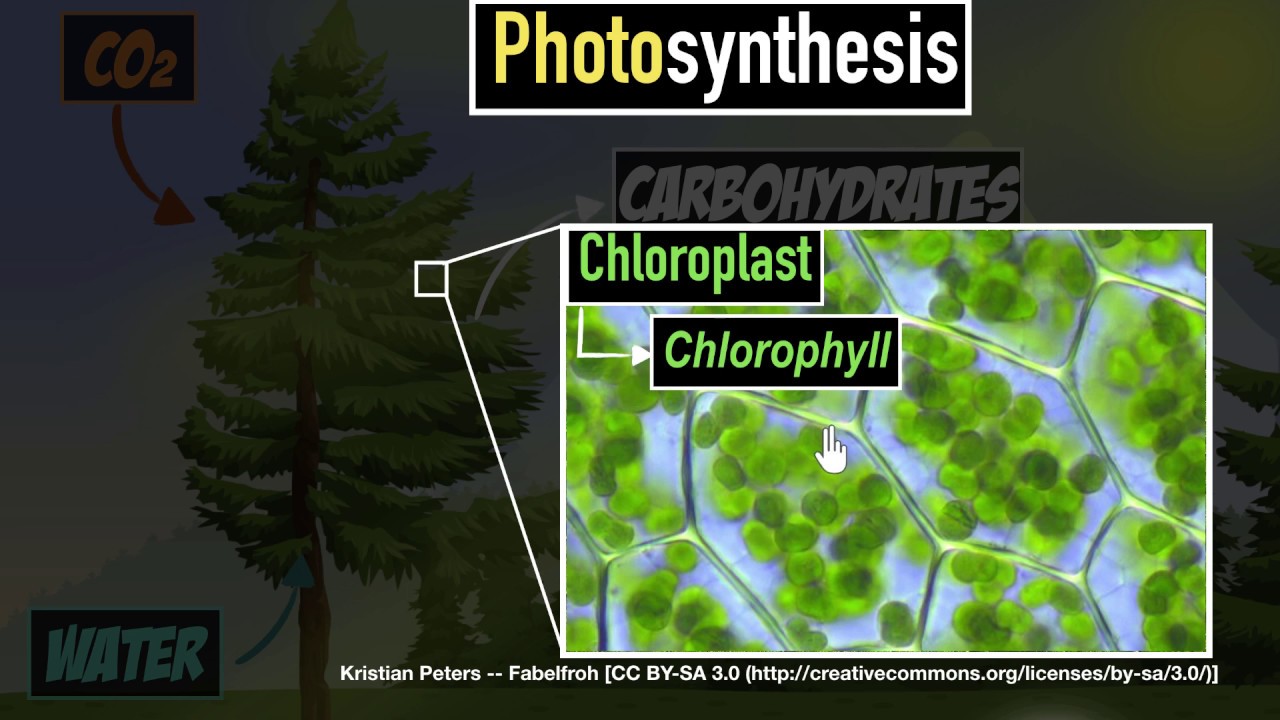






![A4.2 Conservation of Biodiversity [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vKFwYBOsLY8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A4.1 HL Evolution and Speciation [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/u723_BMJN-4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A4.1 Evolution and Speciation [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lxVWFERge-I/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A3.2 HL Classification and Cladistics [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dEE6QzORgpM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A3.1 HL Species Identification [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/n7fncBylKX4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A3.1 Genetic Diversity [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/zzDl_6eKg2c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A3.1 Species Diversity [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7-JCMJ4o__c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.3 HL Viruses [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eQ8CIUbscE8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.2 HL Origin and Evolution of Cells [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fdb0f0pR630/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.2 Organelles and Drawing Cells [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/60Tcywmyr_s/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.2 Cell Structures and Processes [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/E1rGTop1gg0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.2 Microscopy [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yWyYs-vk8DE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A2.1 HL Origin of Cells [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QBfI2OTR8E0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A1.2 HL DNA Structure and Experiments [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZgV57yfPT48/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A1.2 Structure of DNA and RNA [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/knN9csn2wC8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A1.1 HL Properties of Water [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/cZmxVFlOEwc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![A1.1 Properties of Water [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1e8mbEeaIGU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Sinusoidal models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/20IvoNKC_j8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Cubic models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Cw0Rv_bprnI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Direct and inverse variation models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_g7_xWFNUc0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Exponential growth and decay models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_PDGqdVjyig/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Quadratic models example [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vxkYYM75P3k/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Quadratic models intro [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/U8yzBpLEG5g/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Linear models [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_mH4eEjoiEM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Modelling in general [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-6z5IRs37J8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Solving using technology [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5738QD1pXsQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Drawing and sketching graphs [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_WGt6Losl-c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Graph features [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pwURKXdbmV0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Parallel and perpendicular lines [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/AK6jOwp05po/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Linear functions [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wso7p6J_RKA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Inverse functions [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0efE0wbdSNI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Functions, domain, range [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4ahzjn_BAu8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Solving trig equations with your GDC [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lCEnE8keric/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Solving complicated trig equations by hand [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KFYRW0D2ufg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Transformations example [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XSsoFZ37hVE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Trigonometric transformations [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8BwspZZrZ8c/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Trigonometric identities [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/iItOcNW_9lk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Exact values - more difficult 2 [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-XHz4YUjJeg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Exact values - more difficult 1 [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7tNRxvfOg-o/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Tangent, quadrants, special triangles [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KI0gE8m3t5Q/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Sketching graphs of sin, cos, tan [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/69WwCibrU54/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Cosine and sine in unit circle [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Qe2jJeldbDk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Arc length and sector area [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/739B9ejkjVE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Radians and the unit circle [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/d4XlggA3f9g/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Area of a triangle [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/l15jGM9zYP8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Cosine rule [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5xrB2uUb4Lw/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Sine rule - ambiguous case [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gnz_qItiRzg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Sine rule [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CN-BnhQ9wfE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Bearings, angle of depression/elevation + navigating by the stars! [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/zQh0a1DRyJg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Right angle trigonometry - SOH CAH TOA [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PV0RTQ-WCCY/maxresdefault.jpg)
![2D and 3D geometry [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Bx2kjEPyxn0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Distance and midpoint in 3D [IB Maths AA SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/uOxnrUkPl_0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Chi-squared GOF (Goodness of Fit) test [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/9iWGC7I8JD0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Chi-squared independence test [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-gOGlMBbYJ4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Chi-squared independence test intro [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/J24RLXkUHqA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Spearman’s rank coefficient [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/VTztAJIllg4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Inverse normal [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ouuypWc7okU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Normal distribution - more advanced [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DlAWBoLNs14/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Normal distribution -intro [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/IBKjwZ9umg0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Binomial distributions [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4SVMx3uNyd4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Expected value [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EhOjmLWvufc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Tree diagrams [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MJKuiSB7AQE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Venn diagrams [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/WHHa2k_6VdU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Conditional probability [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dphS5uN6vvk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Combined events [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XWEE6jJgCaA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Probability basics [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/x3bIRp7axUw/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Linear regression of y on x [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nBhmX6jCOg0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Box and whisker plots [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Q_pK-vMDgeo/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Cumulative frequency [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/k6xoTWp0DZA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Standard deviation and variance [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QbNf1-R_XVc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Sampling and outliers [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xFeE-r2XvSk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Using your calculator for basic stats [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/j2qbreXqbXQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Introduction to statistics [IB Maths AI SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bh3OOaWO0tc/maxresdefault.jpg)
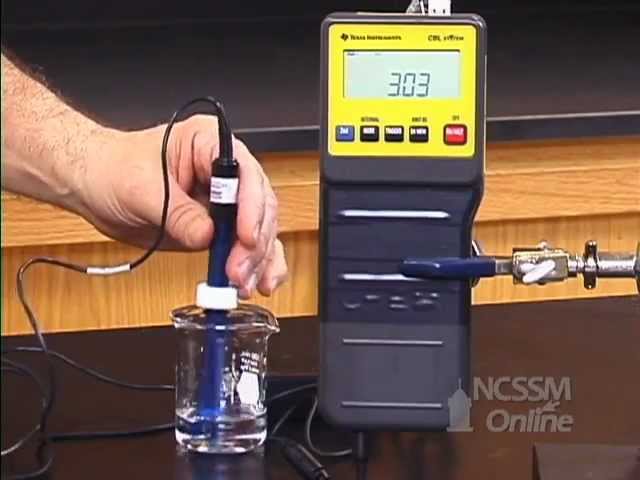
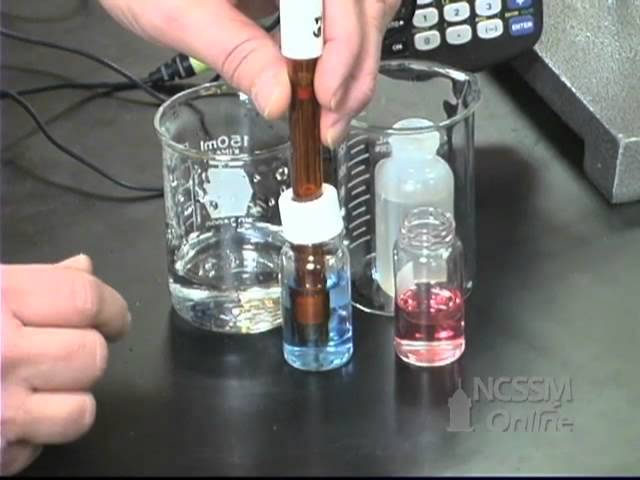
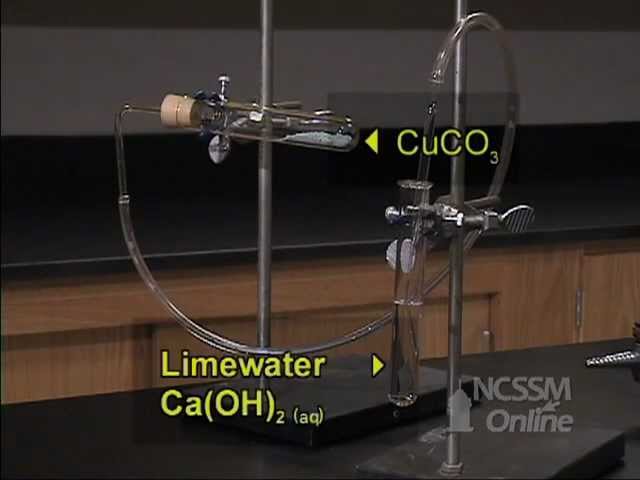
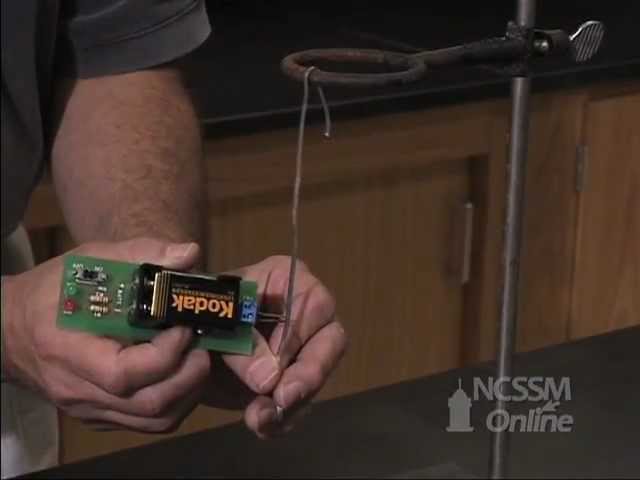

























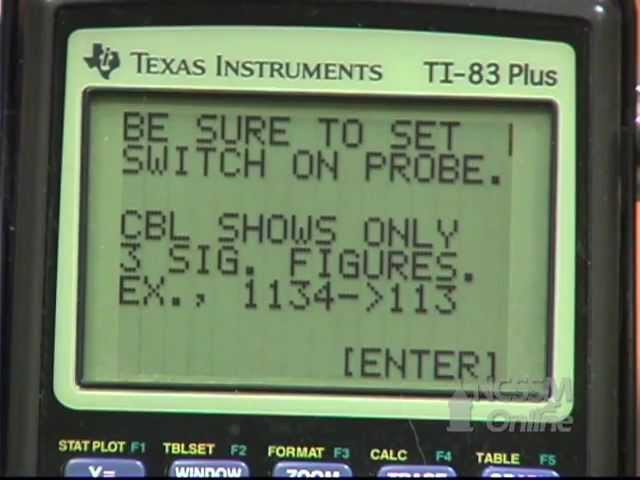









































































![D4.3 HL Climate Change [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qFI13v1iJS0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.3 Climate Change [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EbVA2OfGsro/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.2 HL Ecological Succession [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/RklGemIdDPQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.2 Sustainability [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qDDfRW8CaVU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.2 Stability [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EAbp26IMxgE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.1 HL Natural Selection [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/o_PcXW7QQsg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D4.1 Natural Selection [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Rg8TwlaJZFI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.3 Homeostasis [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nKmXluCB6Js/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.2 HL Gene Linkage and Chi Squared [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tKkraA6rcZI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.2 HL Dihybrid Crosses [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bc-Lt7LaQdA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.2 Analysis of Inheritance Patterns [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/63zX_oDU_P8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.2 Applications in Inheritance [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TJgbnxKXvEk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.2 Principles of Inheritance [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/YRCCuPvOA0s/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.1 HL Fertilisation and Pregnancy [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ju5y7PcO4eQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.1 HL Gamete Production [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jFs7eFLHOMw/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.1 Plant Reproduction [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/s7fbzKjr7aM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.1 Human and Animal Reproduction [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nnPd6FVpPvE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.3 HL Water Potential [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dyJ-mkQJvFc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.3 Water Movement [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gmhw4Bkaif4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.2 HL Genetic Expression [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0mHb3Y5Z4A4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.1 HL Control of Cell Division [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SGzvl-r5aT8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.1 Meiosis [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dpEaR6AUcdQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D2.1 Cell Division and Mitosis [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/i9XPl4ePyxU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.3. HL Genetic Modification [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-z8k5fapbh4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.3 Mutations [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HdM5tXf7M-E/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.2 HL Protein Synthesis [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dFYBBFEKg6E/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.2 Protein Synthesis [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ybso-VivjF8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.1 HL DNA Replication [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OzXIsbkybbk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D1.1 DNA Replication [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CSisaIHxAPk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![D3.3 HL Role of the Kidney [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Ikmndyc_nMM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C4.2 Carbon Cycling [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Oo5JnJP-XEw/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C4.2 Energy Flow Through Trophic Levels [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/THl10RlEPFU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C4.2 Energy Flow Through Ecosystems [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/8vRkGP1JXuc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C4.1 Communities [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4eMUCjxJOuI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C4.1 Populations [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0TGYkZLfi9w/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.2 HL Defence Against Disease [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pewElcG1YTs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.2 Defence Against Disease [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QMgzQZPqlKs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.1 HL Plant System Integration [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/La_3mb7pX7U/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.1 Feedback Control [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/3NlkZ-PIGwo/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.1 Hormone Integration [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/IEFMgsSBXR4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C3.1 Nervous System Integration [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Y0ub4jfl7lE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C2.2 HL Neural Signalling [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7Eol3hSLZ9A/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C2.2 Transmission Between Neurons [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/UJVGAqG2pBc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C2.2 Transmission Along Neurons [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SkxA2sGI6GM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C2.1 HL Signalling Mechanisms [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gU9pamT_Y48/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C2.1 HL Signalling Molecules and Receptors [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7CjPaKhyPPs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.3 HL Light Independent Reactions [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/RYasV6aHv_8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.3 HL Light Dependent Reactions [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HqYebhEQu4o/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.3 Photosynthesis [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/I6hn6eiF5bI/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.2 HL Cell Respiration [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/r3b5QpTUsKM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.2 Cell Respiration [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/P8qMsVmrg-k/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.1 HL Enzymes and Metabolism [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/YOS2OGX9L8w/maxresdefault.jpg)
![C1.1 Enzymes and Metabolism [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fSuwI9bjgJs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B4.2 Adaptations to Niches [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wwdATrl-OqE/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B4.2 Nutritional Niches [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HJEx-HrnD1Q/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B4.1 Adaptations to the Environment [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/dcr6HKLvRiM/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.3 HL Joints and Locomotion [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Vtf1s9vUEww/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.3 HL Muscle Structure [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wT6WhBTy7Hg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.2 HL Transport in Plants [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/iWLxi9Xh35E/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.2 HL Transport in Animals [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tkv0Z_SUdv4/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.2 Transport in Plants [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/AwgOrrrvGds/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.2 Transport in Animals [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wgBvMkybdyo/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.1 HL Transport of Respiratory Gasses [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/F66K2WUlGdA/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.1 Gas Exchange in Plants [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/M3Q2JHoX_hc/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B3.1 Gas Exchange in Animals [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1OqMFq43spw/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.3 HL Cell Specialisation [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-ydRCYwF3D8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.3 Cell Specialisation [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/86EDjDREYbk/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.2 HL Organelles and Compartmentalisation [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/x_UBoZ8xCN8/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalisation [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xnEplUF0xO0/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.1 HL Membranes and Transport [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/W0HVn85Zc3Q/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B2.1 Membranes and Transport [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ooDOkq8w3NU/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B1.2 HL Proteins [IB Biology HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OfFO8t54_Fg/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B1.2 Proteins [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7-i-VDkZuQs/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B1.1 Lipids [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-fzIaXjSrNo/maxresdefault.jpg)
![B1.1 Carbohydrates [IB Biology SL/HL]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eV--VWunHUU/maxresdefault.jpg)




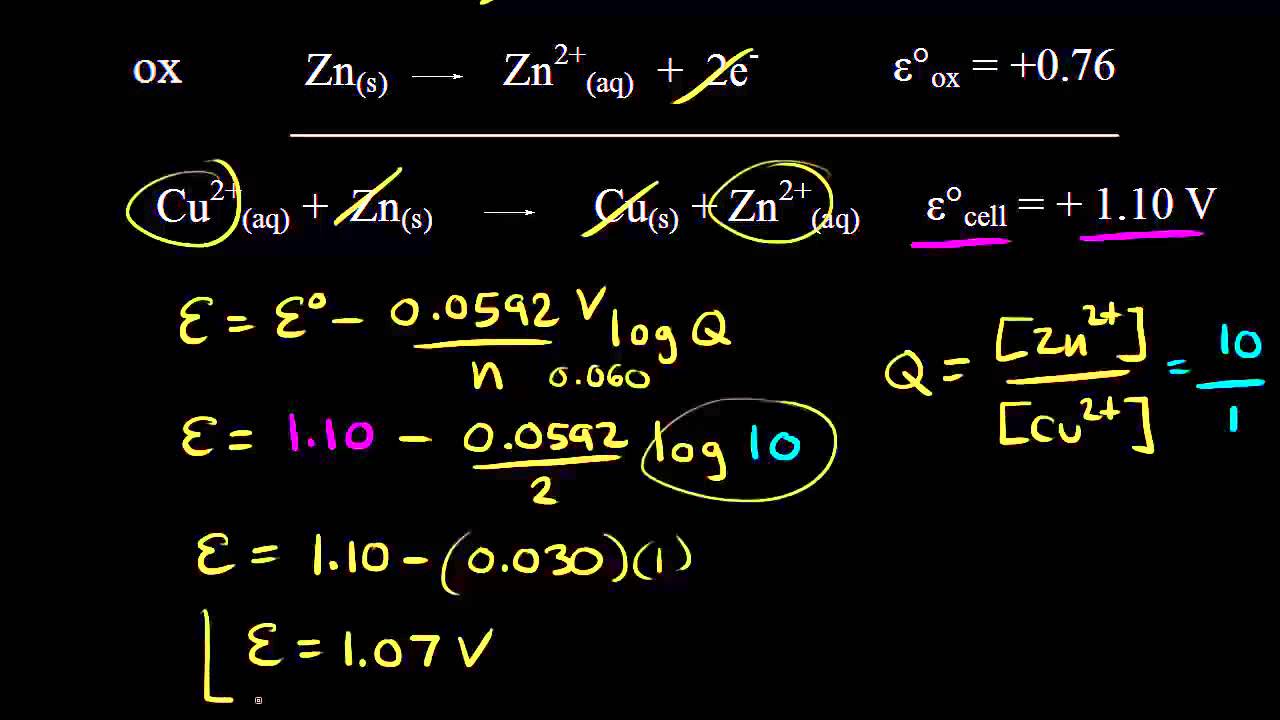
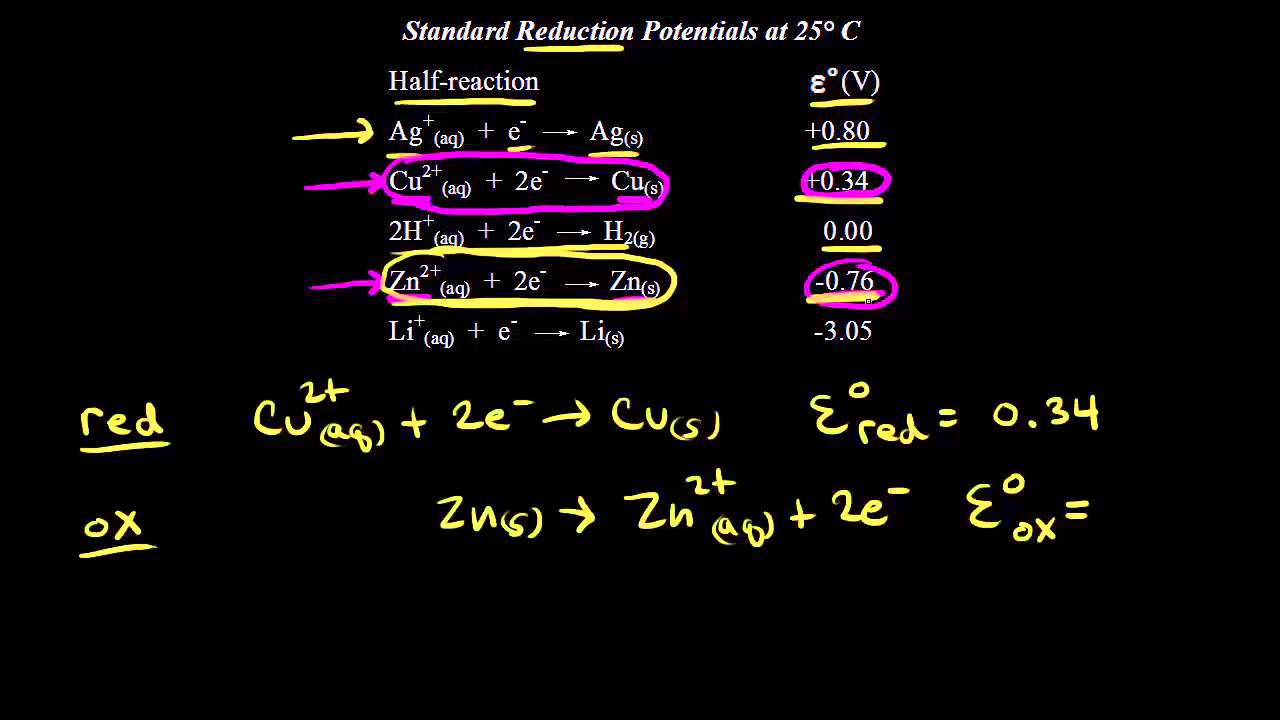














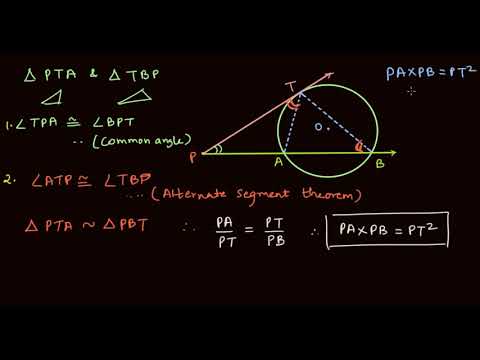







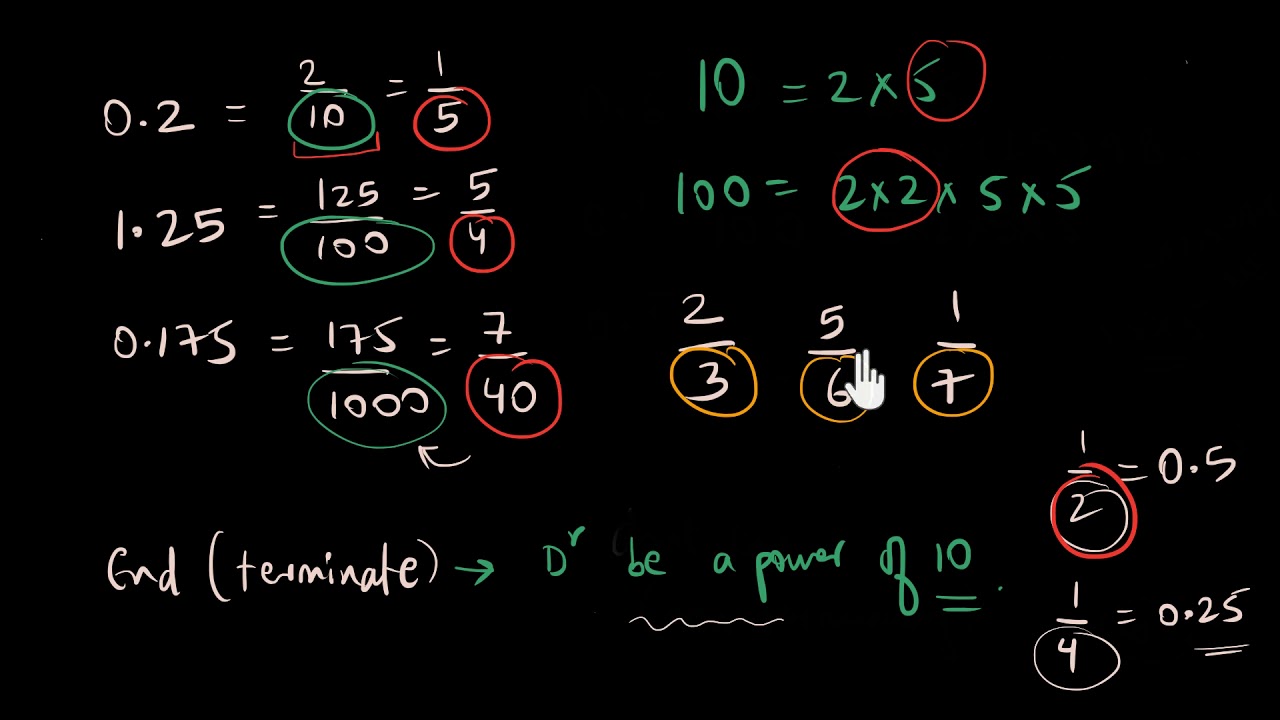
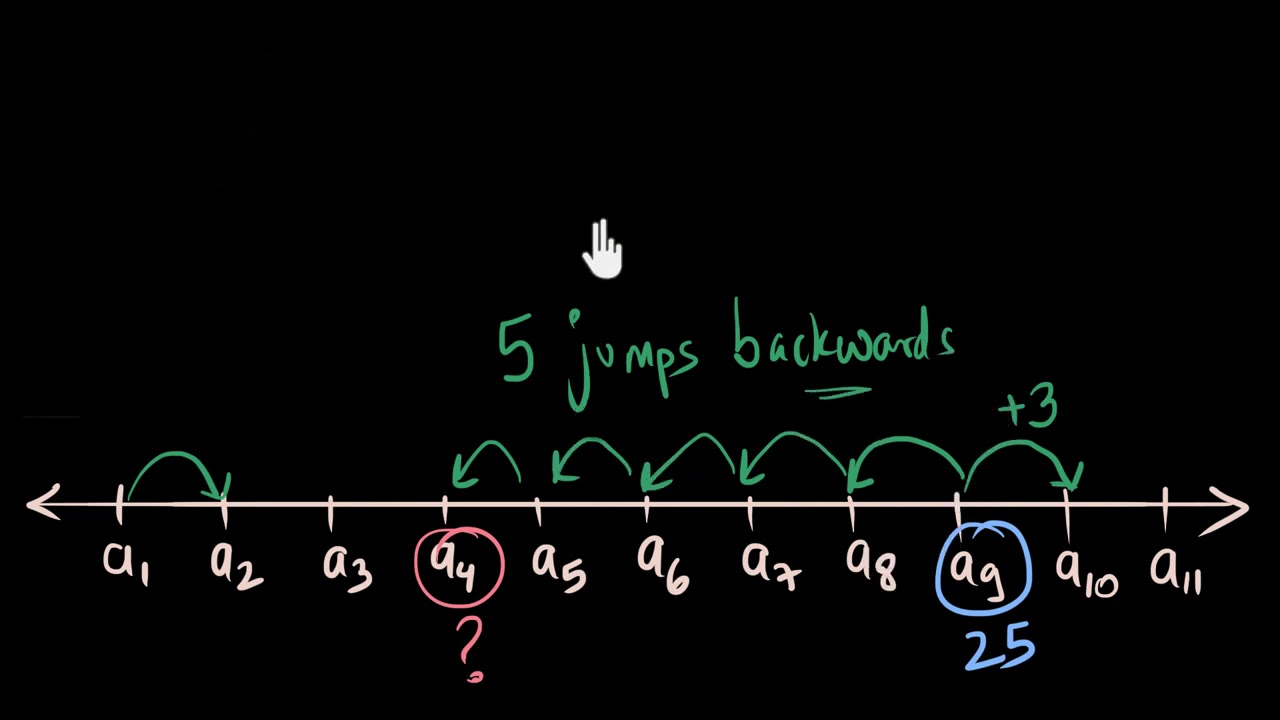

![The Periodic Table of the Elements in Chemistry - [1-2-12]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CTwua04Ykso/maxresdefault.jpg)










































































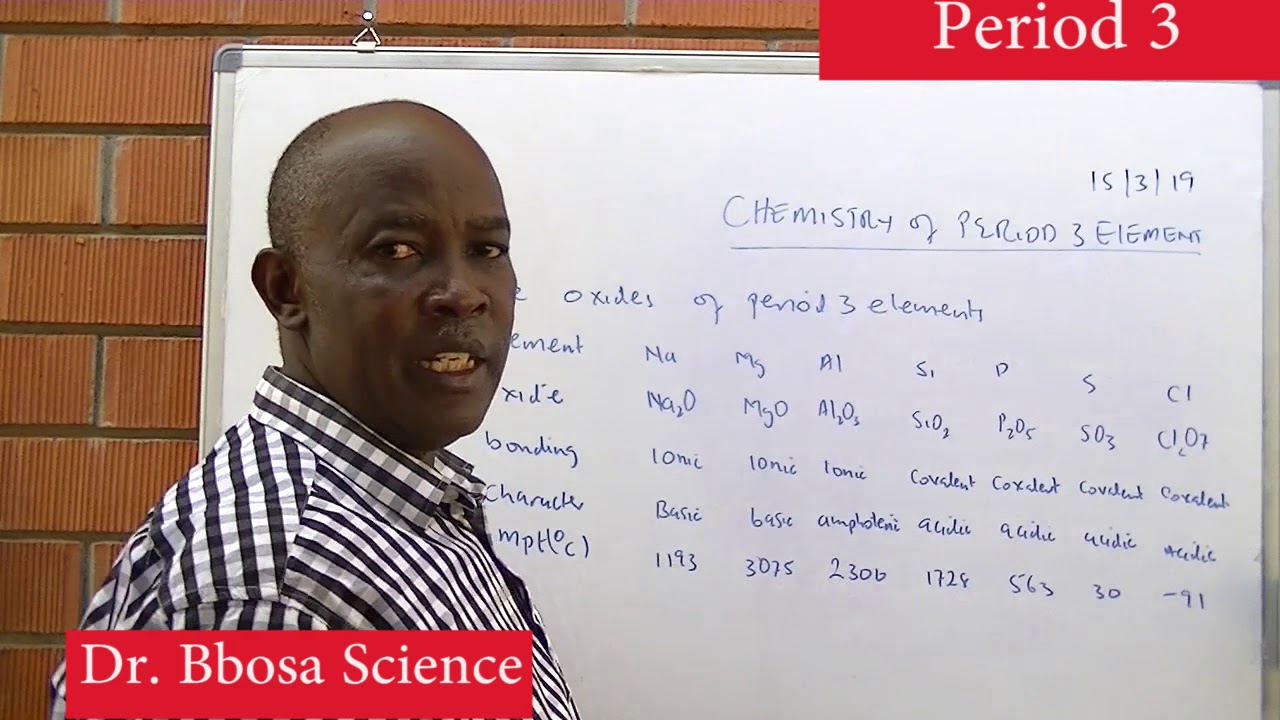






















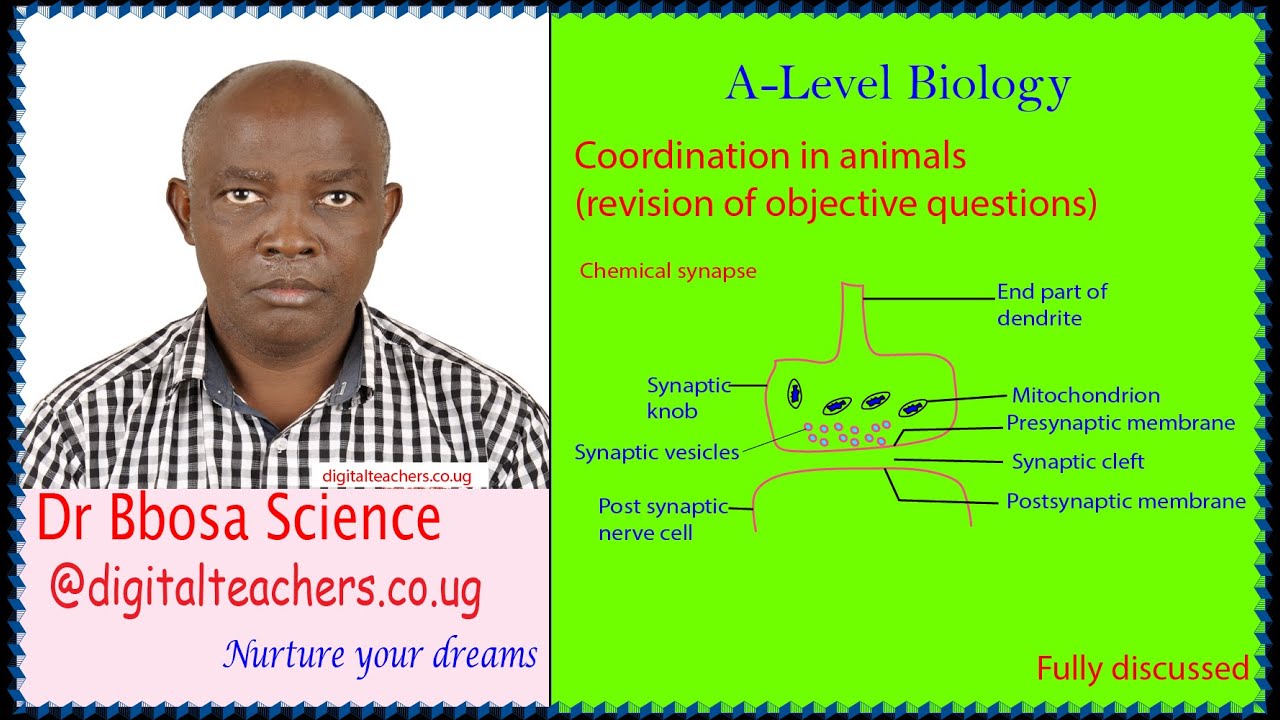


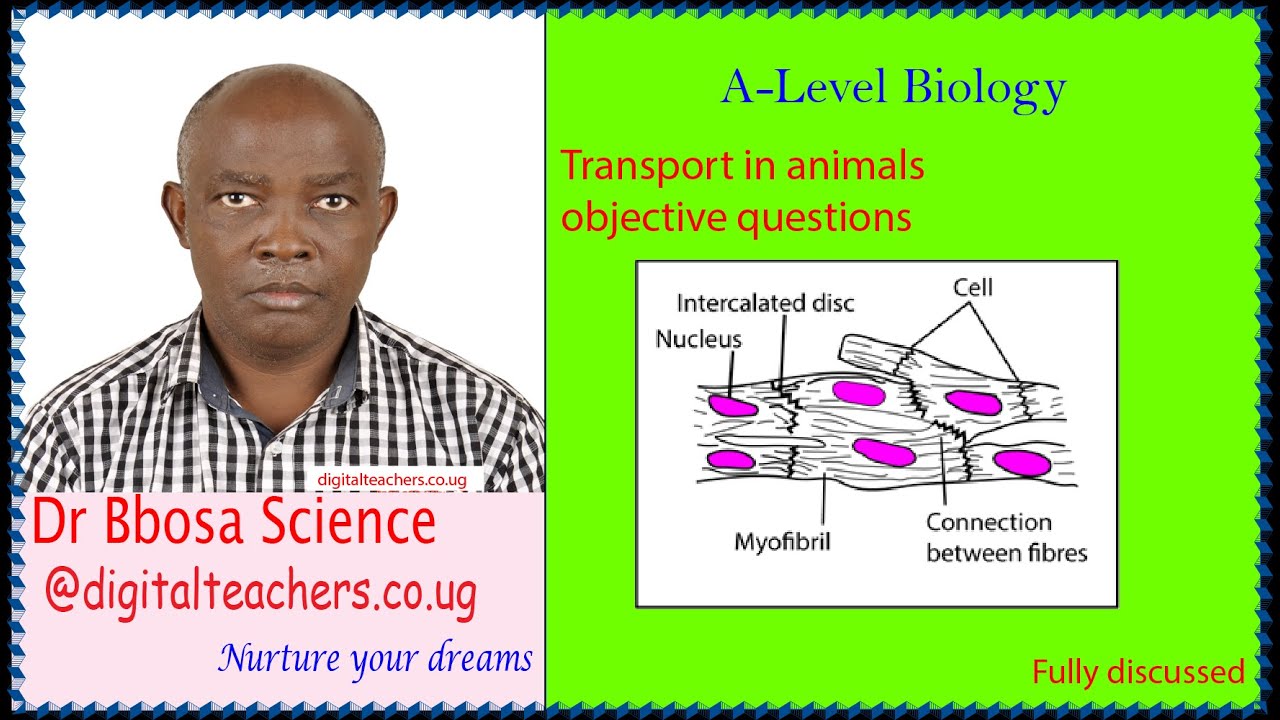







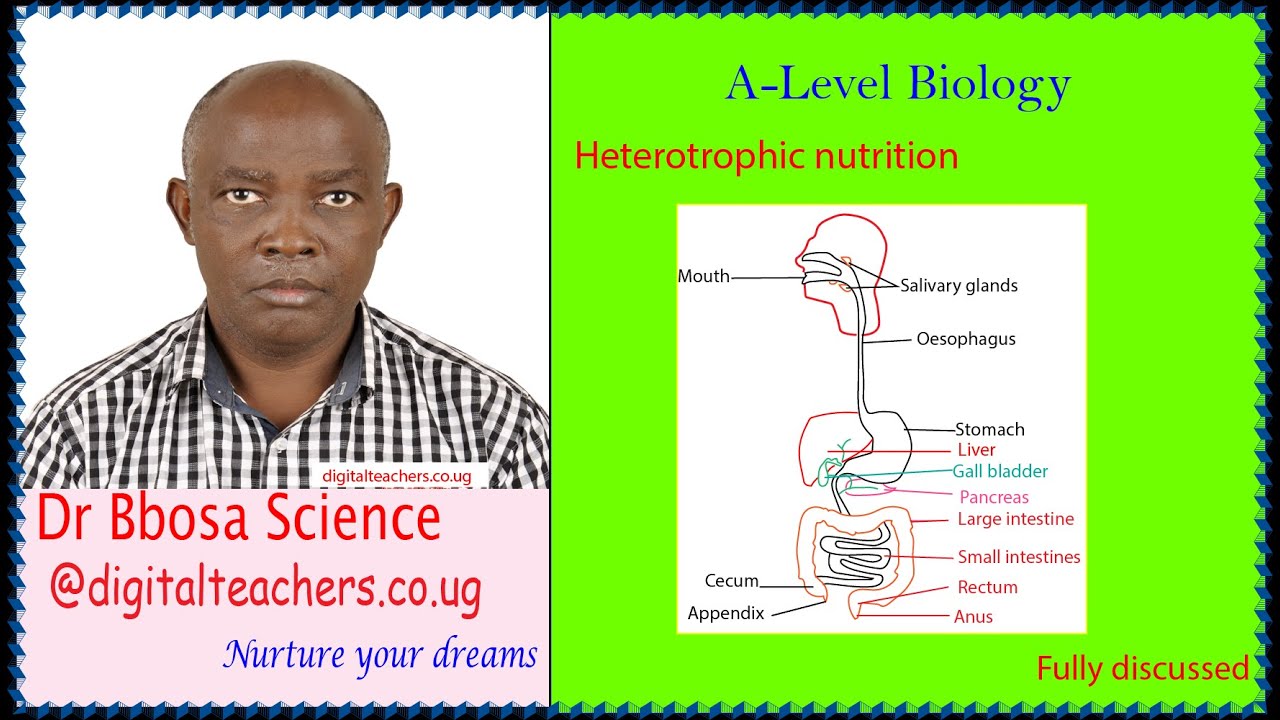
























































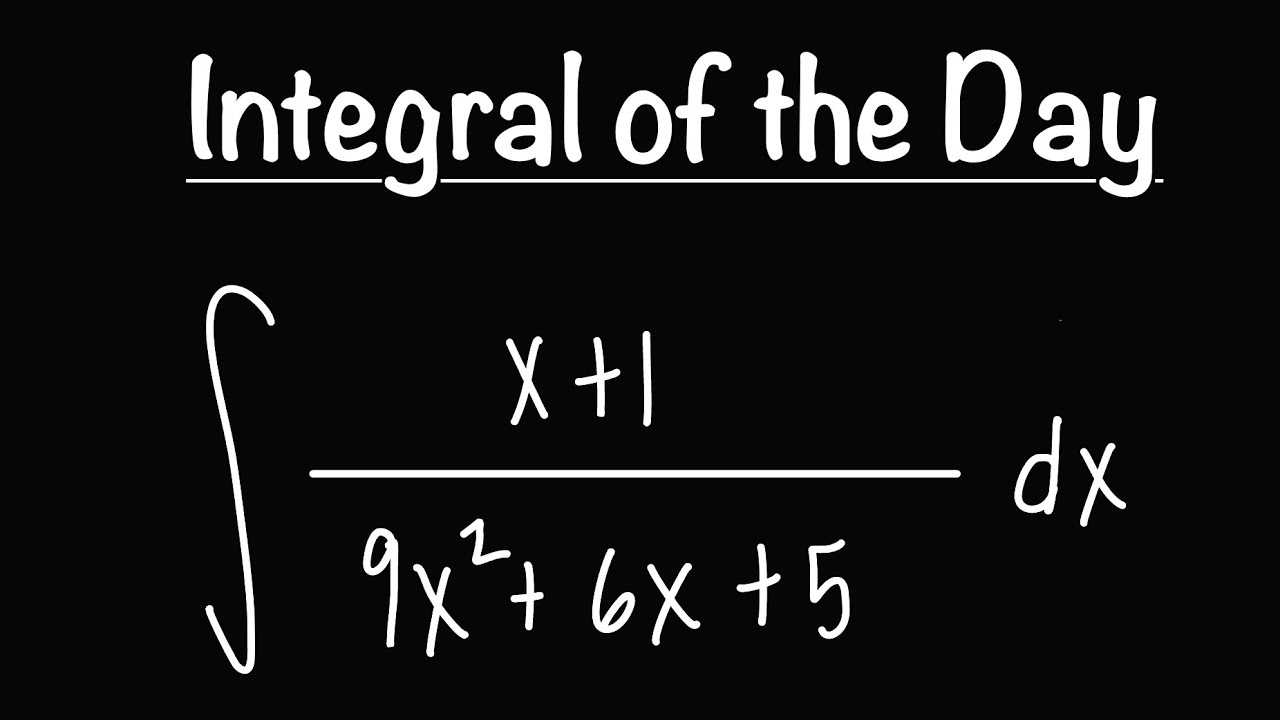



![🔥Trigonometry [2019 UACE P425/1-No.11]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/7IOo7KvQsFU/sddefault.jpg)
![🔥Trigonometry [2019 UACE PURE MATHEMATICS P425/1-No.2]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TvF6P1BV8XQ/hqdefault.jpg)
































































![[NON-STOP] 24 HOURS OF VICTORIOUS PRAYERS IN 2023 - APOSTLE JOSHUA SELMAN | PROPHETIC CHANTS 2023](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/v1sQgwdPa4Y/maxresdefault.jpg)





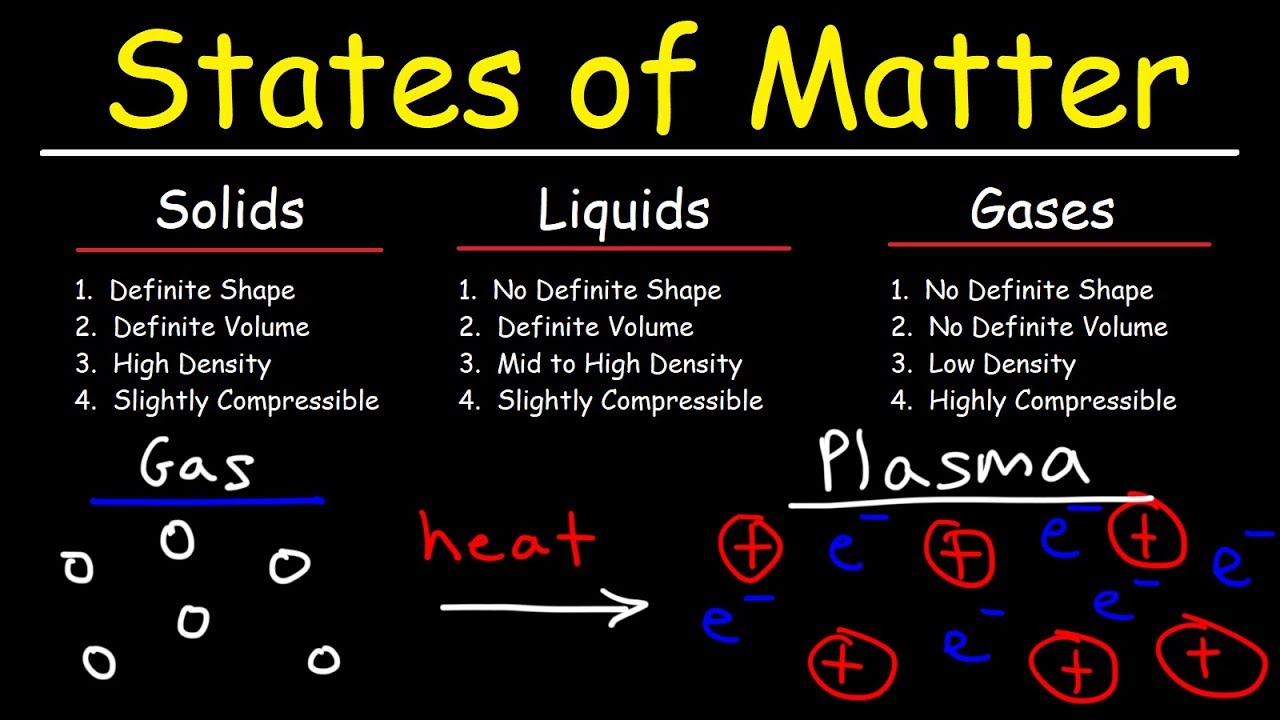




































































































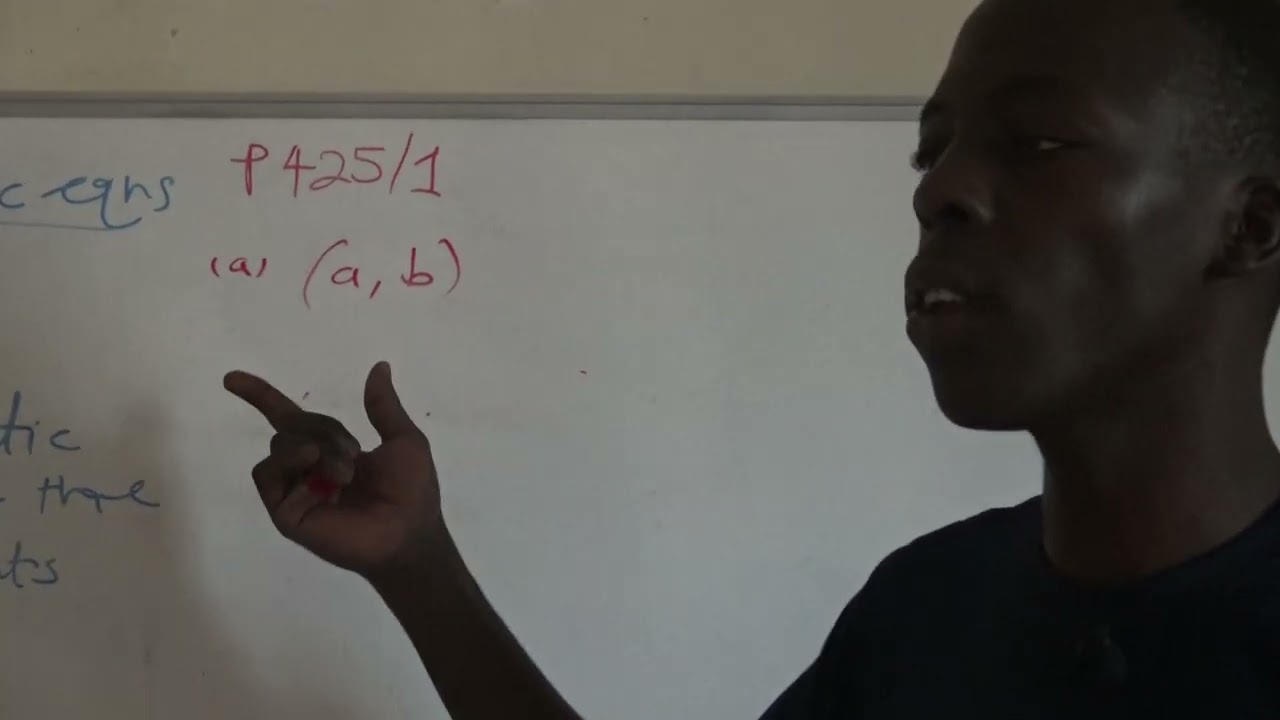

















![KUMUSIFU MUNGU JEHOVA [ PART 1]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_zRdBTDVxJs/maxresdefault.jpg)

![KUSIFU MUNGU JEHOVA [PART 2]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eaMpyPaIMZs/maxresdefault.jpg)


![UBUHAMYA [ iyunvire nawe ukuntu Imana ikoribitangaza] kanda hano wunve ububuhamya bukomeye](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BKWDpO3FXIA/mqdefault.jpg)